A gas field is a deposit that is rich in gas. In other words, an area with lots of gas that we can extract. In this context, gas refers to natural gas and not gasoline. Some people, especially in North America, use the term ‘natural gas field.’ In the same way that we call a deposit that is rich in oil an oil field, those rich in gas are gas fields.
We can write this term in two ways. We can write it as one word, i.e., gasfield, or as two words, i.e., gas field.
Merriam-Webster dictionary says that a gas field is:
“A district where natural gas is produced in commercial quantities.
However, Oil & Gas UK is more specific; it says that a gas field is:
“A field containing natural gas but no oil.”
Depth of oil and gas
Usually, organic sediments 1,000 to 6,000 meters below the earth’s surface generate oil. These sediments generate oil at 60 °C to 150 °C. Sediments deeper down generate gas, and at higher temperatures.
The deeper the source of the natural gas, the drier it is. In other words, the smaller the proportion of condensates within the gas.
Oil and gas are both lighter than water. Therefore they tend to rise from their sources. Rising oil or gas either gets trapped by a non-permeable stratigraphic trap, or it seeps to the surface.
We extract the oil or gas that did not seep to the surface by drilling.
The term ‘gas field’ refers to both onshore and offshore geographical areas where we can extract natural gas profitably. Onshore means on the land, while offshore means out at sea.
The largest gas field
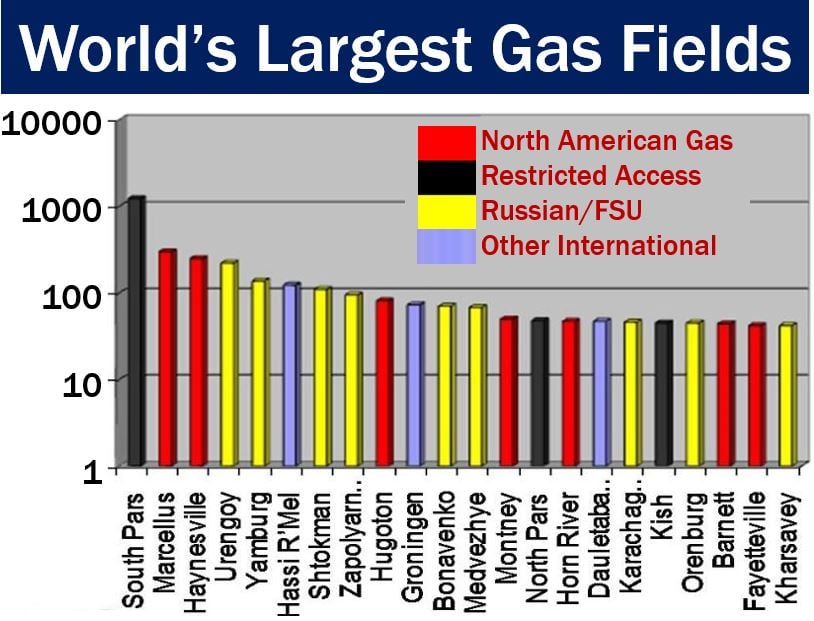
The South Pars/North Dome gas field is the world’s largest by far. It belongs to Qatar and Iran.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) says that the field holds approximately 51 trillion cubic meters or 1,800 trillion cubic feet of in-situ natural gas. It also holds about 7.9 billion cubic meters or 50 billion barrels of natural gas condensates.
In fact, the South Pars/North Dome field holds more recoverable gas than all the other fields in the world combined. It covers an area of 3,700 square miles (9,700 square kilometers).
The world’s second and third largest gas fields are both in Russia.
The price of natural gas rose early in this century. Drillers subsequently revisited fields that oil and gas companies had previously deemed not economically viable. If a business, project, gas field, etc. is viable, it means we expect it to make a profit year after year.
The McMoran Exploration, for example, drilled further than 32,000 feet (9,754 meters) below the Earth’s surface. It was the deepest test well in the history of gas exploration. The McMoran Exploration was at the Blackbeard site in the Gulf of Mexico.
