The Creative Industries consist of companies and organizations that transform ideas, imagination, and human creativity into products. The products from these industries entertain us, inform us, and enrich our lives.
Organizations concerned with the generation or exploitation of knowledge and information form part of the creative industries. Some people use the terms Cultural Industries (especially in Europe) or Creative Economy. In the Caribbean and Latin America, it is commonly referred to as the Orange Economy.
The term does not refer just to for-profit organizations. According to many interpretations, it includes various organizations such as non-profits, cooperatives, and other entities that engage in the creation, production, and distribution of cultural, artistic, or knowledge-based products and services.
There are various interpretations of the term. As you can see below, the British Government, which was the first entity to define the “creative industries,” gave it a business and wealth-creating slant:
“Those industries which have their origin in individual creativity, skill and talent and which have a potential for wealth and job creation through the generation and exploitation of intellectual property.”
If we look around, we can see the influence of the creative industries everywhere. We can see it in our clothes, commercial and residential buildings, music, and books. It is also in adverts, apps, video games, films, digital artwork, and theater productions.
From Art to Technology
The creative industries cover a wide spectrum.
They include traditional fields like:
- Visual Arts: painting, sculpture, crafts, photography, ceramics, and installation art.
- Performing Arts: theater, dance, music, opera, circus arts, and performance art.
- Publishing: books, magazines, newspapers, academic journals, e-books, and blogs.
- Film and Television: movies, documentaries, TV shows, web series, animated films, and reality TV.
They also encompass rapidly evolving sectors powered by technology:
- Design: graphic design, product design, fashion, web design, interior design, industrial design, and architecture.
- Software Development: video games, apps, plugins, websites, software tools, interactive media, and mobile technology.
- Advertising and Marketing: campaigns that tell stories and drive sales, digital marketing, social media strategies, and brand management.

The Impact of the Creative Industries
The creative industries are much more than just fun and games. Their impact on our academic, working, and everyday worlds has been significant:
-
Economic Powerhouse
They employ millions of people, drive technological advancements, foster entrepreneurship, and contribute massively to global trade. They also boost local economies and represent a significant source of tax revenue for governments.
According to Britain’s Creative Industries Council, the sector was worth £124.6bn ($155bn) in the UK in 2022.
-
Cultural Drivers
The creative industries preserve heritage, shape our understanding of the world, promote cultural diversity, enhance intercultural understanding, and fuel social dialogue.
-
Innovation Engine
The arts and tech-driven sectors often collaborate, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. For example, think of the way computer animation transformed filmmaking.
-
Wellbeing and Education
Engaging with the arts can improve mental health, boost creativity, enhance cognitive development, enrich cultural literacy, and enhance learning experiences across subjects.
According to an article from Physician Health, a section of the American Medical Association, published on August 1, 2023, “There’s a strong connection between art and mental health.”
-
Environmental Sustainability
The creative industries increasingly incorporate sustainable practices, promoting environmental awareness and pioneering eco-friendly solutions in production and design.
Brands like Stella McCartney, for example, lead the way in using organic materials and advocating for ethical fashion practices.
Examples of innovation
Here are some examples of innovation in the creative industries since the end of the eighteenth century:
- Lithography (1796) – Revolutionized the printing industry.
- The Phonograph (1877) – First device to reproduce recorded sound.
- Technicolor (1916) – Introduced color to moving pictures.
- Electric Guitar (1931) – Transformed music genres with new sounds.
- Multitrack Recording (1950s) – Allowed layered recording of different instruments.
- Digital Art (1960s) – Merged computing with visual arts.
- Pixar’s Computer Animation (1986) – Developed the first computer-animated feature film, “Toy Story.”
- E-books (1990s) – Changed the publishing industry by providing instant access to books via digital devices.
- Streaming Services (Late 2000s) – Transformed access to music, movies, TV shows, and documentaries with on-demand streaming services.
- Virtual Reality (2010s) – Brought immersive experiences to gaming, education, and arts through advanced VR technology.
- Augmented Reality (2010s) – Merged digital content with the real world.
What new inventions will our future generations see over the next couple of centuries? Perhaps interactive holographic displays, AI-driven personalized storytelling, virtual reality travel experiences, or sentient digital art installations?
Opportunities and Challenges
The creative industries offer interesting and exciting careers for people with different passions and talents. Artists, designers, filmmakers, musicians, writers, marketers, animators, choreographers, sound engineers, game designers, and developers have roles to play.
