Consumer Behavior or Consumer Buying Behavior are all the aspects that affect consumers’ search, selection, and purchase of products. We can use the term for the purchases of services too. Consumer behavior also includes the post-purchase stage. Consumer behavior is an area of research within the business field of ‘marketing.’
A consumer is a person, organization, or economic entity that buys a good or service and does not sell it on. I other words, they ‘consume’ it.
This consumption process is central to the economy, as it drives demand and influences production cycles across industries
To understand consumer behavior, companies need to know why customers bought something and what pushed them to buy. They also need to know what trends are developing in society.
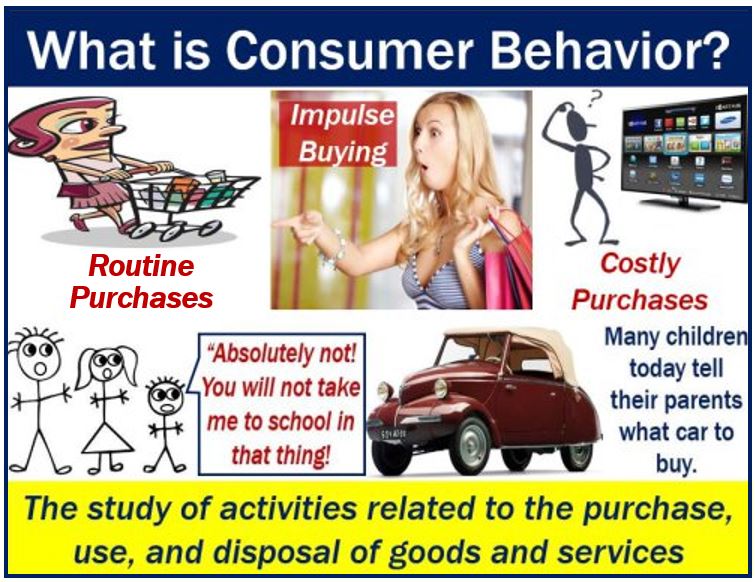
An example of a new trend developing in society is children’s influence on their parents’ purchases. Kids today are major factors in the purchase of expensive products. In fact, many parents today will not purchase a car if their children do not like it. This was not the case forty years ago.
Consumer behavior – a process
When attempting to buy something, our consumer behavior consists of a process.
First, we need to recognize a problem. In this stage, we aim to satisfy a need or want. For example, let’s suppose we need to iron our clothes.
Second, we carry out research. During this step, we actively look for ways to satisfy our need. For example, we can iron clothes traditionally, use a vapor iron, or take them to the dry cleaners.
Third, we evaluate alternatives. Based on the information we have gathered, we decide which choice best meets our need or want.
For example, we may decide that taking the clothes to the dry cleaners helps them last longer. However, buying an iron might be a better choice if we want to save money over the long-term.
Fourth; this is the purchasing stage. This is when we decide to buy the best option to meet that need or want.
Lastly, there is the post-purchase evaluation stage. In this stage, we evaluate our purchase. In other words, we determine whether the purchase was worth it. Did it satisfy our need? Did the product or service bring satisfaction after we used it?
For example, we decided to get the iron, because we can iron whatever we like whenever we like. We do not have to wait days. Therefore, the purchase brought satisfaction.
Consumer behavior – companies need to know
Likewise, a business has to have in mind that there four types of consumer behavior.
Routine shopping
The shopper buys without having to do much research, there is low involvement, and usually at low cost. For example, the thought behind what to buy in our weekly supermarket shopping is relatively simple.
Limited decision making
The buyer occasionally purchases the product after somebody recommended it. They do a little research, i.e., it is not as time-consuming as buying an expensive product.
For example, when a woman wants to dye her hair, she may ask friends for a reliable option. Put simply; she only needs to check a few options.
Extensive decision making
People spend much longer deciding when they are considering an expensive product. Consumers spend time carrying out research and comparing multiple products. They check product ratings and also ask friends or sales professionals.
The process takes longer to complete. For example, when buying a TV, people spend a long time going to different shops and comparing products.
Deciding what house to buy may take weeks or even months.
Impulse buying
The customer had not planned to buy. When I am waiting at the checkout in a supermarket, I might suddenly buy some chewing gum. It is an impulse buy because I had not planned to purchase gum.
Supermarkets know that consumers are impulsive, especially when it comes to chocolates, candy, and gum. Consequently, they place those products near the checkout.
