Debt finance or debt financing mainly refers to borrowing money by either taking out a bank loan or issuing debt securities. A debt security is any kind of debt instrument that can be purchased or sold between two parties and has basic terms defined.
Debt finance involves raising funds by borrowing money from a lender, with a promise to pay back at a later date – usually with interest.
The terms of the debt finance will depend on how much is borrowed and the borrower’s creditworthiness. There are two main types of debt finance:
– Taking out a loan
– Issuing debt securities
 Debt finance refers to borrowing money either in the form of a loan or selling securities. The advantage of debt financing, as opposed to equity financing, is that you do not lose ownership – a disadvantage is that your monthly expenses will be higher and your company is at greater risk of getting into financial trouble.
Debt finance refers to borrowing money either in the form of a loan or selling securities. The advantage of debt financing, as opposed to equity financing, is that you do not lose ownership – a disadvantage is that your monthly expenses will be higher and your company is at greater risk of getting into financial trouble.
Debt Security
A debt security is a financial instrument that works like an IOU (I owe you). The debt security issuer promises to repay the investor the amount he or she paid (lent) on or by a specified date – this date is when a debt security ‘matures’ – typically with interest.
Debt securities, just like equity securities, can be traded – investors can buy and sell them. Investors like this feature. There are many types of debt securities, including:
– Bonds: such as junk bonds, high yield bonds, eurobonds and several others, which have a maturity of at least one year.
– Medium Term Notes: which have a maturity of up to thirty years.
– Commercial Paper: these are similar to bonds but mature earlier – less than 12 months.
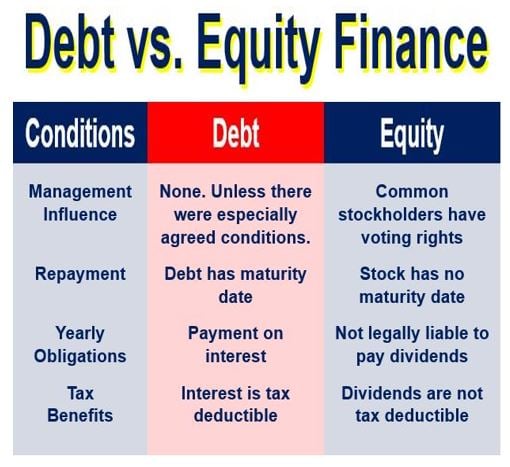 Businesses can utilize several financing options, which are mainly broken into two categories: debt finance and equity finance. Debt involves borrowing money that has to be repaid at a later date, while equity involves raising funds by selling interest in the business.
Businesses can utilize several financing options, which are mainly broken into two categories: debt finance and equity finance. Debt involves borrowing money that has to be repaid at a later date, while equity involves raising funds by selling interest in the business.
Bank Loans
There are many types of bank loans, such as:
– Term Loan: a bank loan for a specific amount that has an agreed repayment schedule and either a fixed or floating interest rate.
– Overdraft: sometimes called an arranged overdraft. It means that you can let your bank balance go below zero, up to an agreed amount. For example, if you have an agreed overdraft of $5000, your account balance can go down to (minus) -5000. You can borrow up to your overdraft limit.
– Revolving Facility: also known as revolving credit. The borrower can withdraw, repay and redraw the loan repeatedly in any manner and any number of times, until the revolving facility expires. This type of loan includes overdrafts and credit card loans. Also known as an evergreen loan.
There are several other types of loans such as bills of exchange or swingline facilities.
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, debt finance is:
“Money that a company or government borrows in order to do business or finance its activities, for example by selling bonds, taking out loans, or using credit.”
Debt financing vs. equity financing
Debt financing and equity financing are two ways a company can raise money.
Equity financing generally means issuing additional shares of common stock to investors. If more shares of common stock are issued and outstanding, the previous shareholders’ percentage of ownership declines.
Debt financing means borrowing the money. The main advantage of this option is that the borrower does not give up ownership. Its main disadvantage is that you have to pay the money back. Too much debt will increase the business’ future cost of borrowing money – and makes life riskier.
Borrowing from friends and relatives
Many owners of startups get their debt finance by borrowing money from relatives or friends, who are more likely to approve flexible terms of repayment than formal lending institutions. Friends and relatives are generally more willing to invest in a new venture or unproven business area, based upon their personal relationship with and knowledge of the borrower.
One possible drawback is that relatives and friends may attempt to become involved in how the business is managed.
If you want to avoid such complications, you need to use the same formal arrangements with friends and relatives as you would with a bank or a distant business associate.
Quotes about debt
“Eurobonds are absolutely wrong. In order to bring about common interest rates, you need similar competitiveness levels, similar budget situations. You don’t get them by collectivizing debts,” (Angela Merkel – a German stateswoman and former research scientist, whohas been the Chancellor of Germany since 2005)
“It is incumbent on every generation to pay its own debts as it goes. A principle which if acted on would save one-half the wars of the world,” (Thomas Jefferson, 1743-1826 – an American Founding Father, 3rd President of the United States)
“Small debts are like small shot; they are rattling on every side, and can scarcely be escaped without a wound: great debts are like cannon; of loud noise, but little danger,” (Samuel Johnson, 1709-1784 – an English writer)
“Further Education should be about the ability to learn, not the ability to pay – everyone who is able should have the opportunity, regardless of their family background. I don’t want to see students struggling with huge debts or frightened off even going to university in the first place,” (Charles Kennedy, 1959-2015 – a Scottish Liberal Democrat politician, leader of the Liberal Democrats from 1999 to 2006)
“Well what would happen is that if Greece defaulted and couldn’t pay its debts, all the Greek bonds that are held in other banking systems across Western Europe would suddenly have no value. You could as a knock-on effect create a banking crisis in Western Europe,” (John Major – a British Conservative Party politician, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1990 to 1997)
“It’s easy to sit in relative luxury and peace and pontificate on the subject of the Third World debts,” (Roger Moore – an English actor and humanitarian who played the British secret agent James Bond in seven feature films)
“Greece’s debts are all denominated in euros, but it isn’t clear who holds how much of those debts. For that reason, the consequences of a national bankruptcy would be incalculable. Greece is just as systemically important as a major bank,” (Wolfgang Schauble – a German politician, Germany’s Federal Minister of Finance since 2009)
Video – Debt financing & equity financing
This Khan Academy video explains what debt financing and equity financing are in easy-to-understand language and examples.
