The Primary Market, also known as a New Issue Market, is where new securities are issued – it is part of the capital market. Corporations, national and local governments, and other public sector institutions can get financing through the sale of new stock or bond issues through the primary market.
Put simply, the primary market creates new securities and offers them for sale to the public.
All companies require capital for their operations. This capital (money) can be in the form of equity or debt. Equity is the stock capital (share capital) of a company. Debt consists of all the loans taken by the business.
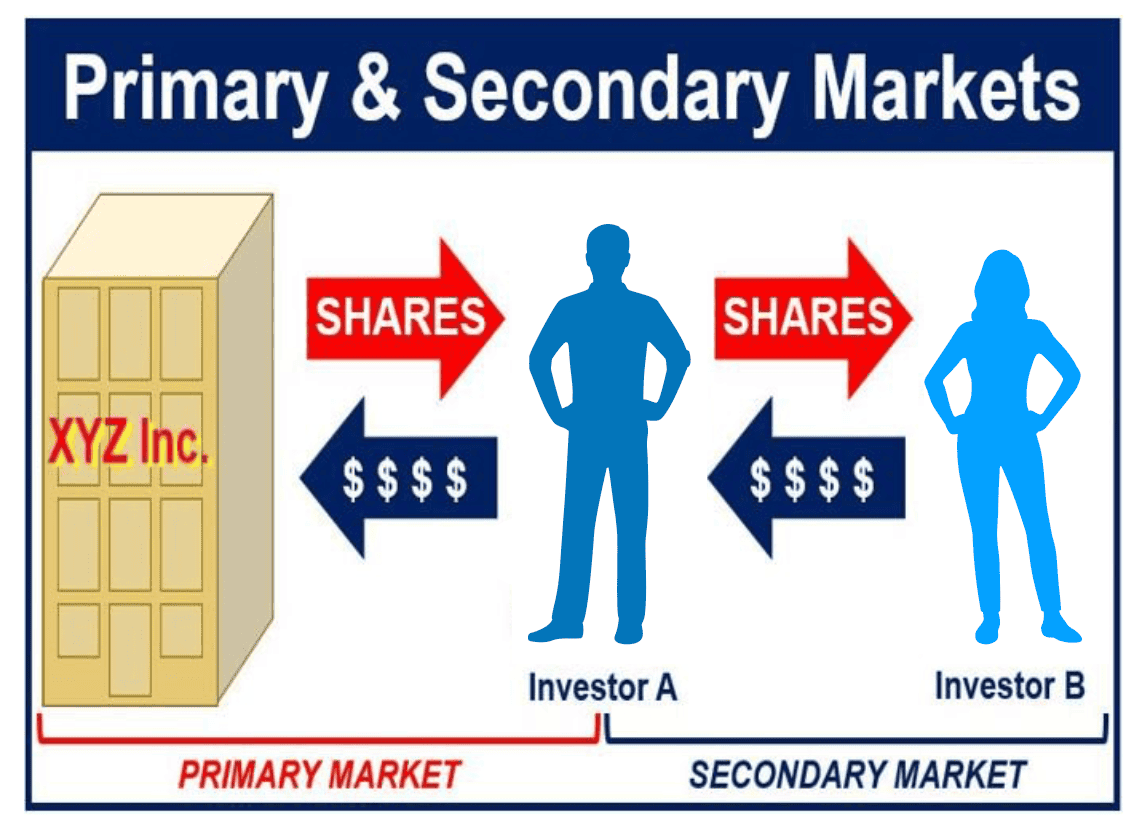
In order to raise capital in the form of equity, a company can sell its shares to members of the public. When shares are sold directly to the public, this is done via the primary market route.
The sale of securities in the primary market is usually done through an investment bank or finance syndicate of securities dealers.
Innovative financial technology companies, also known as fintechs, are increasingly participating in primary markets, offering platforms for companies to manage and facilitate their fundraising activities.
Additionally, the rise of blockchain technology has introduced decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms that could potentially transform primary markets by enabling secure and transparent direct issuance of securities.
Britannica.com has the following definition of the primary market:
“The primary market is where new securities are issued for the first time. It’s the initial step in raising capital for corporations, governments, or other entities. The issuers exchange public securities for money from investors. The exact process varies with the type of security and the issuer’s preferences.”
The primary market and secondary market
In an initial public offering (IPO) and follow-on public offering (FPO), shares are sold in the primary market.
The money earned from the sale of securities in a primary market goes directly to the issuing company.
The primary market is vital for both the capital market and the economy as a whole – it is where capital formation takes place.
The buying and selling of existing shares and bonds (not new securities) occur in the secondary market through a stock exchange, bond market or derivatives exchange.
In the secondary market, the money goes to the investor who is selling the security, and not the company or entity that first issued the security.
In business, the term ‘primary market’ may also refer to a company’s main market, or a country’s main export market. For example, the primary market of corn is human and animal food consumption – its secondary market is ethanol. Most of Mexico’s exports go to the United States – its primary market is the US.
Example sentences
Here are some sentences showing you how we use the terms “primary market” and “secondary market” in context:
Primary Market:
- “To facilitate the launch of its innovative green technology division, EcoTech Corp structured a primary market offering that attracted substantial interest from environmentally conscious investors.”
- “The primary market’s role was underscored when HealthWave Enterprises partnered with a leading investment firm to issue bonds aimed at expanding hospital facilities, demonstrating the market’s potential for societal impact.”
- “With the advent of crowdfunding platforms, smaller startups now access the primary market more easily, democratizing the fundraising landscape for emerging businesses.”
- “The government’s recent infrastructure bonds, issued via the primary market, underscored the market’s importance in supporting public projects critical to economic growth and development.”
Secondary Market:
- “In the secondary market, the fluctuating prices of TechGlobal shares reflected investor sentiment about the company’s latest earnings report, showcasing the market’s responsive nature.”
- “The liquidity provided by the secondary market proved invaluable for small investors looking to adjust their portfolios in response to market trends.”
- “Secondary market transactions in vintage bond issues revealed a growing interest in historical debt as a niche investment area, highlighting market diversity.”
- “Regulatory changes aimed at increasing transparency in the secondary market were welcomed by market participants, who saw them as essential steps towards protecting investor interests and maintaining market integrity.”
Two Educational Videos
These two interesting video presentations, from our sister YouTube channel – Marketing Business Network, explain what the ‘Primary Market’ and ‘Secondary Market’ are using simple, straightforward, and easy-to-understand language and examples.
-
What is the Primary Market?
-
What is the Secondary Market?
