The Sales Cycle is a process that outlines the steps your business takes to turn a potential customer into a paying client.
It encompasses the entire process, step by step, from the moment you identify a lead (a potential customer) to the point when that lead becomes a paying customer by signing an order with your company.
Salesforce.com has the following definition of the term ‘sales cycle’:
“A sales cycle is the collection of sequential stages sales reps follow when converting a prospect into a customer. Think of it like the structure of a deal — the building blocks, like lead qualification and sales calls, that need to be stacked in a specific order so it’s possible to drive deals to close.”
Sales Cycle vs. Sales Funnel
The sales cycle and the sales funnel are related concepts, but they are not the same.
-
The Sales Cycle
This is the process a salesperson follows to turn a prospect into a customer, covering steps like prospecting, qualifying, presenting, and closing.
-
The Sales Funnel
The sales funnel represents the customer’s journey from awareness to purchase, narrowing down from many potential customers to a few buyers.
In other words, the sales cycle focuses on the salesperson’s actions, while the sales funnel focuses on the customer’s journey. Both are interconnected, as the sales cycle guides *prospects through the sales funnel.
* A prospect is somebody who you think could turn into a paying customer – a prospective customer. For the rest of this article, the term ‘prospect’ will also include ‘customer,’ and vice versa. The same applies to ‘product’ and ‘service.’
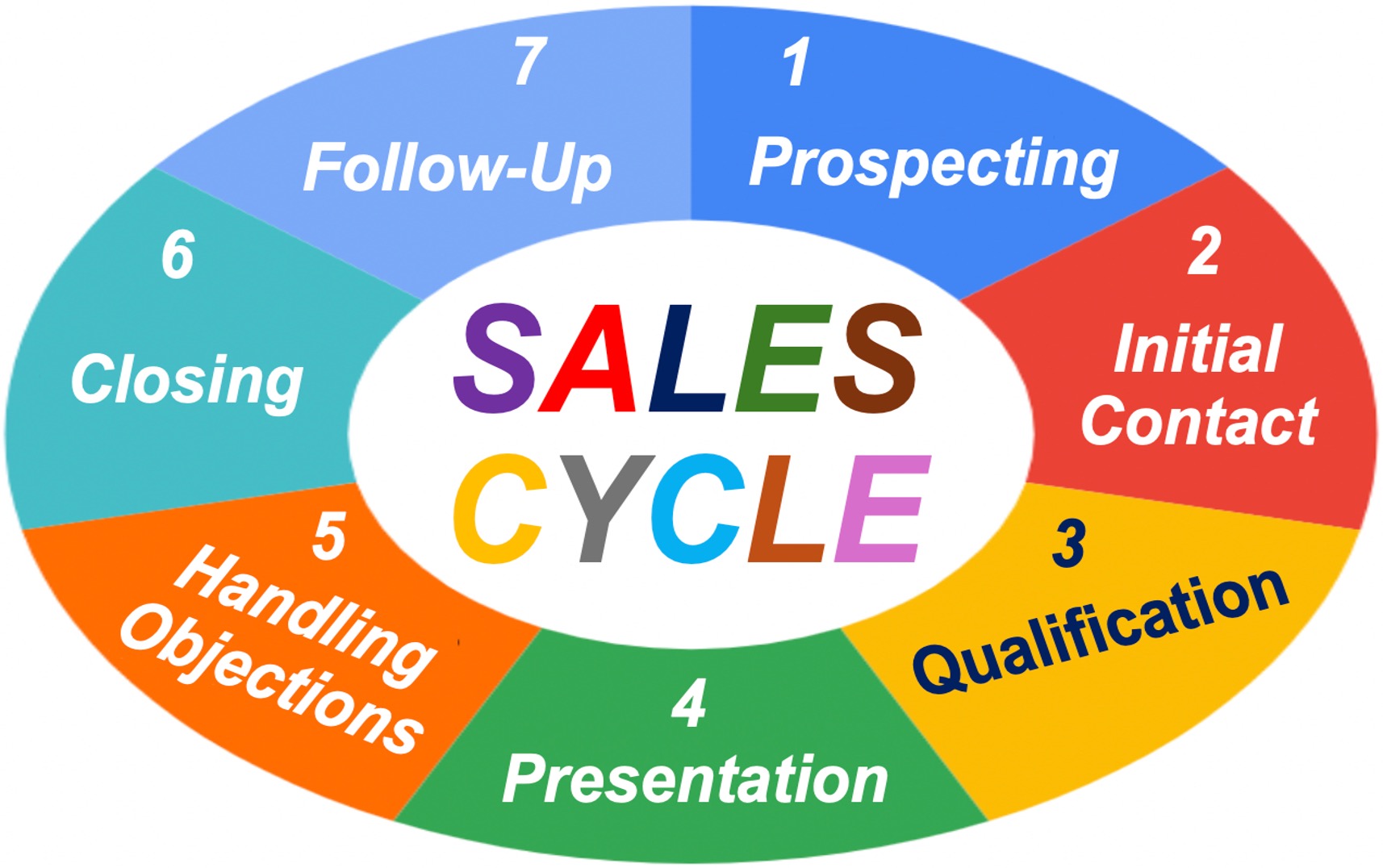
The Sales Cycle Stages
Understanding the sales cycle is crucial for improving your sales strategy and effectively guiding prospects through their buying journey.
