US Inflation continues to show signs of easing, providing further confidence that the *Federal Reserve’s recent decisions to cut interest rates may have been the right move.
* The Federal Reserve System, commonly known as the Federal Reserve (or simply the ‘Fed’), is the central bank of the United States, responsible for managing monetary policy and regulating the banking system.
The core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index, which excludes volatile food and energy costs, rose just 0.1% in August, marking a smaller-than-expected increase and falling below the 0.2% recorded in July.
On an annual basis, core inflation stood at 2.7%, up slightly from July’s 2.6%, but still in line with expectations.
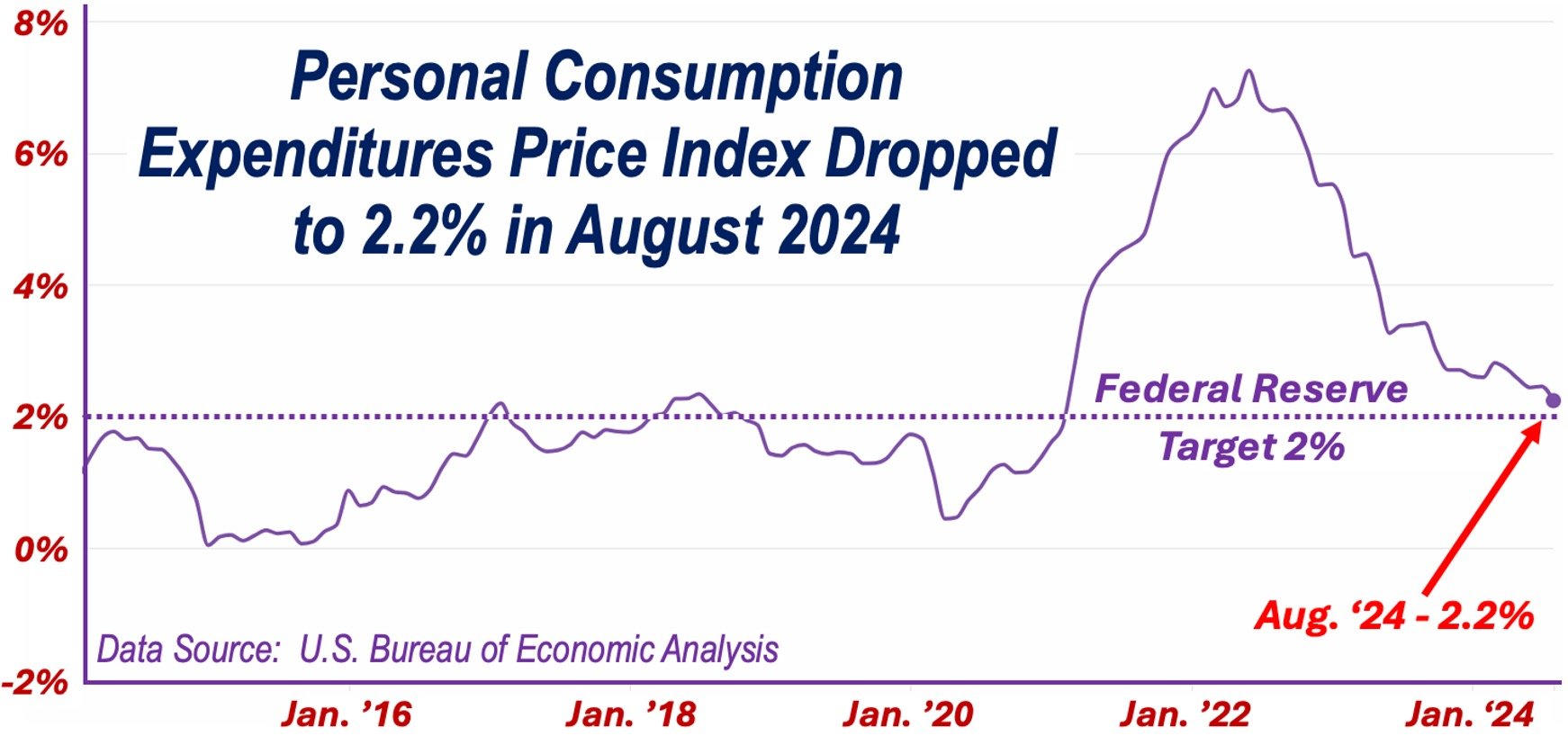
The broader PCE inflation, which includes all categories, showed a 2.2% increase from the prior year, the lowest since February 2021. This slight rise came in below forecasts of 2.3%, and down significantly from July’s 2.5%, adding to a string of favorable inflation data.
The combination of steady price moderation and declining energy costs has helped to maintain a positive outlook on the Fed’s approach to managing inflation and interest rates.
A Strong Case for Continued Rate Cuts
The consistent drop in inflation figures, combined with signs of a cooling labor market, suggests that the Federal Reserve may continue cutting interest rates.
Investors are now speculating whether the Fed will opt for a smaller 25 basis point cut or a larger 50 basis point cut at their next meeting.
A number of Fed officials, including Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell, have highlighted the central bank’s growing confidence in inflation moving toward their target of 2%.
This sentiment is supported by data showing that inflation pressures have eased in recent months. As a result, there is a strong case for further rate reductions, potentially providing relief for businesses and consumers alike.
Core Inflation Remains a Focus
Despite the positive data, core inflation—which excludes food and energy prices—remains a key point of concern.
The core PCE index rose 0.1% on a monthly basis, aligning with expectations but signaling that inflation has not entirely receded.
Some Fed officials, including Governor Michelle Bowman, have expressed caution, suggesting that the labor market’s strength and other economic factors may require a more measured approach to rate cuts.
However, the overall inflation data gives the Fed more room to maneuver. As wages and non-housing service prices decline, economists remain hopeful that inflationary pressures will continue to lessen in the months ahead.
Investor Sentiment and Economic Outlook
Investors have reacted positively to the latest inflation readings, with the stock market posting gains as traders bet on further rate cuts.
The S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average have both seen solid weekly increases, signaling optimism about the economic outlook.
Wall Street is closely watching for continued progress on inflation, as it would likely lead to more favorable borrowing conditions and lower interest rates.
The PCE inflation data also comes at a time when economic growth is holding steady, with second-quarter GDP growth being revised upward to 3%.
This robust economic performance further supports the case for additional rate cuts without fear of spurring higher inflation.
Final Thoughts
The Federal Reserve appears to be on track to continue cutting interest rates as inflation trends in a favorable direction.
While core inflation remains slightly elevated, the broader measures of inflation are moving closer to the Fed’s 2% target.
Investors and policymakers alike are optimistic about the prospect of further rate cuts, which could provide relief to both consumers and businesses, easing borrowing costs and supporting economic growth.
