Back end is the operations part of a business. In other words, it is the part that customers and members of the public rarely see or hear. Back end refers to the ‘behind the scenes’ operations.
Back end departments or offices provide the services that allow businesses to function. Examples include administration, accounting, personnel (HR or human resources), document handling, and communications data processing.
The meaning of the term contrasts with its ‘front end’. The ‘front end’ is the part of a company that outsiders frequently see and hear. The sales, marketing, and public relations (PR) departments are part of the ‘front end.’
Investment banks use the terms back office and front office, rather than back end and front end.
In network marketing, the term refers to the commission that independent agents receive. Specifically, from the sales revenue of agents who recruited the independent agents.
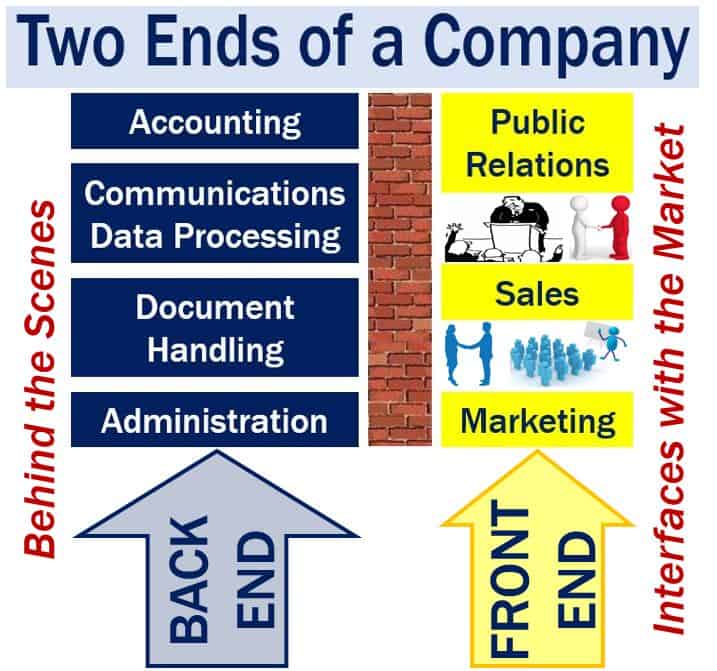
Put simply, ‘back-end’ can be described as the ‘behind-the-scenes’ operations hub of a business that customers don’t typically interact with. Back-end offices or departments deliver essential services that constitute a business’s functionality, such as accounting, administration, data processing, and document handling.
Back end sales
Back end sales are products that companies sell to existing customers. In other words, sales made to customers who have already bought.
Back end business is the profit center of most companies. The majority of businesses are willing to even sell at a loss with their initial sale with a customer. This is because they hope that the customer will come back many times.
The margins on those repeat sales will more than make up for the initial low profits. In fact, the repeat sales will more than make up for any initial losses.
The majority of firms do not realize how profitable this part of the business can be. They concentrate very little on this aspect of marketing. This is a big mistake. In fact, in virtually every single sector, the winners are those that focus on back end sales.
Back end – IT and telecoms
In IT, we use back end and front end to describe program services and interfaces relative to their initial user. The initial user may be a program or a person. The two terms also have this meaning in telecommunications. IT stands for information technology.
A back end program or application serves indirectly in support of the front end services.
MBaas or BaaS is a model for providing a mobile app and web app for developers. MBaas stands for mobile backend as a service, and BAAS stands for backend as a service.
Developers use MBaas to connect their applications to backend cloud storage and APIs (application programming interfaces) exposed to back end applications. They also use the model to provide features such as push notifications, user management, and social networking services integration.
