What is medical tourism? Definition and meaning
Medical Tourism, also known as Medical Travel or Health Tourism, refers to traveling to another country for medical treatment.
Many factors influence the decision to travel overseas for medical care. For some, the decision is driven by affordability, while for others, it is the only way to receive specific treatments not available in their home country.
Medical tourism has evolved significantly over time. While it traditionally involved patients from less-developed countries seeking unavailable treatments in more developed nations, the trend has now shifted. Increasingly, people from developed countries are traveling to developing nations to access more affordable medical care.
The majority of medical tourists pay for their care at the time of service. Private companies or medical concierge services are often used to find foreign healthcare facilities.
Medical tourism – a huge market
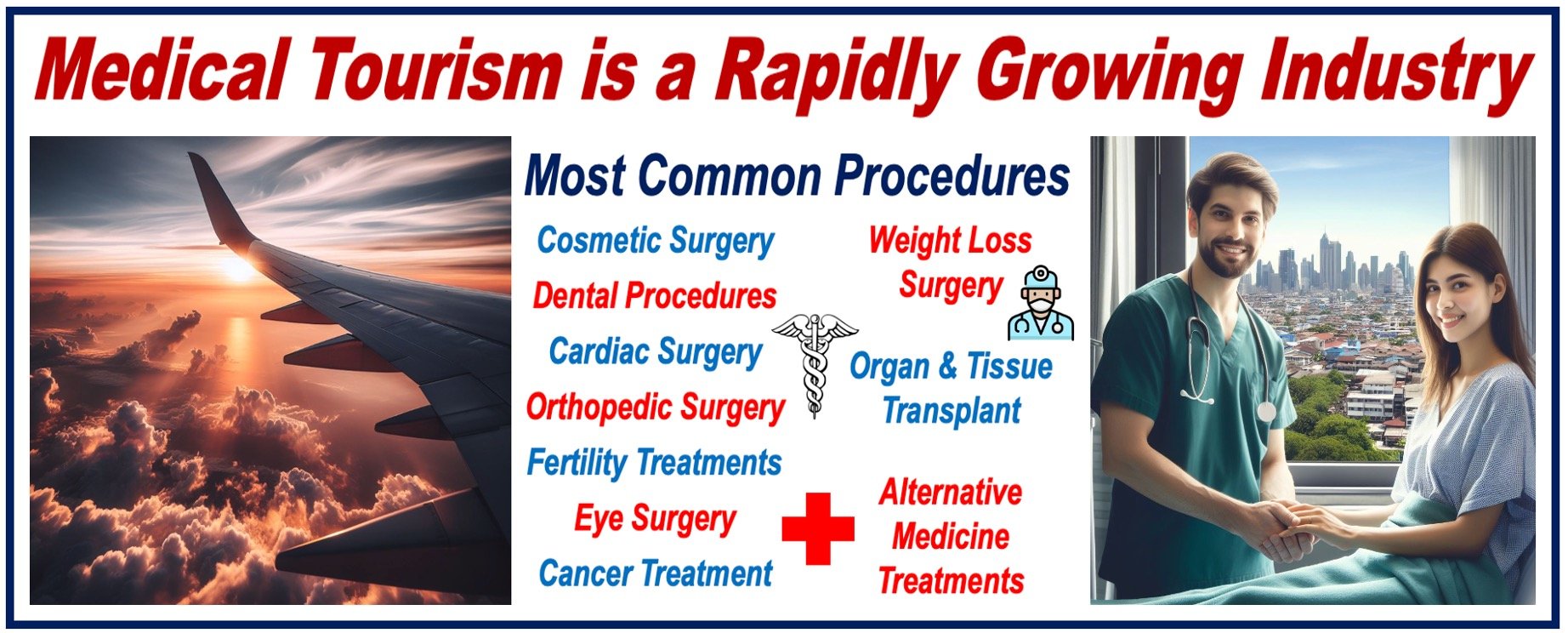
Medical tourism is now a worldwide, multibillion-dollar phenomenon. It is market-driven and shaped by medical, economic, social, and political forces.
A study by Vantage Market Research reports that the global medical tourism market should surpass $43.7 billion by 2030. From 2023 to 2030, it is expected to exhibit a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 32.9%.
According to an article published by finance.yahoo.com:
“Key trends in the global medical tourism sector encompass the surging demand for cosmetic surgery and dental care, a rise in seeking overseas alternative therapies and wellness treatments, and an increasing appetite for top-notch, cost-effective healthcare.”
The main reasons patients go abroad for medical treatment
There are many reasons why people choose to go abroad for a medical procedure, such as:
- Low cost – particularly in the US among people with no insurance or inadequate insurance.
- To avoid waiting lists – this is common among those who live in countries with a national health service, such as the UK and Canada.
- The procedure is not available in the patient’s home country.
- Combining medical care with a vacation abroad.
- Privacy.
Furthermore, advancements in telemedicine and digital health are increasingly facilitating pre- and post-operative consultations for medical tourists, enhancing the continuity and quality of care.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
“Medical tourists pursue medical care abroad for a variety of reasons, including decreased cost, recommendations from friends or family, the opportunity to combine medical care with a vacation destination, a preference to receive care from a culturally similar provider, or a desire to receive a procedure or therapy not available in their country of residence.”
The risks of medical tourism
The CDC warns about some possible risks, such as:
- Issues with communication. Misunderstandings may occur if patients receive care in a country where they are not fluent in the language.
- Poor quality or counterfeit medications in some countries.
Popular medical tourism destinations
The following quote comes from Wikipedia:
“Popular medical travel worldwide destinations include Canada, Cuba, Costa Rica, Ecuador, India, Israel, Jordan, Malaysia, Mexico, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, United States. Popular destinations for cosmetic surgery include Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, Mexico, Turkey, Thailand and Ukraine.”
International healthcare accreditation
There is a global effort to ensure that healthcare services are up to a certain standard. International healthcare accreditation is the process of certifying healthcare programs in the interest of patient safety.
For medical tourists, a facility with an international healthcare accreditation provides some insight into the quality of treatment.
In the United States, the accreditation group Joint Commission International (JCI) was formed in 1994. JCI accreditation is considered by many healthcare professionals to be the gold standard in global health care. According to JCI, it “identifies, measures, and shares best practices in quality and patient safety with the world.”
A complete list of JCI-accredited organizations can be found here.
Video – What is Medical Tourism?
This interesting video, from our sister channel in YouTube – Marketing Business Network, explains what ‘Medical Tourism’ is using simple and easy-to-understand language and examples.

