 Researchers at the University of Tokyo have created an algorithm that analyzes social media data to predict consumer purchases.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have created an algorithm that analyzes social media data to predict consumer purchases.
The research, published in The Leadership Quarterly, was conducted by Associate Professor Toshihiko Yamasaki and his team from the Graduate School of Information Science and Technology at the University of Tokyo.
“I posed two questions to my team: ‘Is it possible to calculate the similarity between different brands based on the way customers engage with them on social media?’ And, ‘If so, can brands use this information to improve the way they market themselves?'” said Yamasaki. “And with some time, effort and patience, they came back with a simple but confident answer: ‘Yes!'”
One of the main challenges that companies have faced in the past is the sheer amount of work required to carry out an analysis of social media data. However, with the advent of machine learning things are now a bit different.
“In the past, many companies improved their marketing strategies with the use of customer surveys and projections based on their sales data,” explained lead researcher Yiwei Zhang. “However, these are time-consuming and imprecise. Now we have access to and expertise in tools such as machine learning and complex statistical analysis.”
The team combined statistical modeling techniques with learning-based image recognition to create an algorithm that analyzes and categorizes photos and hashtags relating to a brands’ followers; revealing certain patterns of behavior of consumers towards different brands.
A representation of a statistical network researchers used in their algorithm:
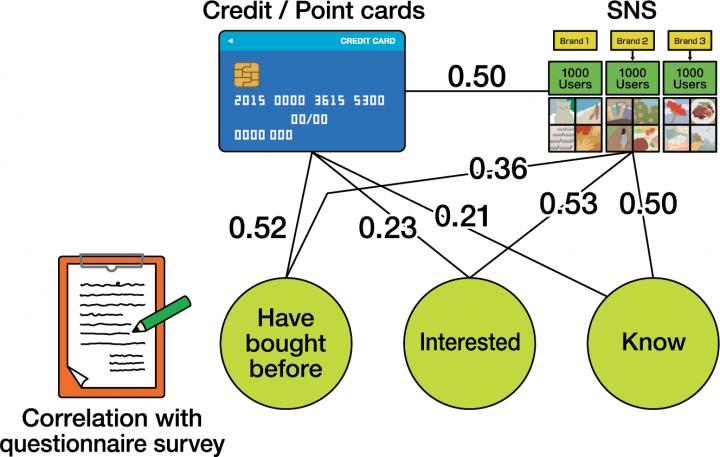
“We evaluated our proposed algorithm against purchase history and questionnaires, which are still useful to provide context to purchase information,” continued Zhang. “The experimental results show that credit card or point card companies could predict customers’ past purchasing behavior well. Our algorithm could accurately predict customers’ willingness to try new brands.”
“To visualize what has not been visible before is always very interesting,” concluded Yamasaki. “People might say that professionals already ‘see’ these kinds of patterns, but being able to show the similarity between brands numerically and objectively is a new innovation. Our algorithm is demonstrably more effective than judging these things based on intuition alone.”
Journal Citation
Ryan K. Gottfredson, Christopher S. Reina,
Exploring why leaders do what they do: An integrative review of the situation-trait approach and situation-encoding schemas,
The Leadership Quarterly, 2019, 101373, ISSN 1048-9843,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2019.101373.