Let’s take a closer look at each stage:
-
Prospecting
The first step in the sales cycle is prospecting. This is where you identify potential customers who might benefit from your product.
Your goal during this stage is to build a list of leads who match the criteria of your target audience. Effective prospecting requires research and a good understanding of who your ideal customer is.
-
Initial Contact
Once you have your list of prospects, the next step is to make contact. This can be done through various channels such as email, phone calls, or social media. You might even opt for a face-to-face visit.
Your objective here is to introduce yourself, your business, and what you offer. In some cases, you may also want to make sure you have secured a second appointment.
It’s important to make a positive first impression and to communicate the value that your product can bring to the prospect.
-
Qualification
Not every prospect will be a good fit for what you’re selling. The qualification stage involves determining whether the prospect has a genuine need for your product, the budget to purchase it, and the authority to make the buying decision.
By asking the right questions, you can identify whether it makes sense to move forward with this potential customer. Listen carefully to their answers. Never underestimate the importance of active listening. The world’s most successful salespeople have one common trait: They are excellent listeners
-
Presentation
If the prospect is qualified – a good fit for your product – you then move on to the presentation stage.
This is where you showcase your product, highlighting how it meets the prospect’s needs.
Your presentation should be tailored to their specific concerns, pain points, and business objectives.
* Pain points are specific problems or challenges your prospect faces, which your product aims to solve.
It’s an opportunity to demonstrate the value your product brings and how it can solve their problems.
-
Handling Objections
Your prospects will typically have concerns or objections that need to be addressed before they’re ready to buy. These might include questions about price, features, product reliability, return policies, support options, compatibility with existing systems, or the implementation process.
You must listen carefully to their objections, address their concerns directly, and provide reassurance that your product is the best solution for their needs.
-
Closing the Sale
Once objections are addressed, your next move is to close the sale. This step involves asking for the prospect’s business, that is, asking them to place an order.
Whether it’s signing a contract or making a payment, this is the moment where the prospect becomes a customer.
Effective closing techniques can make a significant difference to your *conversion rate.
* Your conversion rate is the percentage of prospects that you manage to convert into paying customers. For example, if you visited or contacted 20 prospects last month and 4 placed an order, your conversion rate is 20% or 1-in-5.
-
Follow-Up
The sales cycle doesn’t end with the sale. Following up with your new customer is essential for building a long-term relationship. In some cases, depending on what you are selling, follow-ups can also be effective in reducing cancellations.
This step ensures that they are satisfied with their purchase and opens the door for future business opportunities, such as upselling or referrals.
Compound Nouns with ‘Sales’
A compound noun is a term that consists of two or more words. ‘Sales Cycle’ is a compound noun. In the world of business, there are many compound nouns starting with the word ‘sales.’ Here are some of the most common one, plus their meanings:
-
Sales Team
A group of employees within a company responsible for selling the company’s products or services.
-
Sales Strategy
A plan or approach developed by a company to promote and sell its products or services to customers.
-
Sales Pitch
A persuasive presentation or talk that a salesperson gives to convince potential customers to buy a product or service.
-
Sales Target
A specific goal or objective set for a salesperson or sales team to achieve within a given time frame, usually in terms of revenue or units sold.
-
Sales Force
The collective group of salespeople who work for a company, responsible for selling its products or services.
A potential customer who has shown interest in a product or service and may eventually make a purchase.
The model that represents the stages a potential customer goes through from initial awareness to the final purchase, narrowing down at each step.
-
Sales Forecast
An estimate or prediction of future sales revenue based on historical data, market analysis, and other factors.
-
Sales Representative or Salesperson
An individual employed by a company to sell its products or services to customers, often working directly with clients to meet their needs.
The use of technology and data analysis to understand customer behavior, market trends, competitive activity, customer preferences, buying patterns, and sales opportunities.
Sales intelligence enables businesses to make informed decisions, personalize customer interactions, and improve conversion rates.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and mastering each stage of the sales cycle can significantly improve your ability to convert prospects into loyal customers.
By guiding your prospects carefully through each step, you can maximize your sales success and accelerate your company’s growth.
