Work-related stress is the negative reaction that employees have to excessive pressures or other types of demands placed on them in the workplace. Work-related stress can affect anyone at any level of an organization. Studies suggest that the problem is widespread and not present in just certain industries, jobs, or sectors.
The Health and Safety Executive of Northern Ireland (HSENI) has the following definition of work-related stress:
“The adverse reaction people have to excessive pressures or other types of demand placed on them at work.”
We feel stress when we cannot cope with pressures and other problems. When those pressures and other issues came from the workplace, we call it work-related stress. Another term with the same meaning is occupational stress. The term work stress is also possible.
Work-related stress can build up
Stress in the workplace can build up. In other words, it can gradually get worse. This type of stress can arise when we have to deal with unexpected responsibilities. If we have to address issues and pressures for which we do not have the necessary skills, our ability to cope suffers.
When there is a lack of perceived support, stress levels typically increase. Work-related stress is common when the worker has little or no control over work processes.

When too much or too little is demanded of us
Workers experience stress when the demands of their work exceed their ability to cope. Coping means being able to balance your job requirements with your capabilities. In other words, balancing the demands and pressures placed on you with your knowledge and skills.
If a manager gives an employee a tight deadline on a project that they feel unprepared for, they will probably start to feel undue pressure. This pressure could lead to work-related stress.
Occupational stress is not only the result of too many demands but may also be caused by too few demands.
According to HSENI:
“Stress can also result from having too few demands, as people will become bored, feel undervalued and lack recognition.”
“If they feel they have little or no say over the work they do or how they do it, this may cause them stress.”
Managing work-related stress
MIND says that good stress management is crucial in the workplace. MIND is a British mental health charity that began in 1946 as the National Association for Mental Health (NAMH).
People who have to endure high levels of work-related stress are at risk of developing mental health problems.
Depression, for example, is a mental health problem that can affect people in the workplace. Occupational stress can also lead to anxiety disorders.
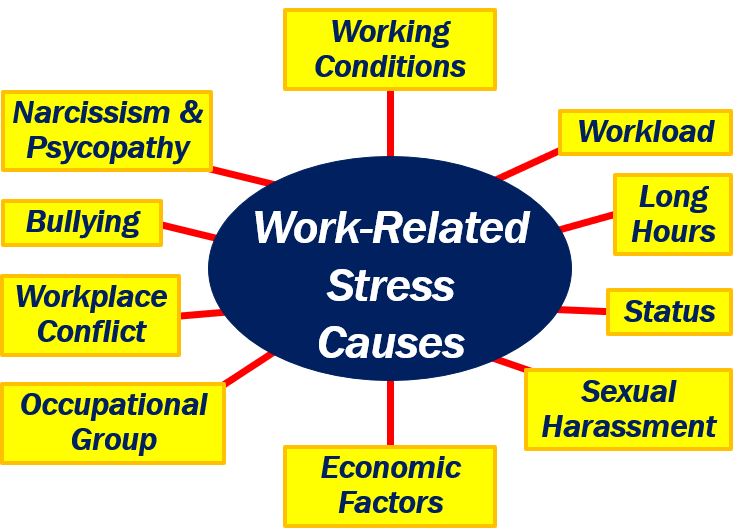
Origins of work-related stress
The workplace is full of stressors. A stressor is either something that causes stress or a chemical or biological agent that causes the release of stress hormones. In this article, the word means something that causes stress.
Below are some sources of occupational stress:
- Barriers or obstacles to career development.
- Horrible bosses. A boss might be incompetent, spiteful, aggressive, or abusive.
- Harassment in the workplace. This may be in the form of racial slurs, degrading comments, or gender harassment. There are many different types of harassment. We also use the term workplace bullying.
- The workplace is a hotbed of infighting and drama. In other words, a ‘toxic environment.’
- A negative workload.
- The worker has to work too many hours.
- Financial pressures.

