An insurance deductible is the amount of money a policy holder has to pay in an insurance claim before the insurance provider covers any expenses.
The US National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) defines a deductible as the “portion of the insured loss (in dollars) paid by the policy holder.”
A deductible is subtracted, or “deducted,” from the policy holder’s claim payment.
Health insurance plans typically have an annual deductible, while other types of insurance have a deductible per claim. Deductible amounts vary depending on the plan and can be split into individual or family deductibles.
Examples of insurance deductibles
- Alex has a medical emergency which costs $10,000. His health insurance policy has an annual deductible of $1,000. Alex must pay the first $1,000 of covered services out of pocket. After the deductible ($1,000 in this case) has been subtracted from the claim payment, the insurance company covers the remaining $9,000.
- Jack gets into a car accident and has to pay $6,000 to fix the vehicle. His deductible is $800. The deductible ($800) is subtracted from the total ($6,000) and his insurance provider pays the remaining $5,200 to repair his car.
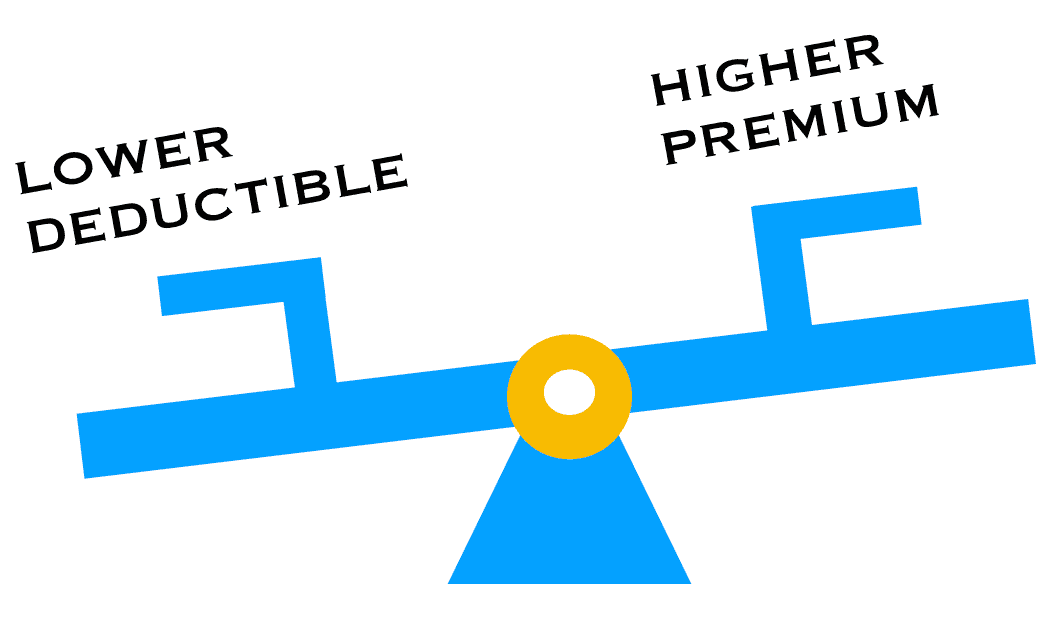
Insurance premiums are usually cheaper when higher deductibles are involved. The higher the deductible, the lower the cost of insurance. This is because a policy holder takes on more risk with a higher deductible, while the insurance provider takes on less risk.
Deductibles are used by insurance providers to limit “nickel and dime” insurance claims and because of “moral” and “morale” hazards associated with certain policies.
