Kano Model Analysis is an analysis of consumer preferences relating to goods or services based on the Kano Model. Put simply; Kano Model Analysis is an analysis technique that producers use to assist with differentiating product features.
The Kano Model is a simple and versatile technique for determining which features a good or service should have. Dr. Noriako Kano, professor of quality management at Tokyo University of Science, developed the Kano Model in 1984.
According to Dr. Kano, people consider much more than simply a product’s functionality when they purchase something. Their emotions and impressions also drive them to choose certain products.
In other words, it is not only what a product can do that influences our purchasing decision. How it makes us feel, i.e., its touch, look, and even smell, also has a significant impact.
There are product features that we expect, others that delight us and we did not expect, and some that we dislike.
For example, when we purchase a new refrigerator, we all expect it to keep food and drinks cool. However, we are also delighted if it has Bluetooth and communicates with us online.
Kano Model Analysis – customer satisfaction
The Kano Model classifies product attributes based on how customers perceive their effect on customer satisfaction.
These classifications guide producers and sellers when they are designing new products. They also help producers know how to upgrade new products.
Put simply, Kano Model Analysis helps us determine when good is good enough, and when adding more is better.
When deciding how to design new products or upgrade existing ones, Kano Model Analysis is useful for:
- Concept development.
- Analyzing competitive goods and services.
- Identifying customer needs.
- Determining which functional requirements are important.
The Kano Model addresses different types of customer requirements:
- Basic needs. By satisfying these needs, the company can get a product into the market.
- Performance needs. Only by satisfying these needs can the product remain in the market.
- Excitement needs. If a product satisfies excitement needs, it excels, i.e., it becomes world class.
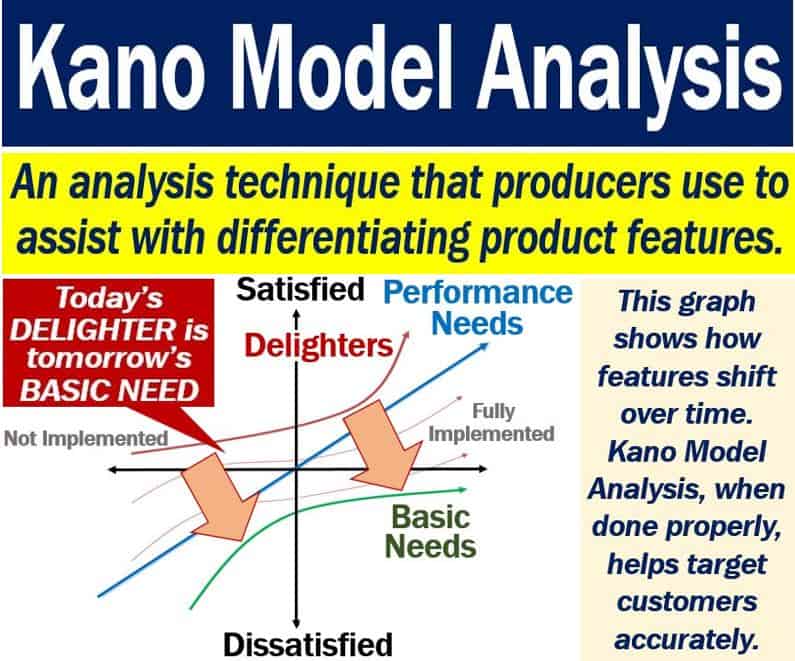
Kano Model analysis in summary
- Kano Model Analysis helps producers identify unspoken needs before prioritization.
- The Analysis helps prioritize consumer needs.
- Producers need to link their Kano Analysis with their multi-generational project plan.
- Producers need to be aware that consumers’ expectations and needs change over time.
Needs are always changing. For example, the most important features in consumers’ breakfast foods today is not the same as 40 years ago.
Obesity is currently a serious problem. Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing diabetes type 2. It also makes us more likely to die prematurely and suffer from several chronic diseases.
Consumers today have become aware of obesity’s health risks.
Therefore, how many calories a meal contains now matters much more than before. Customers want to reduce how many calories they consume during breakfast.
In fact, we want to consume fewer calories during lunch and dinner (supper) too. We even want low-calorie or low-carb between-meal snacks.
Features yesterday, today and tomorrow
Furthermore, many products’ features that once delighted customers are today essentials. They are features that the customer now expects and even takes for granted.
For example, customers were extremely happy when cars first started having electric windows. Today, however, consumers expect electric windows.
If you try to sell a new car today with manual windows, nobody will want to buy it. What was once a delightful extra has today become an essential feature.
Also, remember that what people expect today may not meet minimum expectations one day in the future. Let’s suppose that in a few decades’ time, talking to your car is a basic requirement. Opening and closing the windows just by pushing a button by then simply won’t do.
