 Neural Networks are a set of algorithms and have been modeled loosely after the human brain. Computer scientists have designed them to recognize patterns. We also call them Artificial Neural Networks or ANNs.
Neural Networks are a set of algorithms and have been modeled loosely after the human brain. Computer scientists have designed them to recognize patterns. We also call them Artificial Neural Networks or ANNs.
Neural networks are not themselves algorithms, but rather frameworks for many different machine learning algorithms that work together. The algorithms process complex data.
A neural network is an example of machine learning, where software can change as it learns to solve a problem.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence
Machine learning is part of AI (artificial intelligence). Humans have the ability to ‘learn from experience,’ the term ‘machine learning’ refers to this ability when it exists in machines.
Artificial intelligence consists of sophisticated software technologies that make devices such as computers think and behave like humans.
The algorithms in the neural network ‘learn’ to perform tasks by considering and analyzing new data. They generally gain knowledge without being programmed for it. In other words, they improve on their own.
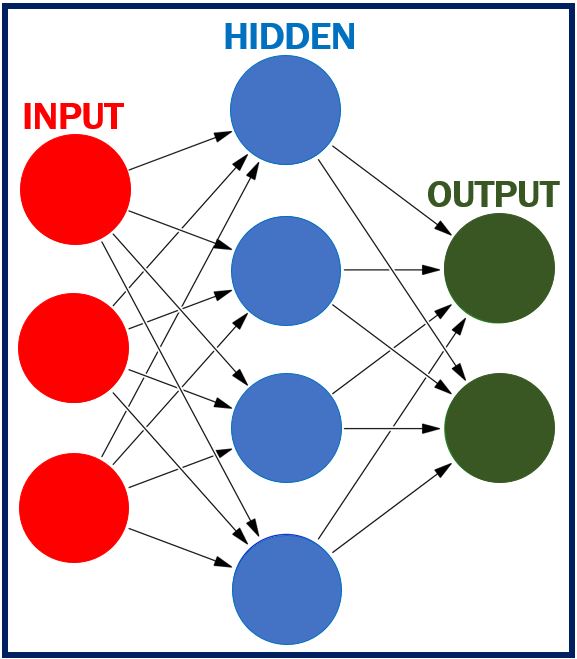
Neural networks – an example of machine learning
The algorithms in a neural network might learn to identify photographs that contain dogs by analyzing example pictures with labels on them. Some have the label ‘dog’ while others have the label ‘no dog.’
The algorithms gradually learn that dogs have four legs, teeth, two eyes, a nose, two ears, fur, and a tail. They automatically generate identifying traits from the learning material that they process.
Put simply; a neural network is a set of algorithms that tries to identify underlying relationships in a set of data. They do this using a process that mimics the way our brain operates.
A neural network can adapt to change, i.e., it adapts to different inputs. It can do this on its own, i.e., without our help.
Three ways neural networks can learn
Neural networks can learn in one of three different ways:
- Supervised Learning – a set of inputs and outputs are fed to the algorithms. They then predict the outcomes after being trained on how to interpret the data.
- Unsupervised Learning – the learning occurs without human help. The algorithms use data that is neither labeled nor classified. They act on that data without guidance.
- Reinforcement Learning – this involves taking suitable action to maximize reward in a particular situation. The algorithms learn, depending on the feedback you give them. This is a bit like helping someone find something by telling them whether they are getting warmer or colder.
Video – What is Artificial Intelligence
This Market Business News video provides a brief and simple explanation of AI.
