
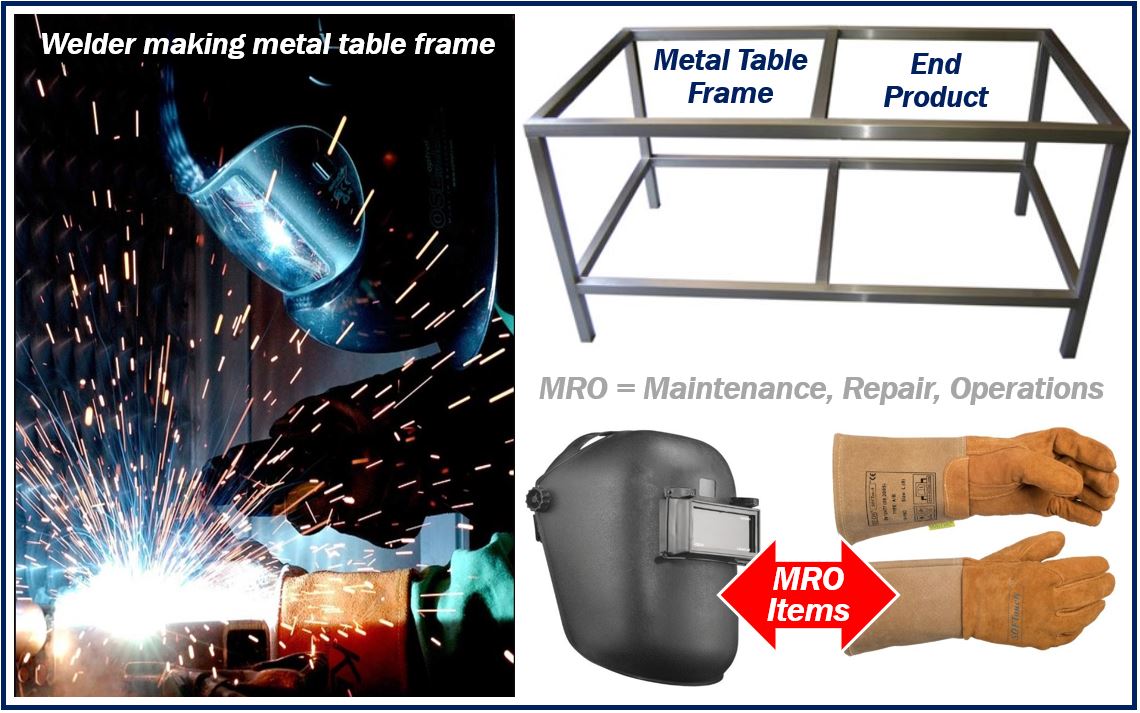
MRO Items are products and materials a company purchases and uses, but they do not end up as part of its finished products. MRO stands for Maintenance, Repair, Operations. Businesses use MRO items to keep things running. They are supplies that are consumed in the production process, however, they do not become part of the end product. Neither are they central to the company’s output.
Production workers may, for example, wear goggles and gloves. Therefore, their employer has to purchase goggles and gloves. However, goggles and gloves are not part of the company’s end product. They are examples of MRO items.
Consumables, for example, are MRO items, as are industrial equipment, and plant upkeep supplies.
We can either say ‘maintenance, repair, operations items’ or ‘maintenance, repair, and operations items.‘ It is possible to replace the word ‘items’ with ‘supplies.’ It is also correct, in this context, to use the word ‘operations’ in its singular form, i.e., ‘operation.’
My Accounting Course has the following definition of the term:
“Maintenance, repair, operations (MRO) items are products and materials purchased by a company that are not directly employed in its manufacturing process. These products are mostly used to keep the business’ operations running.”
MRO items – vital part of businesses
Maintenance, repair, operations items are a vital part of most businesses. In some companies, they represent a significant part of the purchase budget.
These types of purchases exist in both manufacturing and service businesses. A cleaning company, for example, has to buy detergent, soap, and several other items.
Although we do not hear people use the term much in the world of business, MRO items have a major impact on a company’s efficiency and bottom line. Bottom line, in this context, means profits, net earnings, net income, or earnings per share.
Direct purchases vs. indirect purchases
Companies have two main types of purchases: direct purchases and indirect purchases.
-
Direct purchases
Direct purchases, direct materials, or direct spend are items that go into the end product. In other words, they form part of the product that the company sells.
An airplane maker would put all the items in the cabin toilets in this category.
-
Indirect purchases
Indirect purchases or indirect materials are all the things a company buys to operate the business which do not end up in the end product. MRO items belong to this category.
The MRO market is massive. W. W. Grainger, Inc. is an American Fortune 500 industrial supply company based in Lake Forest, Illinois, USA. Its website lists more than 220,000 MRO-related products, including paper towel dispensers, gloves, goggles, and floor scrubbers.
