What is the Pharmaceutical Industry? Definition and Examples
The Pharmaceutical Industry is all about the discovery, development, production, and sale of pharmaceutical products. Examples of pharmaceutical products are drugs and vaccines. The word ‘drugs’, in this context, means medications.
Wikipedia says the following about the industry:
“The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets drugs or pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure them, vaccinate them, or alleviate symptoms. Pharmaceutical companies may deal in generic or brand medications and medical devices.”
The pharmaceutical industry is massive. Drug companies, such as Pfizer, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, GSK, Bayer, and Sanofi are also known as pharmaceutical companies.
Pharmaceutical companies are commercial businesses that are licensed to research, develop, and market (sell) drugs, typically in the context of healthcare.
Global Pharmaceutical Industry
Since the beginning of this century, the global pharmaceutical market has grown considerably. Total global revenues reached $1.42 trillion in 2021, up from $1.27 trillion in 2020.
The 2021 total was 3.6 times bigger than it was at the beginning of the century ($390 billion).
Pharmaceutical Companies
-
Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
In the world of medications, there are pharmaceutical and biotech companies. Biotech companies’ products are derived from living organisms while those of pharmaceutical companies typically have a chemical basis.
-
Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Drugs
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) makes both pharmaceutical and biotechnology drugs. Its leading medication for rheumatoid arthritis, Humira (adalimumab), is a biotechnology drug. Darzalex (daratumumab), J&J’s anti-cancer monoclonal antibody medication, is a pharmaceutical drug.
-
Oldest Pharma Company
The Merck Group in Germany, which was founded in 1668 or 354 years ago, is the world’s oldest pharmaceutical company. Headquartered in Darmstadt, it employs 60,000 workers today and is present in sixty-six countries.
-
Lots of Departments
Apart from accounting, human resources, legal, sales, and marketing, pharmaceutical companies also have the following departments:
- Research & Development
- Clinical Trials
- Regulatory Affairs
- Drug Development
- Medical Affairs
- Operations
- Quality Control/Assurance
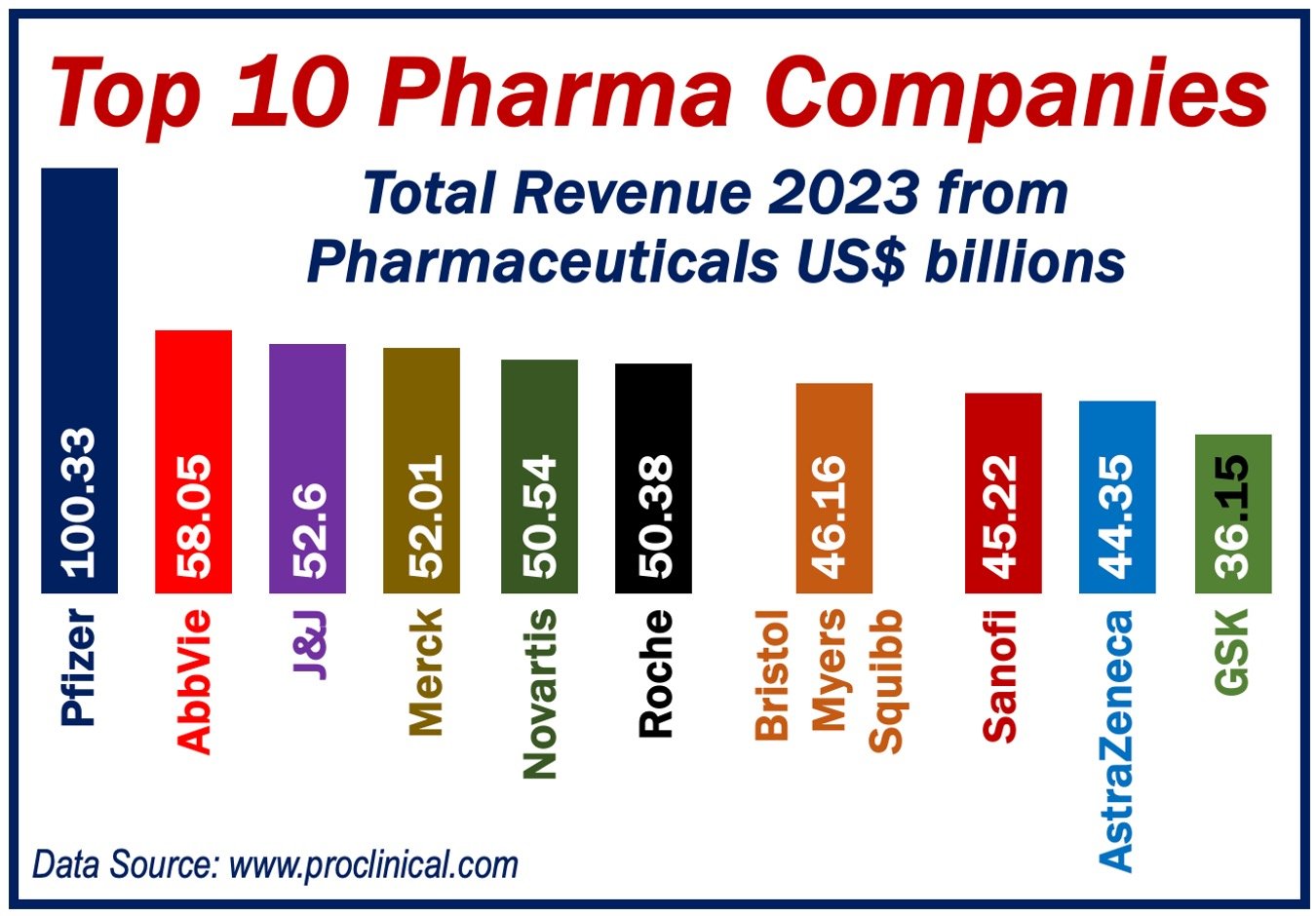
-
The Coronavirus Pandemic
While the coronavirus pandemic meant disaster for many companies across the globe, this was not the case for some pharmaceutical multinationals. Of Pfizer’s $72 billion in drug sales worldwide in 2021, $37 billion was generated from their COVID vaccine.
AstraZeneca’s COVID vaccine helped boost total global sales by 41.5% in 2021; the company also gained two spots to number 9 position in the world.
-
Discovery and development of new drugs
Getting new drugs onto the market takes a very long time and costs huge amounts of money. R&D departments of pharmaceutical companies carry out research on hundreds of different compounds. However, only a tiny fraction of them eventually become drugs that can be marketed.
Industry experts say that the cost of developing a successful new drug, known as a New Chemical Entity or NCE, is approximately $1.3 billion.
Etymology of Pharmaceutical
Etymology is the study of the origin of words and how their meanings and usages developed over time.
According to the Online Etymology Dictionary, the adjective pharmaceutical, with the meaning “pertaining to pharmacy or the art of preparing drugs,” first entered the English language in the 1640s. The word pharmaceutic, with the same meaning, emerged in the 1540s.
The term comes from the Late Latin word Pharmaceuticus, meaning “of drugs,” which came from the Greek word Pharmakeutikos. The Greek work Pharmakeus means “preparer of drugs.”
Compounds phrases
There are dozens of compound phrases with the word ‘Pharmaceutical’ in them. Here are some with their meanings, and their usage in a sentence:
-
Pharmaceutical Regulation
The regulations that govern the development, approval, and sale of drugs within a country or region.
For example: “The new cancer drug is currently undergoing rigorous pharmaceutical regulation before it can be marketed.”
-
Pharmaceutical Sciences
The disciplines involved in the creation, development, and manufacture of drugs and therapies.
For example: “Her degree in pharmaceutical sciences equipped her with the knowledge to develop innovative drug therapies.”
-
Pharmaceutical Policy
The policies that relate to the development, provision, and use of medications within a health care system.
For example: “The government’s pharmaceutical policy was revised to make essential drugs more accessible to the public.”
-
Pharmaceutical Care
The direct, responsible provision of medication-related care for the purpose of achieving definite outcomes that improve a patient’s quality of life.
For example: “Pharmacists play a crucial role in providing pharmaceutical care to ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.”
-
Pharmaceutical Pricing
The pricing strategies and controls for drugs, which may include price ceilings, subsidies, or other financial dynamics. For example:
“The debate on pharmaceutical pricing has intensified, focusing on the balance between company profits and drug affordability.”
-
Pharmaceutical Formulation
The process in which different chemical substances, including the active drug, are combined to produce a final medicinal product.
For example: “His expertise in pharmaceutical formulation was vital in developing the new extended-release tablet.”
-
Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS)
An Australian government program that provides subsidized prescription drugs to residents of Australia to ensure that all Australians have affordable and reliable access to a wide range of necessary medicines.
For example: “Thanks to the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, her medication costs were significantly reduced.”
-
Pharmaceutical Quality Control
The operational techniques and activities used to fulfill the requirements for quality in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring the production of consistent and effective products.
For example: “The company’s strict pharmaceutical quality control procedures ensured the safety and efficacy of their drugs.”
-
Pharmaceutical Biotechnology
A field that uses living cells and cell materials to research and produce pharmaceutical and diagnostic products that help treat and prevent human diseases.
For example: “Advancements in pharmaceutical biotechnology have led to breakthroughs in personalized medicine.”
-
Pharmaceutical Analysis
The process of chemical analysis and testing of pharmaceutical products to ensure quality, efficacy, and safety.
For example: “Accurate pharmaceutical analysis is critical in certifying that medications meet all regulatory standards.”
2 Videos
These two educational videos, from our sister YouTube channel – Marketing Business Network, explain what ‘The Pharmaceutical Industry’ and ‘Pharmaceutical’ are using simple, straightforward, and easy-to-understand language and examples.
-
What is the Pharmaceutical Industry?
What is Pharmaceutical?