Signs of work-related stress
If workers begin acting differently, it might be a sign that they are stressed. Management should be on the lookout for signs of stress in employees.
Below are two lists of signs of stress in teams and individual employees:
Signs of work-related stress in employees
- Employees change in the way they act. For example, they might arrive to work later or take more time off. They might also be more nervous and irritable.
- How they feel or think may change. There may be mood swings, loss of motivation, confidence, and commitments. Reactions may be more emotional. Also, they may become more withdrawn.
Signs of work-related stress in teams
- There are more arguments.
- The number of reports of stress increases.
- Complaint and grievance numbers go up.
- People are off sick more often.
- Staff turnover accelerates. In other words, employees leave the company at a faster rate.
- Performance suffers.
The Health and Safety Executive for the whole of the UK has the following advice if there are signs of stress:
“Acting early can reduce the impact of pressure and make it easier to reduce or remove the causes. If managers are worried that an employee is showing some of these signs, they should encourage them to see their GP. These signs can be symptoms of other conditions.”
“If there is something wrong at work, and this has caused the problem, managers should take action.”

Work-related stress – health risks
Several studies have indicated that high levels of occupational stress can make us ill. Some of these illnesses are serious, and even fatal.
-
Greater risk of cancer
In China, a team of researchers analyzed data on 280,000 male and female employees in N. America and Europe. Work-related stress, they found, increased the risk of developing colorectal and esophagus cancers. It also raised the risk of lung cancer.
-
Higher risk of cardiovascular diseases
Any disease that involves the heart or blood vessels is a cardiovascular disease.
Scientists at University College London examined data on 600,000 men and women in the US, Japan, and Europe. They found a link between occupational stress and working long hours and a moderately raised risk of stroke. They also identified a greater risk of coronary heart disease.
The researchers said:
“This review of evidence from over 600,000 men and women from 27 cohort studies in Europe, the USA and Japan suggests that work stressors, such as job strain and long working hours, are associated with a moderately elevated risk of incident coronary heart disease and stroke.”
“The excess risk for exposed individuals is 10-40 % compared with those free of such stressors.”
Working from home is not stress free
Some people say that working from home, i.e., teleworking, is the solution. The notion that working from home is stress-free is a myth. Teleworking means working from home or anywhere else that is away from the main workplace.
Researchers at Baylor University found that the likelihood of experiencing work-related stress at home is not necessarily less than in the office. What matters is either how you manage stress or what type of person you are (and possibly both).
Implementing flexible work schedules and promoting a culture of open communication can significantly mitigate work-related stress, fostering a more adaptable and resilient workforce.
Compound phrases with “stress”
A compound phrase is a term that consists of two or more words. An example is the term “Work-relates stress.” Let’s look at some more compound phrases containing the word “stress” that are used in the world of business and finance:
-
Stress Testing
A simulation technique used on asset and liability portfolios to determine their reactions to different financial situations.
Example: “The bank conducted rigorous stress testing to ensure it could withstand a sudden economic downturn.”
-
Stress Interview
A deliberate job interview strategy designed to put the candidate under severe psychological stress to assess performance under pressure.
Example: “During the stress interview, the panel bombarded him with rapid questions to see how he’d handle the high-pressure environment of the trading floor.”
-
Stress Response
The physical, mental, or emotional reaction that occurs in response to external pressures, which in the workplace can affect decision-making and performance.
Example: “The trader’s stress response to the volatile market was to diversify the investment portfolio to mitigate risk.”
-
Stress Management
Techniques and programs aimed at controlling a person’s levels of stress, especially chronic stress, typically for the purpose of improving everyday functioning.
Example: “The corporation implemented a stress management program to improve employee wellbeing and productivity.”
-
Stress Analysis
A method in financial analysis to evaluate the robustness of assets by putting them under scenarios of extreme strain
Example: “The finance team performed a stress analysis on the proposed budget to prepare for any potential shortfalls.”
-
Stress Absorption
The ability of an organization or system to withstand or manage operational stress without compromising performance.
Example: “The company’s robust risk management framework was critical for stress absorption during the unexpected market crash.”