MRO buyer (manager) job description
We call people who focus on MRO items MRO buyers or MRO managers. They are responsible for the preparation and issuance of purchase orders for maintenance, repair, and operations. These items are crucial for the company to function.
Regarding an MRO buyer in a manufacturing business, PayScale writes:
“In a factory, machines gradually break down, and an MRO buyer is responsible for getting the materials needed to fix the machines. The job requires regular interaction with the factory staff to know what supplies are required, although the majority of the job is done in solitude and on the computer.”
Tasks include:
- Managing all aspects of buying and distribution. At the same time, taking into account cost-effective solutions.
- Fostering a team atmosphere, communicating with clients, and reporting on progress.
- Assessing purchase orders for both accuracy and adherence to regulations.
- Strategic sourcing of required items.
- Receiving quotes from sellers and comparing them against requirements and the company’s budget.
- Managing the supply base to include renewal agreements.
- Assisting suppliers in problem solving as well as tracking corrective actions.
Example of MRO items – a car factory
There are three types of MRO items: 1. Maintenance supplies, 2. Repair components, and 3. Operations supplies.
1. Maintenance supplies
This includes lubricants, oils, and greases for machinery maintenance.
2. Repair components
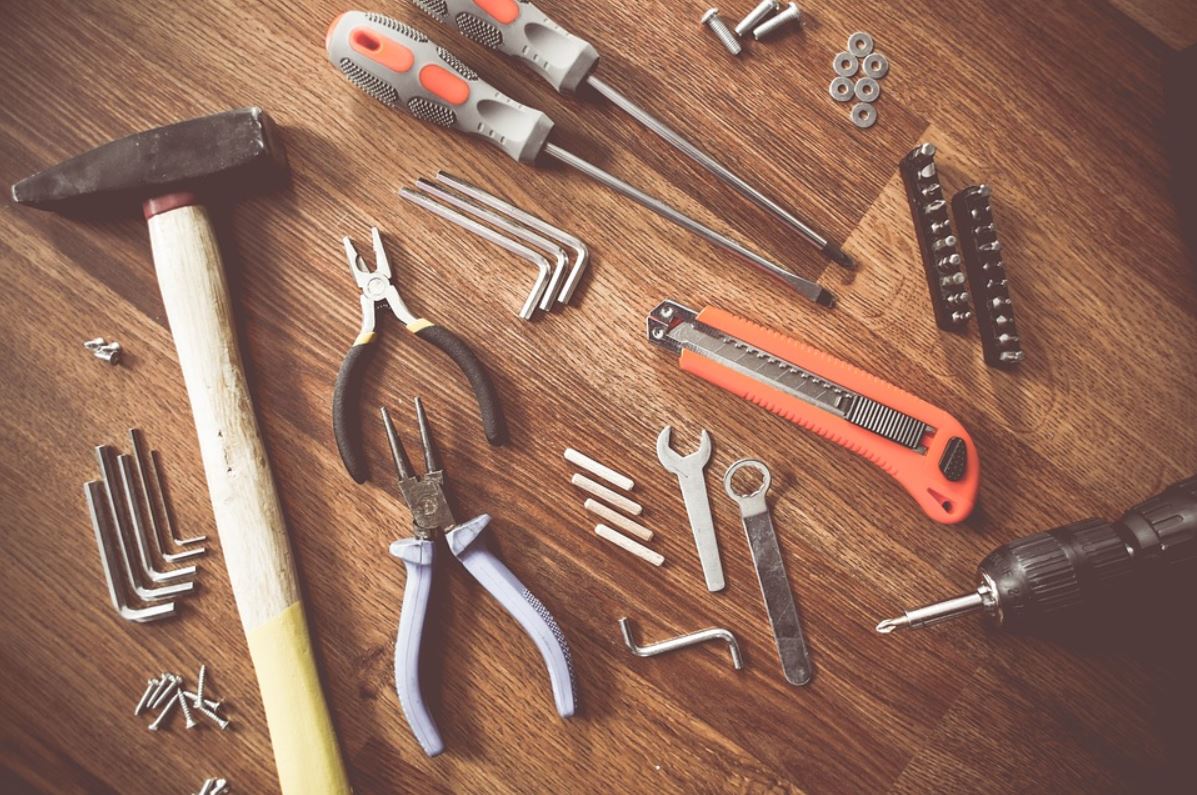
These consist of spare parts for the manufacturing equipment, such as conveyor belts, pumps, and motors. We should also include tools like screwdrivers, hammers, and wrenches.
3. Operations supplies
Examples include safety equipment such as helmets, goggles, and gloves, cleaning supplies like brooms, mops, and industrial cleaners, and office supplies like pens, paper, and ink.
All these items ensure that the factory can operate smoothly, the environment is safe for workers, and the administrative tasks are supported. However, they do not end up as components in the cars that are sold to consumers.
Video – What are MRO Items?
This video presentation, from our YouTube partner channel – Marketing Business Network, explains what ‘MRO Items’ are using simple and easy-to-understand language and examples.
