Before you embark on a trip, you probably have checked the map for the locations of the closest local coffee shops or popular restaurants you want to experience. If you did, you are using geospatial data. You also made sure to use the GPS location tracker on your smartphone to catch every tourist spot and event. You captured memorable moments and tagged the locations on your social media posts.
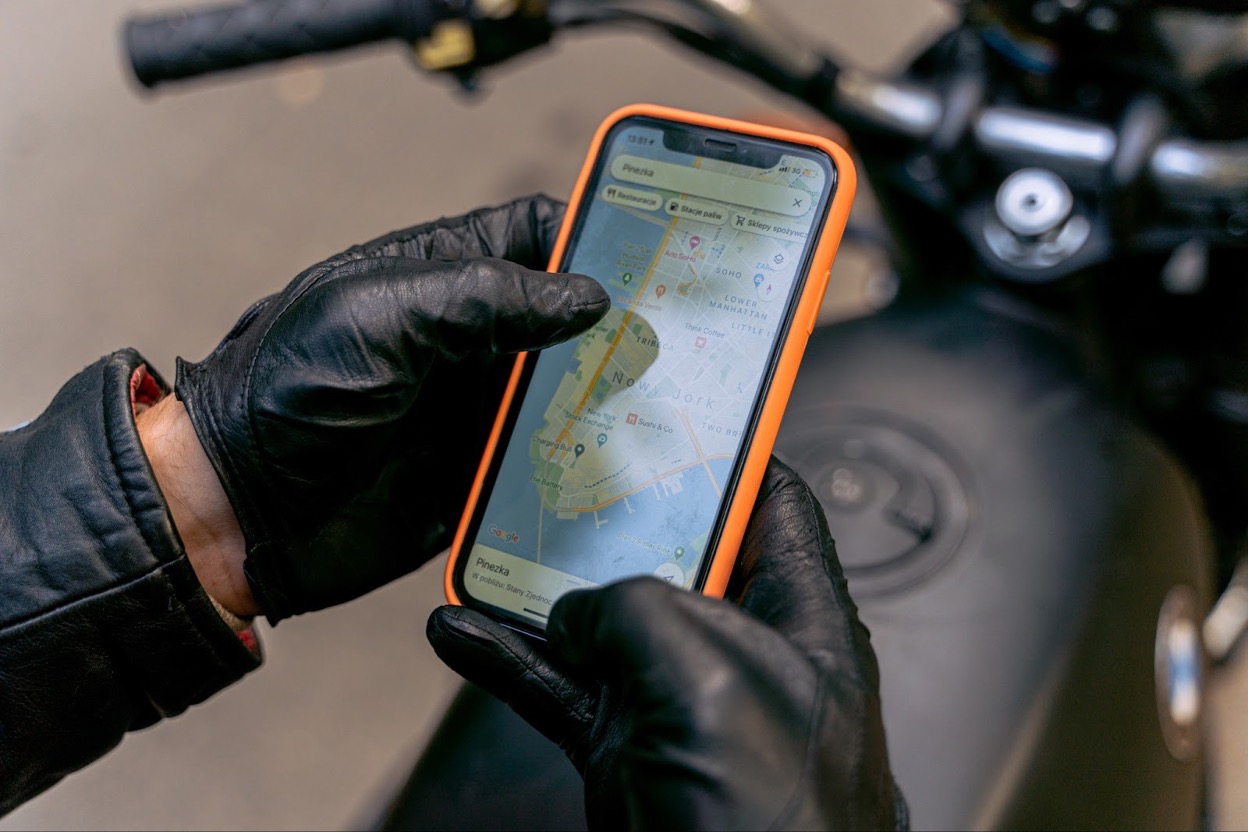

Geospatial data is known to visualise geographical elements on the surface of the Earth, like soil, vegetation, water, structures, and even economies, in quantitative or qualitative descriptions. Observing the Earth’s complex geographical features through geospatial data plays a vital role in making predictions and understanding phenomena and patterns.
From environmental impacts to business and retail to the location tracker on your smartphone, there are many ways to explore and use geospatial data.
How does it work?
Geospatial data is crucial across many disciplines and in almost every industry. Over time, its uses have expanded from its contribution to military strategies to providing information about a location to being an integral part of every institution. The use of geospatial data has increased in the last decade resulting in the generation of large volumes of data, technologies, and a wide variety of applications creating positive impacts on society and economies.
One use of geospatial data in changing the way the world works is integrating it into a GIS (geographic information system). GIS manages, analyses and connects data to a map to present patterns and relationships. GIS platforms have advanced in the last decade, creating milestones like cloud platforms. The next generation in-demand GIS – cloud platform offers efficient data analysis support to the organisation and helps optimise resources.

Geospatial data for public sector
Governments use these data and maps for urban land use mapping, habitat assessment, agriculture, public health, environmental management, and conservation of natural resources. The data are then processed to produce scalable representations like a detailed vector-based image, 2D, or 3D models to guide the construction of resilient infrastructures, present flood or landslide hazard data, land cover, or metal content of the soil.
For Business
Companies and organisations in our modern world have become more data-driven – collecting and analysing digital information to back up decisions. Businesses realise the value of data as marketing assets to make accurate solutions.
One of the most significant outputs in the big world of data is geospatial data. Moreover, the geospatial data can also specifically help represent and measure socio-economic statuses and the progress of societies.
The strategic planners of organisations use geospatial data to assess future shifts in geographical aspects and analyse how these interpretations will impact their business decisions.
Large companies gather data, for example, to tailor fit products and services to the current socio-economic statuses of customers. You can also harness this advantage and become a user and producer of data. In many countries, the real estate industries are benefiting from location technologies. Many countries integrate statistical data with geo maps to assess economic growth and changes in local development.
You can also responsibly integrate the geospatial data with web surfing and social media data to better understand the online activities of your community and the aspects related to communication and network infrastructures.
Its Social Impact
Non-profit organisations use geospatial data to learn details of the location and processes on the ground and track inequalities among demographics to develop advocacy campaigns. They also widely use geospatial data in 3D models for disaster risk management, especially in geographically isolated and disadvantaged areas.
The technology also helps save the cost of outsourcing work and has proven crucial for planning and improving overall efficiency in targeting poverty, food security, and clean energy, among many others.
Geospatial data is also an important tool in studying trends in the prevalence of COVID-19. In a recent study conducted, the results of the geospatial data analysis show the hot spots for the disease and the living conditions in the affected areas. The data provides information to authorities to recognise geographic risk and reach out to these disadvantaged areas.
Geospatial data as an overall power tool
Apps on your mobile phone, tablet and desktop help bring geospatial data encoded in the systems to live for everyone to experience and use in everyday tasks. Going back to the tracker on your smartphone, when you ask for a virtual map for the “nearest coffee shop”, the technology does not only provide you with a location.
It also creates a buffer area of interest, choosing more spots within your radar, calculating distance, and creating a route for you.
It is incredible to discover its application in the modern world and discover more ways to strengthen the technology. There is no doubt that it presents opportunities for sharing and collaboration.
The future is bright for using geospatial data to help create networks in your community. Now is the most exciting time to be involved in the industry, advance the resources, and enjoy the benefits of the world of data.
Interesting related article:

