Most people see video streaming companies like Hulu and Netflix as only entertainment providers. However, These companies are also tech giants that rely on networking technologies and digital broadcasting to offer people the ability to watch videos from anywhere in the world.

Thanks to the increase in the demand for video content, media streaming sites have been on the rise. As a result, there are abundant choices for any video content you need. Unlike the early days, the internet speeds available today are fast, and the technologies used by these content service providers have advanced further.
According to WatchTVAbroad, it is possible today to stream Paramount+ in any country, and not just if you are inside the United States.
Here’s a quick break down of the tech that powers all your favorite video-streaming platforms listed on streamingwars.com, including Amazon Prime Videos, Hulu, and Netflix.
How Video Streaming Works on the Internet
Leading streaming services like Netflix and Amazon Prime video have spent millions of dollars developing their proprietary streaming infrastructure. This infrastructure helps them to beam on-demand content on the internet while supporting live streaming of events like sports. These streaming service providers have also mastered how to distribute the content to an increasingly connected landscape of varying screens and devices.
In the current on-demand culture, people consume content based on their personal preferences and on the time they choose. The videos also need to be available through all devices, including tablets, mobile phones, PC, and media streaming devices. For this reason, sites like Netflix use a custom video streaming system that creates room for a backhaul reduction to give the users a great experience.
Netflix uses Amazon AWS’s CDN infrastructure to cache stream data from the POP while restricting the data required from their cloud hosting services. This leading streaming service cuts down its operational expenses that way.
On the internet, streaming happens in five steps. As such, you must understand these five steps if you plan to launch a streaming site like Netflix.
1. Ingestion
Video streaming requires either live or recorded content. With live content, the signal transmitted from the site where the live event is being captured and played is the ingestion.
2. Transcoding
After the video is recorded, it’s transcoded, meaning that it’s converted from its original format to another.
3. Management
That involves stuff like content protection, dynamic ad insertion, and digital rights management.
4. Delivery and Playback
This step involves delivering the final video stream to the viewers on multiple devices through the internet. However, the process is a little more complex than it sounds, though you must understand how things work at this stage.
After transcoding the video is available in several formats, allowing users to view the content on all screen sizes. For instance, if the original video had 4K resolution, then transcoding will help you to create 1080p, 720p and 480p streams. This crucial step is necessary as your viewers won’t have the same display capabilities and network speeds.
5. Chaos Engineering
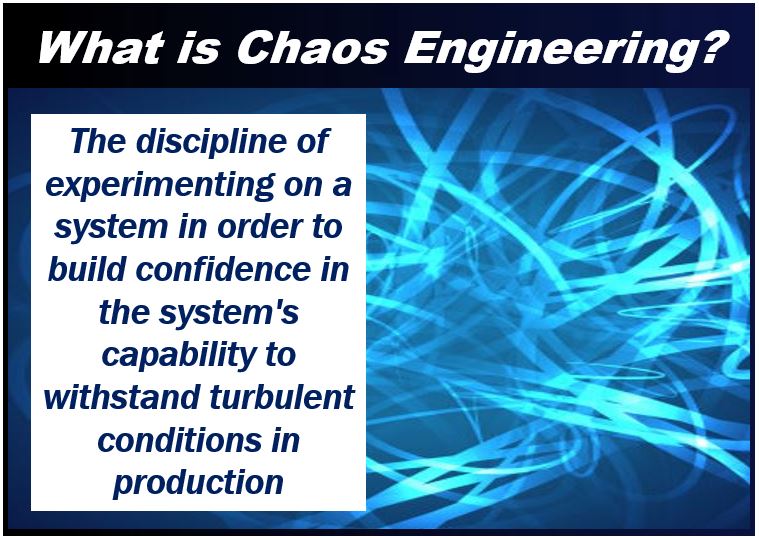
Netflix is not only popular for creating award-winning movies and TV series, but it’s also hailed for developing the chaos engineering discipline. This famous approach makes the resilience of complex, modern technology architecture better, and their infrastructure has only continued to evolve over the years. Today, this streaming giant serves over 100 million viewers, spread across over 190 countries worldwide.
For people planning to launch their video streaming sites using Netflix’s business model, it’s important to prepare for the growing demand in the streaming market. Netflix created the term chaos engineering, a term used to mean running experiments in the systems to identify minor glitches before they evolve into problems.
Interesting related article: “Is it legal to use a VPN with your Favorite content streaming platform?“

