The Underground Economy is part of any economy where transactions occur illegally, i.e., away from official eyes. We also call it the shadow economy, black economy, or informal sector.
People who work in the underground economy do not declare their incomes. In other words, the tax authorities have no official records of their activities or transactions.
The activities and/or transactions that occur in the underground economy are illegal for two main reasons:
- A transaction that would otherwise be licit does not adhere to government reporting requirements.
- The product or service is illegal.
Narcotic drugs (illegal or illicit drugs), and prostitution in most jurisdictions, are examples of illegal goods and services. Informal labor and contraband, for example, are licit transactions that have not complied with official regulations. The smuggler did not pay import duties on an imported product.

Underground economy varies in size
The underground economy varies in size significantly across the world. It represents approximately 7% and 8% of total GDP in the United Kingdom and the United States respectively. However, in Russia it makes up 50% of GDP, and more than 50% in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Beyond GDP impact, the underground economy also affects the labor market, often providing jobs in areas where official employment opportunities are scarce or overly restrictive.
Advancements in digital payment technologies and cryptocurrencies are increasingly facilitating anonymous transactions, potentially expanding the reach and complexity of the underground economy.
According to the Encyclopedia of Chicago:
“The underground economy involves the exchange of goods and services which are hidden from official view. Examples of such activities range from babysitting ‘off the books’ to selling narcotics.”
“Over time, the underground economy has changed as lawmakers redefine what is legal or what is to be taxed. How far “underground” an activity is depends not only on its legal status but also on the capacity of government to enforce laws and/or collect taxes.”
Economist Friedrich Schneider, who works at the Johannes Keplet University of Linz in Austria, carried out a study on the US underground economy. He estimated that it represented 7.2% of GDP in 2007. He did not include prostitution, weapons trading, or illegal drug dealing in his estimate.
-
Costs to participants
In most cases, the underground economy serves willing customers. However, the fact that it is hidden typically imposes unique costs on the participants, such as bribes.
It also creates opportunities for monopoly, has no quality control, and may even encourage violence. Quality control refers to a system which manufacturers use to make sure their products meet specifications.

The dealings in the underground economy do not form part of a nation’s official GDP (gross domestic product). It is a system that uses mostly cash and never keeps official records. If there are records, the perpetrators keep them in secret or ‘number two’ accounts.
Underground economy – stigma
Even though the underground economy represents a significant percentage of GDP in developing countries, it carries a stigma. People perceive it as troublesome and impossible to manage.
However, for the poorest people in those economies, it provides essential income. It is also their only chance to earn a living in many cases.
Since the 1960s, the underground economy has been growing. Integrating the informal sector into the formal one is a challenge. However, it is something that most governments of the emerging economies are attempting to overcome.
In a closed economy, the underground economy is a vital service its citizens. In Cuba, North Korea, and the former communist countries of Eastern Europe, it has thrived.
Underground economy and strict legislation
The black economy thrives when the government becomes too strict. In other words, when laws restrict an economic activity for specific goods and services. It also thrives when the government taxes one sector too heavily.
-
US Prohibition
From 1920 to 1933, Americans were not allowed to buy or sell alcoholic drinks. We call this period the Prohibition. During the Prohibition, the American underground economy never had it so good.
-
UK tobacco
Over the past forty years, taxes on cigarettes and other tobacco products in the United Kingdom have increased considerably. Unfortunately, so has the black market in smuggled cigarettes.
-
Criminal and non-criminal activities
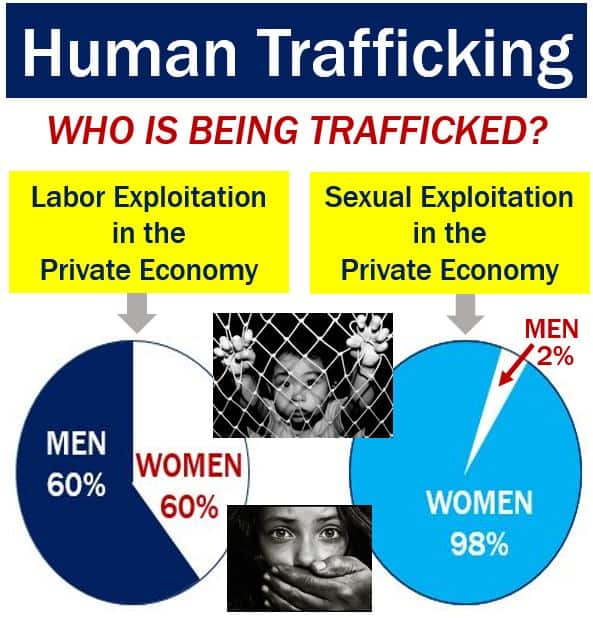
Only some of the underground economy involves criminal activities. Selling illegal narcotic drugs, weapons (without a license), and trafficking human beings, for example, are criminal activities.
However, selling chewing gum at the traffic lights of Cairo or Mexico City is not a criminal activity.
What is illegal when you sell gum at the traffic lights is not declaring that income. It might also be illegal to sell something without a license in some cases. However, the act of selling gum is not ‘criminal’.
