What is Development Economics?
Development Economics, also called Economics for Development, studies how to help low income countries become wealthier, i.e. nations that are going through the transition from being an agricultural economy to an industrial one.
Development economics shows how economic analysis can help us better understand the big themes of this century. Globalization and trade, poverty and wealth inequality, for example, are the big themes of the century.
Development economics also looks at how and why some countries have succeeded in their development goals while others have failed.
Why was Argentina’s income per capita higher than Canada’s in 1930. However, it is less than one third of Canada’s today. A development economist should be able to answer that question.
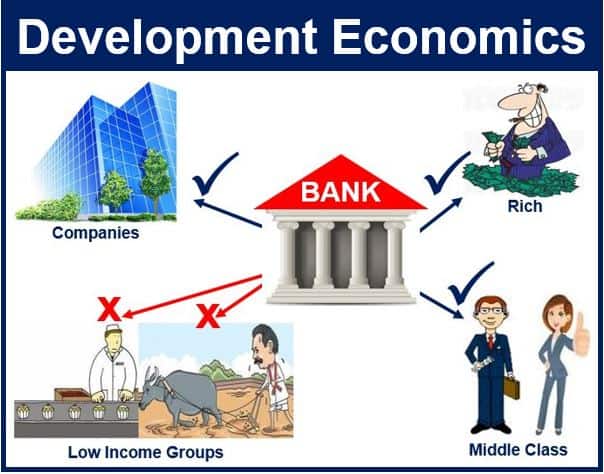 If lower income people have no access to loans and other financial services, which is a common problem in many nations, the whole economy suffers, development economists say.
If lower income people have no access to loans and other financial services, which is a common problem in many nations, the whole economy suffers, development economists say.
Economic challenges
This branch of economics tries to explore some of the economic challenges that the poorest countries in the world face.
The focus of development economics is not just on promoting economic growth and structural change. It is also about improving citizens’ health, education, and workplace conditions. This may be done through private or public channels. We can also promote it through both channels.
Development economists specialize in a wide range of themes, including:
- How does rapid population growth affect development?
- Do countries have to go through a process of structural transformation? If so, how does this happen?
- How dependent is the process of development on education. Is it also dependent on health care provision? And if so, to what extent?
- In this rapidly globalizing economy, how important is it for nations to become involved in international trade, i.e. importing and exporting goods and services?
- How can low-income and emerging nations achieve sustainable development?
- What have the human and economic costs of the HIV/AIDS epidemic been?
Development economics entails the creation of methods and theories that help determine policies and practices than can be put into action either at national or international level. This may involve using mathematical methods, restructuring market incentives, or both.
Development economists draw on theories that they may have encountered in both macro and micro modules. They subsequently combine them with evidence gathered from target nations.
According to studyingeconomics.ac.uk:
“By studying development economics, you will have the opportunity to apply the tools of economic analysis to the problems and challenges facing less-developed countries, and to begin to understand why some countries have been able to go through a process of economic and human development whilst others have languished.”
World Bank – Development Economics
The World Bank’s mission is principally geared toward the economic development of emerging and low-income nations. There is much more to economic development than simply focusing on GDP growth.
It organizes an Annual Bank Conference on Development Economics (ABCDE), where experts, policymakers, and businesses exchange and present new ideas in development.
“The conference aims to promote the exchange of cutting-edge research among academics, policymakers, and development practitioners.”
The 2015 ABCDE was held in Mexico City on June 15-16. The Bank of Mexico and the World Bank hosted it. The conference’s theme was ‘Productivity, Growth, and the Law’. The aim was to look at the main drivers of productivity. There was also a special focus on the role of the law, institutions, and norms.
According to ft.com/lexicon, the term means:
“The study of how to increase wealth in countries that are changing from an agricultural economy to an industrial one.”
Video – Development Economics
In many low income countries, access to loans is only possible among middle class, rich people and prosperous businesses. Poor people with ideas have no way to borrow money. The whole economy suffers. This video explains how improving financial services and financial systems helps alleviate poverty.

