
Although it is now being phased out, LIBOR has long been the benchmark rate used to estimate short-term interest rates. The rate that a chosen number of reputable international banks charge one another for sizable loans serves as the foundation for LIBOR.
Unbelievably, “LIBOR” may be influencing how much you pay for your mortgage. It’s one of that financial jargon that you may choose to gloss over and conclude doesn’t relate to you.
A popular benchmark for interest rates is LIBOR.
Despite having a long history, it will be phased out after 2021, which might have an impact on a lot of adjustable rate mortgages and other consumer loans in the US. Despite scandals and fraud, it’s still widely used today, despite being phased out.
Additionally, if you have an ARM, it is probably impacting your interest rate since lenders all around the globe use LIBOR rates as a benchmark for future interest rates and as a prediction of future loan expenses.
It’s a benchmark rate based on what is referred to as a “reference rate,” which is the estimated average interest rate that a number of top international banks would charge one another for short-term loans.
How Does My Mortgage Affect LIBOR?
If you’re applying for a mortgage, you may be curious about the variables that determine the rate you pay. As a “basis,” LIBOR is the first parameter that lenders look at when determining the pricing of different kinds of ARM loans.
Then they will additionally take into account elements like your credit score, debt-to-income ratio, down payment amount, and more to more precisely establish your interest rate. The LIBOR rate, which banks charge one another rather than specific borrowers, is not the amount you’ll see in your interest computation.
Instead, you will pay an interest rate that is indexed to LIBOR and based on your unique situation, which influences the lender’s assessment of your ability to repay the loan.
Or more specifically, how much risk they believe they are taking on based on your prior credit history and ability to pay your bills. If you are having financial difficulties and cannot pay the interest, then use same day loans online direct deposit.
Here’s why it only applies to certain kinds of mortgages, however. A broad range of mortgage loan options, including ARMs and fixed-rate mortgages, was probably provided to you when you were looking for a loan and consulting a specialist about the best financial solution for your needs.
Because ARMs provide lower monthly payments at the beginning of their terms, many homeowners choose them, especially in property markets where prices are higher.
Why Is the LIBOR Phasing Out?
It was uncovered in the wake of the Great Recession, which lasted from 2007 to 2009, that certain financial firms had been manipulating LIBOR via the interest rates they reported. A number of institutions were hit with significant penalties as a consequence of the LIBOR affair, and several people were sentenced to jail.
Since that time, LIBOR has gradually lost part of its credibility and the number of transactions relying on it has been declining. The Financial Conduct Authority of the United Kingdom said in August 2017 that LIBOR will be completely phased out by the end of 2021.
Since then, the phaseout has been postponed, but it is still going. After June 30, 2023, the entity that oversees LIBOR will stop publishing the LIBOR index, according to their announcement.
How Do Loans And LIBOR Interact?
It may seem that LIBOR, the rate at which banks lend money to one another, has little impact on typical borrowers. In actuality, however, a lot of financial organizations base the interest rates on their own lending products on LIBOR. The following loan categories may be impacted by LIBOR.
ARMs
Gains in LIBOR are significant if you have a mortgage tied to the rate, which, according to the Council on Foreign Relations, is the case for around 50% of mortgages in the United States.
A fixed interest rate, usually one that is low, is secured with an ARM. The mortgage resets to the current interest rate of that index after that time period is over. There are several other types of ARMs, including the popular one-year and 5/1 ARMs. The first number you see is the length of time you pay a fixed rate (in this example, five years), and the second number indicates how often the rate is adjusted (once a year).
Your monthly payment will be less if LIBOR is lower when the interest rate on your mortgage resets. Your monthly payment will increase if LIBOR rises. For someone who has enough money to absorb an increased mortgage payment, the difference in LIBOR may not signify much, but for others who are barely getting by, a rising LIBOR may be disastrous.
Interest rates were historically low during most of the beginning of 2021 because of the COVID-19 epidemic. Nevertheless, rates are starting to rise once again despite inflation, thus ARM borrowers will experience an increase in their rates with LIBOR or its successor. The equity in your house, your credit score, and your employment condition are just a few of the numerous variables that will determine your capacity to achieve that.
HELOCs
You will also be influenced by LIBOR if you have an adjustable-rate home equity line of credit, which is often the case. With a HELOC, you may borrow up to your credit limit and repay it over the class of a draw period, just as with a credit card.
During the draw term of a HELOC, payments typically consist primarily of interest. The interest rates are often LIBOR-based and typically changeable. When LIBOR is low, borrowers may have relatively low minimum monthly payments, but when LIBOR rises, they may experience an increase.
Education Loans
Also often linked to LIBOR are private student loans that are not insured by the federal administration. You may, for instance, take out a student loan with a rate of LIBOR plus 2%. The margin would be determined by the borrower’s and/or cosigner’s creditworthiness. Like with mortgages, borrowers with variable-rate loans are most affected by LIBOR. Your monthly payments may change yearly depending on the LIBOR rate if you have a variable-rate student loan.
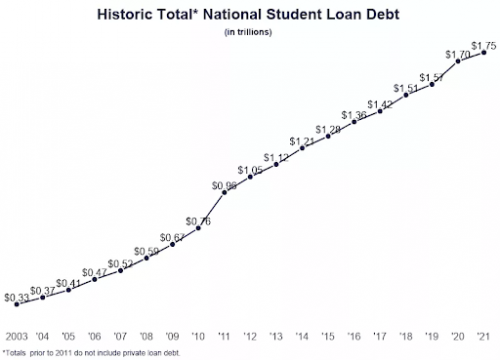
When searching for a mortgage or student loan, being aware of how the LIBOR affects interest rates can help you become a more knowledgeable borrower. Nationwide, 43% of college students report that they have some sort of educational debt. You can also enter this percentage, therefore, you must monitor your credit and finance costs.
Individual Loans
A personal loan is an unsecured debt type that could also be impacted by LIBOR. These loans are often used to finance significant purchases or to consolidate debt with high-interest rates. Although they can have variable rates, personal loans are mostly fixed-rate loans.
When interest rates are very low, a variable-rate personal loan may be appealing since you may potentially pay it off faster and have lower monthly payments. However, if your loan is linked to LIBOR, just like other forms of adjustable-rate debt, your rate will rise as LIBOR does.
In Conclusion
LIBOR affects ARM borrowers, HELOC holders, those with private student loans, and those with personal loans in a variety of ways. It’s important to be aware of how LIBOR can influence your monthly payments so that you can budget accordingly. Understanding how the LIBOR rate is determined can help you make informed decisions about borrowing money.
Interesting Related Article: “Interest Rates, Inflation & Real Estate“