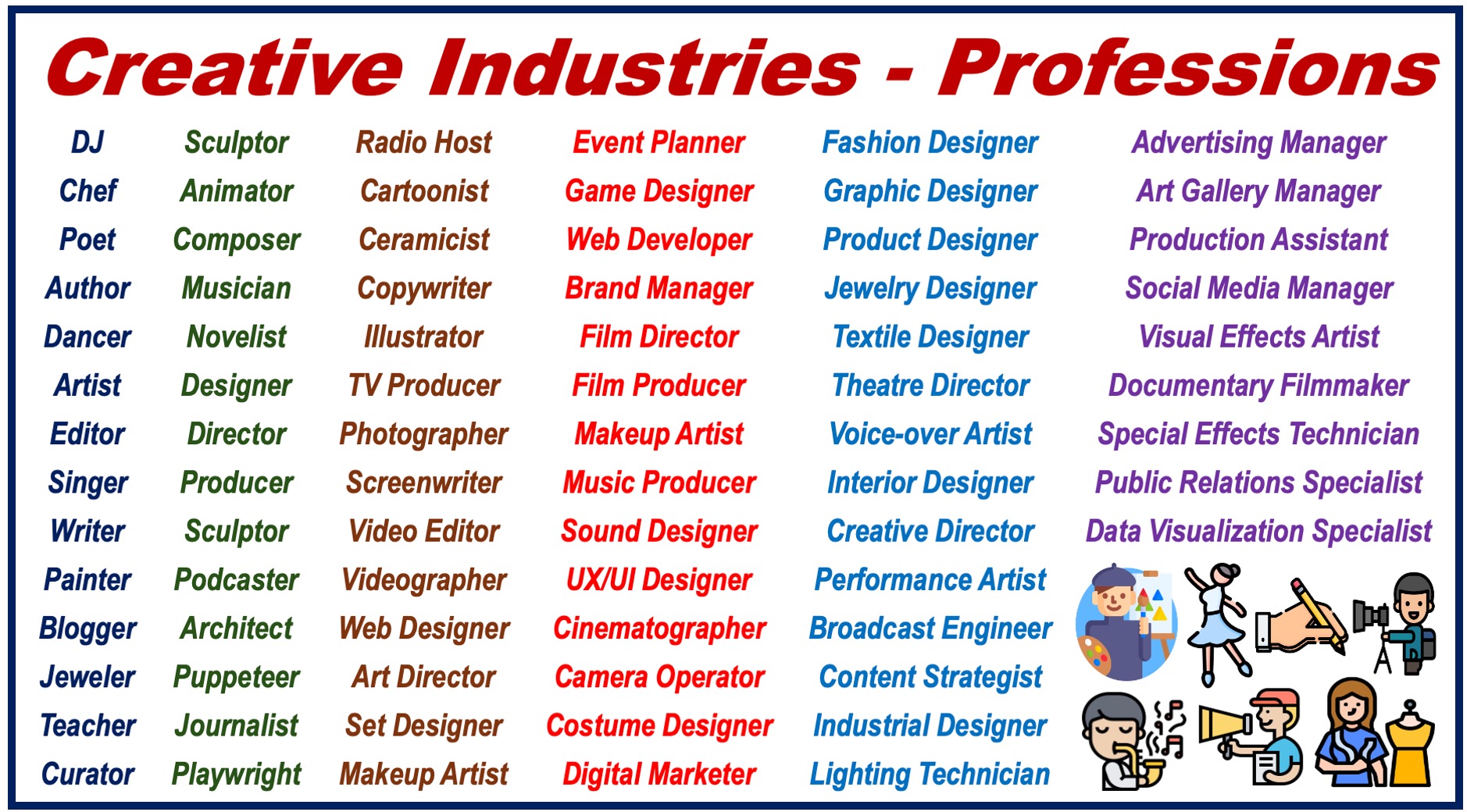
However, some parts of the industry can be fiercely competitive, and finding a stable income can be tricky, especially for freelancers.
As with most sectors of the economy today, technology – especially artificial intelligence and automation – is rapidly changing the landscape.
In 2023, screenwriters in the United States, represented by the Writers Guild of America (WGA), went on strike. They were concerned about several issues, such as fair compensation, residual payments, and job security in the face of the increasing use of streaming services and artificial intelligence in content creation.
The Future is Bright
The demand for skilled creative professionals, high-quality content, and innovative experiences shows no signs of slowing.
As the creative industries are closely intertwined with new technologies like virtual reality and artificial intelligence, we should expect even more amazing opportunities to unfold.
Whether you’re an artist, a tech whiz, a storyteller, a software developer, or simply passionate about creativity, the creative industries are a space where ideas come to life.
