Business Terms, Definitions & Concepts Hub
Decode the language of finance through our financial glossary hub, where you’ll find essential business and financial terms into comprehensive learning experiences. Far beyond simple definitions, each guide delivers in-depth analysis across banking fundamentals, investment strategies, economic theory, and the digital finance revolution reshaping our world.
Our visual learning tools, calculation methodologies, and cross-referenced insights transform abstract financial concepts into practical understanding you can apply immediately.
Explore by Category
Navigate our comprehensive financial knowledge base
Featured Financial Concepts
In-depth guides to essential financial and business terminology

What is a zombie company? Definition and Meaning
A zombie company (or zombie firm, living‑dead firm) is one that cannot stand on its own feet. It survives only because creditors roll over its loans at below‑market rates or because governments, directly or indirectly, prop it up. Most can just cover the interest on their debts; very few make enough cash to pay the
Estimated reading time: 2 minutes
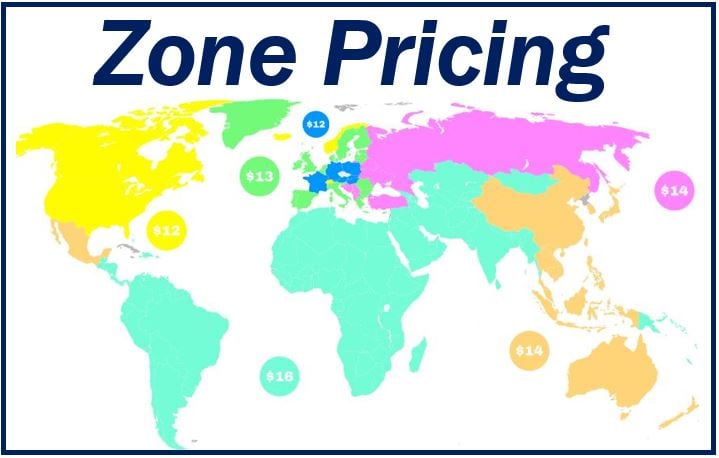
What is zone pricing? Definition and examples
Zone pricing is the process of establishing prices for products and services depending on where people buy them. If a consumer buys something in Zone A and then the same thing in Zone B, they may have to pay different prices. A company may use a zone pricing system to pay for transportation costs. In
Estimated reading time: 2 minutes

What are the five C’s of marketing? Definition and examples
The Five C’s of Marketing are the five most important areas of marketing. When marketing executives make marketing decisions, they should consider the five C’s of marketing. The five C’s stand for: The five C’s act as a guideline when we are creating a marketing plan or devising a marketing strategy. A marketing strategy exists
Estimated reading time: 2 minutes

What is a résumé? Why is it so important?
A clear-cut guide to what a résumé is, why it matters, and how to build one that gets interviews. 1. Résumé ≠ Biography A résumé is a one- to two-page marketing document that sells your most relevant achievements, skills, and credentials for one specific opportunity. Its single job is to persuade the reader to invite
Estimated reading time: 2 minutes