If I pay my gardener to mow my lawn, pay him cash, and he does not declare that income, he forms part of the underground economy.
Gardening is not a criminal activity – it is legal. However, receiving money for it and not declaring that income is illegal.
It is the non-payment of taxes that classifies a licit activity as part of the underground economy. So does not declaring that income.
Measuring the underground economy
The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis said that the underground economy is extremely hard to measure. There are several direct approaches, it adds, including:
- surveys,
- discrepancies between income statistics and national expenditure,
- discrepancies between the actual and official labor force,
- tax audits,
- monitoring transactions,
- tracking the consumption of electricity, and
- analyzing currency demand.
The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis made the following comment regarding the monitoring of electricity consumption:
“This method assumes that electricity consumption is the best physical indicator of both formal and informal economic activity. It has been observed that the electricity/GDP elasticity is usually close to 1.8 So, by using electricity as a proxy for the overall economic activity and then subtracting from it the official estimates of GDP, we get an indicator of informal economic activity.”
“The difference between the growth of electricity consumption and official GDP is then attributed to the growth of the informal economy.”
Underground economy – USA
Writing in Bloomberg in 2013, Joshua Zumbrun wrote that from 18% to 19% of total US income was never reported to the IRS. IRS stands for Internal Revenue Service, i.e., the US tax authorities.
Economists estimated that $2 trillion of undeclared income represented a yearly tax gap of up to $500 billion, Zumbrun wrote.
The British Institute for Economic Affairs (BIEA) estimated that in 2012 the UK’s underground economy was worth £150 billion annually. The figure may appear huge, but a percentage of GDP it is relatively low.
The BIEA also reported that the average for the thirty-four nations that are members of the OECD was 13.4%. OECD stands for Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development.
The report authors added:
“A reduction in the tax burden is therefore likely to lead to a reduction in the size of the shadow economy. Indeed, a virtuous circle can be created of lower tax rates, less shadow work, higher tax morale, a higher tax take and the opportunity for lower rates. Of course, a vicious circle in the other direction can also be created.”
“Given this relationship, the high level of non-wage costs (averaging 39% of total labor costs) and the penalty on individuals who move from earning one third to two thirds of the median wage (averaging 58% of the increase in earnings for a one-earner couple) in the European Union should be a matter of real concern.”
“The latter figure is 79% in the UK and thus low-paid UK workers have a huge incentive to supplement their incomes in the shadow economy.”
As global economies become more interconnected, the challenge for policymakers will be not only to quantify the underground economy but also to understand its dynamic relationship with the digital globalization of trade.
Similar terms
There are many terms which mean the same as or similar to the “underground economy.” Let’s take a look at some of them, their meanings, and how we can use them in a sentence:
-
Black Economy
The black economy refers to economic activities that are illegal or not reported to the authorities to avoid taxes and regulations. It overlaps significantly with the underground economy but emphasizes illegal or illicit transactions.
Example: “Many transactions in the black economy involve cash to leave no paper trail.”
-
Shadow Economy
The same as the underground economy, it encompasses all economic activities that are hidden from official authorities to evade taxes and regulations, including both legal and illegal activities.
Example: “The shadow economy flourishes in countries with high taxation and strict regulations.”
-
Gray Economy
The gray economy consists of activities that are not illegal but are conducted without compliance with regulatory frameworks, operating in a gray area between the formal and informal sectors.
Example: “Freelancers often operate in the gray economy by not reporting all of their income.”
-
Unofficial Economy
The same as the underground economy, the unofficial economy includes economic activities not measured by official statistics due to their hidden, informal, or illegal nature.
Example: “The unofficial economy accounts for a significant portion of the GDP in some countries.”
-
Hidden Economy
The same as the underground economy, the hidden economy includes all economic transactions not reported to the state’s official records, evading taxes and regulations.
Example: “The hidden economy grows when trust in the government’s fiscal policies diminishes.”
-
Cash Economy
The cash economy specifically refers to transactions made in cash to avoid taxation and reporting, a subset of the underground economy focusing on the medium of exchange.
Example: “Small businesses often prefer the cash economy to avoid complex accounting and tax filing.”
-
Second Economy
The same as the underground economy, the second economy includes economic activities that occur outside of the officially sanctioned channels, evading taxes and regulations.
Example: “The second economy can offer services and goods at lower prices due to the lack of tax overhead.”
-
Subterranean Economy
The same as the underground economy, the subterranean economy refers to economic activities that are hidden from government oversight, encompassing both legal and illegal undertakings.
Example: “The subterranean economy includes everything from unreported income to fully illegal trade.”
-
Informal Sector
The informal sector includes economic activities that are not covered by formal agreements or regulated by the government, often lacking legal protection and benefits. It’s broader than the underground economy, including legal activities that are not regulated or taxed.
Example: “Street vendors are a typical example of the informal sector at work.”
Three Educational Videos
These three YouTube videos come from our sister channel, Marketing Business Network. They explain what the terms “Underground Economy”, “Shadow Economy”, and “Black Economy” mean using easy-to-understand language and examples:
-
What is the Underground Economy?
-
What is the Shadow Economy?
-
What is the Black Economy?
