Additive manufacturing (AM) is the process of joining materials to make three-dimensional objects from three-dimensional (3D) model data. AM involves adding layer upon layer until the product is completed.
We can also use the terms freeform manufacturing, additive processes, additive techniques, and additive layer manufacturing. 3D printing is one form of AM. However, many people use it as a complete synonym.
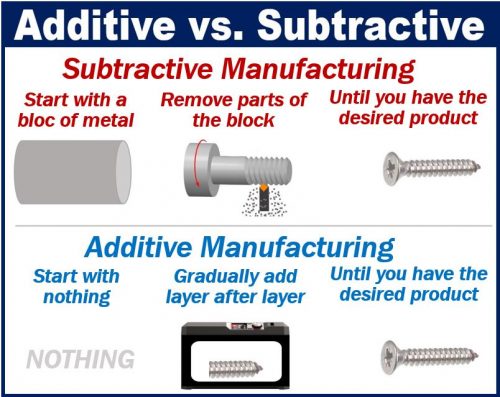
Subtractive manufacturing ‘removes stuff’ until you have made the product. Additive manufacturing ‘adds stuff’ until you have made the product.
Additive manufacturing vs. subtractive manufacturing
The adjective ‘additive‘ means ‘tending to or able to add.’ If a process is additive, it means that it is adding things.
The adjective ‘subtractive,’ on the other hand, means ‘tending to or able to remove or subtract.’ A subtractive process is one that is removing or taking away things.
Subtractive manufacturing
Subtractive manufacturing is the traditional way of making things. You start with a large block of something, and gradually cut away bits of it until you have the desired object.
We also call this process ‘machining.’ Machining involves hollowing, cutting, or taking parts out of a block of something. It could be a block of, for example, plastic or metal.
Additive manufacturing
AM means creating 3D objects by starting with nothing and adding one superfine layer at a time. 3D printing is one type of AM.
Over the past few decades, AM technology has advanced considerably. 3D printers today, for example, can create jet engine turbines, spare parts for vehicles, and even whole houses.
Additive manufacturing – seven categories
According to Loughborough University in the UK, there are seven categories of additive manufacturing:
- Vat Photopolymerization.
- Directed Energy Deposition.
- Binder Jetting.
- Material Jetting.
- Power Bed Fusion.
- Material Extrusion.
- Sheet Lamination.
Individual processes vary depending on the machine technology and material the manufacturer uses.
