In business and finance, Overhead refers to all ongoing business expenses. We also call it the ‘operating expense.’ It is an expense that the owner must pay even when the business does not earn any revenue.
We use the term both in its plural and singular forms, i.e., overhead or overheads. The plural form is more common in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth countries. The singular form is popular in North America.
Put simply, overhead refers to the indirect costs that a business incurs—essentially, all expenses that are not directly tied to manufacturing products (cost of goods sold) or acquiring products for resale (cost of sales).
We use the term for budgeting purposes. We also use it to find out how much a company should charge for its products. If it does not charge the right amount, it cannot make a profit.
Expenses that form part of the overhead include rent, utilities, travel expenditures, repairs, legal fees, insurance, and advertising fees. We also include telephone bills, electricity, labor burden, and direct materials.
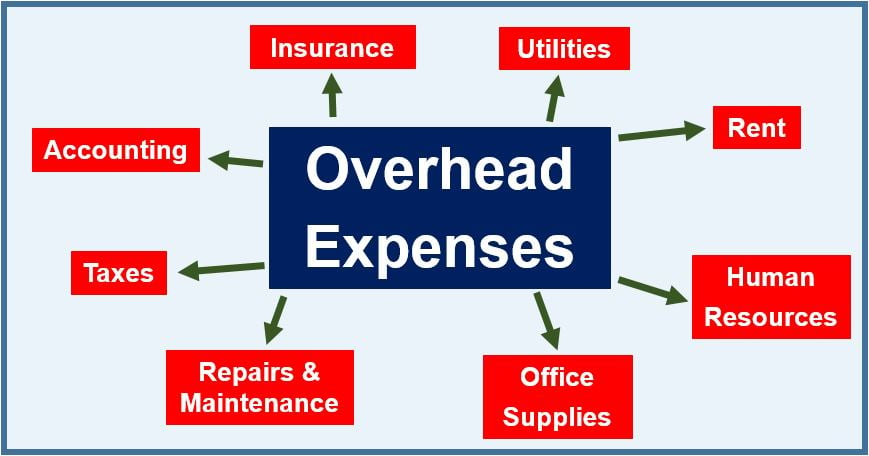
The term refers to all these expenses that keep a business operating.
Manufacturing overhead
Manufacturing overhead represents the costs that support manufacturing. However, they are not linked to specific products or services.
These expenses can either be fixed or variable. In other words, some remain the same on a consistent basis, while others fluctuate.
According to Nasdaq.com has the following definition of the term:
“The expenses of a business that are not attributable directly to the production or sale of goods.”
Fixed overhead costs
These costs remain the same, regardless of the number of units the company produces or sells.
Fixed overhead costs include rental costs, retail sales floor space, etc.
Variable overhead costs
Variable costs are those that do change. In other words, when production rises they go up, and when production falls they subsequently decline too.
Examples include manufacturing machinery electricity, equipment utilities, materials handling wages, and production supplies.
Home business
If you want to set up a company with low overhead costs, a home business is a good option. Startups have a considerably greater chance of success if the entrepreneur begins operating from home.
Bill Gates and Steve Jobs both began with home businesses. In fact, during their first few years, they worked in their garage.
