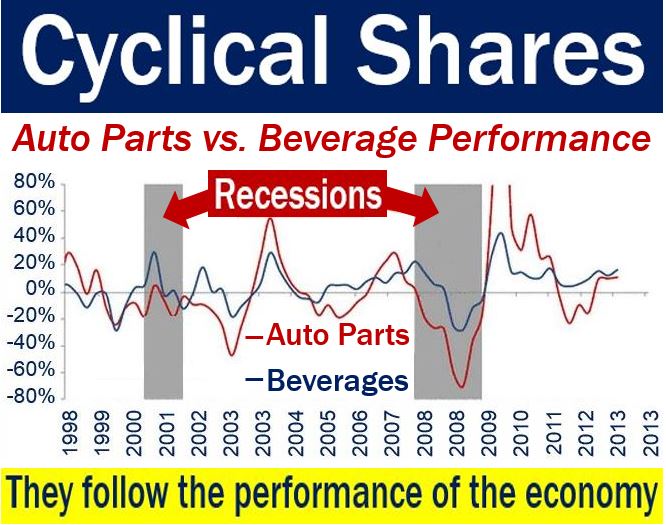
Cyclical Shares or Cyclical Stocks are shares that go up and down in value in tandem with the country’s economic performance. In other words, they perform according to how well or badly the national economy is doing.
When GDP grows strongly, the shares appreciate significantly. GDP stands for gross domestic product. However, they decline in value when the economy is doing badly.
Defensive vs. cyclical shares
The opposite of cyclical shares is defensive shares, which perform better when times are hard. However, they perform less impressively than cyclical stocks during an economic boom.
Most shares are cyclical to a certain extent. In other words, they follow global, national, or regional economic trends.
The rise of sustainable investing has prompted investors to consider the environmental and social governance (ESG) performance of companies, adding another dimension to the assessment of cyclical shares.
Cyclical shares belong to companies whose profits closely reflect the way the national economy moves.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and property developers tend to shadow the national economy’s performance. Therefore, property shares do too.
Demand for property rises when the economy is doing well. However, demand falls during a recession.
Bank shares are also cyclical. During an economic boom, people borrow more, which means more business for banks. More business means more profits.
When an economy is growing strongly, banks tend to charge more. Conversely, poor GDP growth affects bank shares negatively – it brings down their prices.
Discretionary items
The shares of companies that sell discretionary items are cyclical. Discretionary items are those that consumers can afford to buy more when the economy is booming.
Discretionary items are non-essential goods, such as apparel, new automobiles, jewelry, entertainment, and gourmet meals. A vacation abroad is also a discretionary item. Discretionary items are the opposite of essential goods.
When people are worried about their jobs, they hold onto their cars for longer before replacing them.
IT firms are also cyclical. Companies are more reluctant to invest in renewing their computer systems during a recession. Most will postpone such expenditure until the economy picks up.
Examples of defensive shares
Defensive shares or defensive stocks are the opposite of cyclical shares. Defensive shares do not follow the national economic cycles. They do not follow the national economy because they belong to companies that sell things that people need all the time.
Examples of defensive shares include those issued by utility companies – electricity, gas, and water.
Sellers of basic household goods such as toilet paper, toothpaste, bread, and milk tend to have sales that are relatively immune to economic cycles.
The shares of healthcare companies, funeral services, and telecom providers are also defensive.
Even the shares of cigarette makers are defensive. Most smokers are addicted. Therefore, they will usually find the money to get their cigarettes, regardless of their financial situation.
Investment portfolios
A good investment portfolio should contain both cyclical and defensive shares. The two types have their potential merits.
Your portfolio’s relative balance depends largely on your market view and how much risk you are comfortable taking. The balance also depends on your requirements for dividends.
Experts say that in general, growth funds tend to tilt towards cyclical shares. On the other hand, equity income funds have a higher proportion of defensive stocks.
The Telegraph quotes Justin Modray, of Candid Financial Advice, who said:
“In general, since it is difficult to predict the future, it makes sense to hold both types of stock in your portfolio, either directly or via fund managers who tend to favor one or other styles of investing.”
What to do during the cycle
Clever investors will try to identify where in the economic cycle their national economies are. They will subsequently switch their stock mix accordingly.
At the end of a recession, clever investors will probably increase their proportion of cyclical stocks. They will also reduce their volume of defensive stocks.
Professional investors and portfolio managers regularly study the ‘Purchasing Managers Index’ (PMI). The PMI points to how healthy or unhealthy the economy is.
The PMI contains economic indicators derived from monthly surveys of private sector companies. If the PMI rises, it usually means that economic activity is going to increase.
On the other hand, if the PMI falls, economic activity will probably decline.
Advancements in technology and data analysis have led to the development of more sophisticated tools for tracking the economic indicators that signal shifts in cyclical and defensive stock performance.
Cyclical shares – definition
French multinational banking and financial services company Société Générale S.A. says the following about cyclical stock:
“A cyclical stock is a stock highly correlated to the economic activity. When the economy is in a recession, the profits of a Cyclical company tend to drop and so its share price.”
“Conversely, when the economy is in good shape (expansion), the share price tends to go up with the profit growth.”
Barry Ritholtz, an American author and newspaper columnist, said:
“Owning a variety of asset classes means that some part of your portfolio will be doing well when the cyclical turmoil arises.”
“A broadly diversified portfolio includes large capitalization stocks, small cap, emerging markets, fixed income, real estate and commodities.”
Video – What are Cyclical Shares?
This educational video, from our sister channel on YouTube – Marketing Business Network, explains what ‘Cyclical Shares’ are using simple and easy-to-understand language and examples.
