A SWOT analysis is a diagram that helps an organization or person identify key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. With this type of analysis, a company can create new strategies to position itself better in the market. We also call it a SWOT matrix.
In this context, the letters ‘SWOT’ stand for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
SWOT analyses allow companies to identify and analyze key internal factors and external factors.
- The strengths and weakness are internal factors.
- The opportunities and threats, on the other hand, are external factors.
SWOT analysis – internal vs. external factors
What is the difference between internal and external factors?
Internal factors
Internal factors are things that we can control. Let’s suppose the employees in a company are spending too much time fixing computer crashes. That is an internal problem.
To solve the problem, the company could train its workers or get better equipment and software. It is a factor it can control
In a business, we can control the human resource department or how processes are executed.
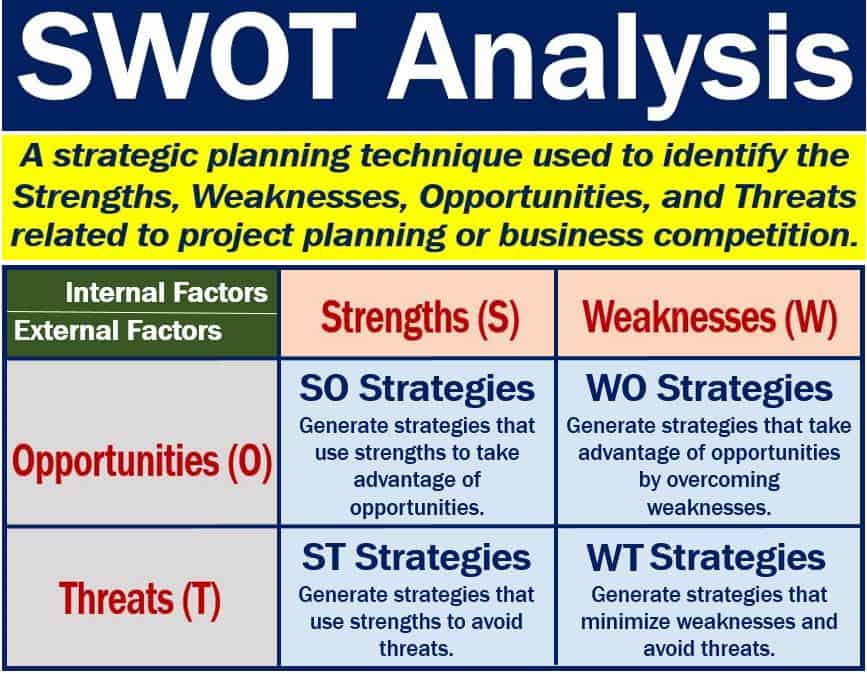
External factors
If new government regulations affect the price of a company’s goods, that is an external problem. In other words, government regulations are external factors.
Businesses have no control over external factors.
Put simply; companies can control internal factors but not external ones.
SWOT analysis – benefits
SWOT analyses provide information on companies’ capabilities and resources. They also look at the competitive environment of organizations.
After analyzing the results of a SWOT analysis, a company can subsequently create a better market strategy.
A SWOT analysis may direct a business to new opportunities. Specifically, opportunities that the company has not exploited.
It can also help managers and directors reduce potential threats by understanding what their company’s current weaknesses are.
People can use this type of planning technique for the whole company. They can also use it for just a department.
Individuals can also use it to develop their careers by identifying their skills, abilities, and opportunities.
How to do a SWOT analysis
Before starting a SWOT analysis diagram, it is important to define what your objective is.
This will ensure that the analysis heads in the right direction. If the study focuses on what matters, you are subsequently more likely to choose the right strategy.
Then you may focus on the internal and external factors.
Strengths
Think of things your company does better than the competition. Do people recognize your brand or product? What is your competitive advantage?
Examine your company’s internal resources and check which ones it is doing best. For example, it may excel in all aspects related to human resources or intellectual property.
Weaknesses
In what areas are your competitors outclassing your company? What is holding your business back? Are there any things you can avoid?
Whatever your business is lacking is, or might be, a weakness. For example, it may not have enough suitably-skilled workers. This is an area that you can control.
Opportunities
Opportunities can help your company grow. Can you turn any changes in technology, laws, or society, for example, into an opportunity?
Consumers today are more aware of and interested in the quality of life of farm animals. Specifically, animals that people eat. Consequently, people are keener to consume free range and organic eggs, chicken, etc.
Can you turn this consumer awareness and spending pattern to your advantage?
Threats
What is stopping your company from growing? There may be obstacles in technology or rules and regulations. Some aspects of society may also represent obstacles.
If your country’s economy is not doing well due to inflation, for example, that could be a serious threat.
Some threats can be completely unexpected if the business environment changes. In some countries, for example, a sudden increase in truck hijackings can be the kiss of death for a business.
SWOT analysis – example
Let’s imagine somebody called Brad wants to evaluate his employment situation. Brad’s SWOT analysis looks at his key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Strength: Brad has a high level of education.
- Weakness: he lacks work experience.
- Opportunity: he can travel and even relocate anywhere.
- Threat: in his city, there are not many jobs available in his field.
Do not confuse the term with GAP analysis. A GAP analysis is a comparison of a company’s performance now with what it could be. There is no examination of strengths, weaknesses, etc.
Performing analyses simultaneously
PEST analysis
Senior management often carries out different types of analyses at the same time. They may perform a PEST Analysis alongside a SWOT Analysis.
A PEST Analysis helps organizations identify opportunities and threats related to uncontrollable external factors. PEST stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological.
Market analysis
People often carry out a market analysis alongside a SWOT analysis. Market analyses aim to predict or anticipate which way prices will go.
They may focus on prices, growth, a market sector, or the whole economy. We often use the term ‘market analysis’ when talking about analyses that focus on stocks, bonds, or commodities.
