What is E-commerce? Definition and examples
E-Commerce is a type of business model that focuses on doing commercial transactions through electronic networks such as the Internet. E-commerce stands for Electronic Commerce. We can also write it without the hyphen, i.e., ecommerce.
Put simply; E-commerce is any business activity that happens online.
Emerging alongside advancements in technology, e-commerce has reshaped the landscape of retail and business interactions worldwide.
Any business can operate using e-commerce platforms. All they need is the necessary technology to provide the service.
TechTarget has the following definition of the term:
“E-commerce (electronic commerce or EC) is the buying and selling of goods and services, or the transmitting of funds or data, over an electronic network, primarily the internet.”
M-commerce, which stands for mobile commerce, is part of e-commerce. However, m-commerce only includes activities in which the user has a smartphone or other handheld wireless devices.
E-commerce – no barriers
With E-commerce, people or businesses can acquire goods electronically without having to worry about time or distance barriers. They can also sell goods.
In other words, with E-commerce, you can buy and sell things whenever and from wherever you like.
Running a business online is generally cheaper than running a traditional one.
For consumers, there is more choice online because we can buy items from all over the world.
-
No retail therapy effect
However, unlike in a traditional store, the online shopper cannot physically touch or smell the product.
There is no ‘instant gratification’ with E-commerce, because the purchaser must wait for their item to arrive.
People who enjoy the therapeutic effects of going to the shops don’t get this from E-commerce. In other words, retail therapy is just not the same when the shopping happens online.
E-commerce – examples
-
Online shopping
Online Shopping occurs when a customer buys through a digital platform.
If you buy something online from, for example, retail giant Amazon, you are online shopping. Online shopping is part of online retailing.
-
Internet Banking
We also call it online banking. Nearly all banks today offer services through their website.
We can transfer money, apply for an overdraft facility, and pay off our credit cards online. An overdraft facility is an arrangement with the bank in which your account may be in debit.
We can also apply for loans and even mortgages on some websites.
-
Electronic payments
Some companies have an online electronic payments service which allows you to perform transactions digitally. They say their service is extremely safe and effective.
Pay Pal, for example, is a global online payments system that supports online money transfers. It is an electronic alternative to traditional paper methods like money orders and checks (UK: cheques).
-
Purchasing tickets online
This E-commerce service helps consumers purchase tickets for concerts and movies. We can even buy bus, subway (UK: underground) and train tickets online.
There is no need go to a ticket office and stand in line. We can purchase the tickets online from the comfort of our homes.
-
Online Auctions
People can place bids and acquire products at competitive prices online.
-
Digital Marketplaces
These are platforms that connect sellers and buyers to trade goods and services online, facilitating transactions between individuals and businesses.
-
Online Food Delivery Services
These services that allow customers to order food from restaurants via an online platform or mobile app, with options for home delivery or pickup.
-
Online Learning
Today, there are many online platforms offering courses, certifications, and educational resources for students of all ages, enabling remote learning and skill development.

E-commerce – transaction types
We classify E-commerce into six types of transactions:
-
Business to Business (B2B)
This is an E-commerce transaction that one business does with another business.
For example, when a retailer buys from a wholesaler, that is a B2B transaction. A retailer is a shop; it sells to consumers. A wholesaler has a big warehouse and sells to retailers.
-
Business to Consumer (B2C)
B2C are transactions that sell directly to final users. For example, when a store like, Macy’s or Ikea sells to a consumer, it is a B2C transaction.
-
Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
C2C are transactions between consumers. For example, if I sell my car to a private individual online, that is a C2C transaction.
C2C transactions exist on eBay and parts of the Amazon website.
-
Government to Business (G2B)
In this type of transaction, the government pays a business.
If the government, for example, pays a company for a software update, that is a G2B transaction.
-
Business to Government (B2G)
B2G transactions occur when a business pays the government. This may occur when a business renews a license or pays government fees online.
-
Consumer to Government (G2C)
G2C transactions occur when individual people pay the government. If I pay my parking fine online, for example, that is a G2C transaction.
‘E’ = ‘electronic’
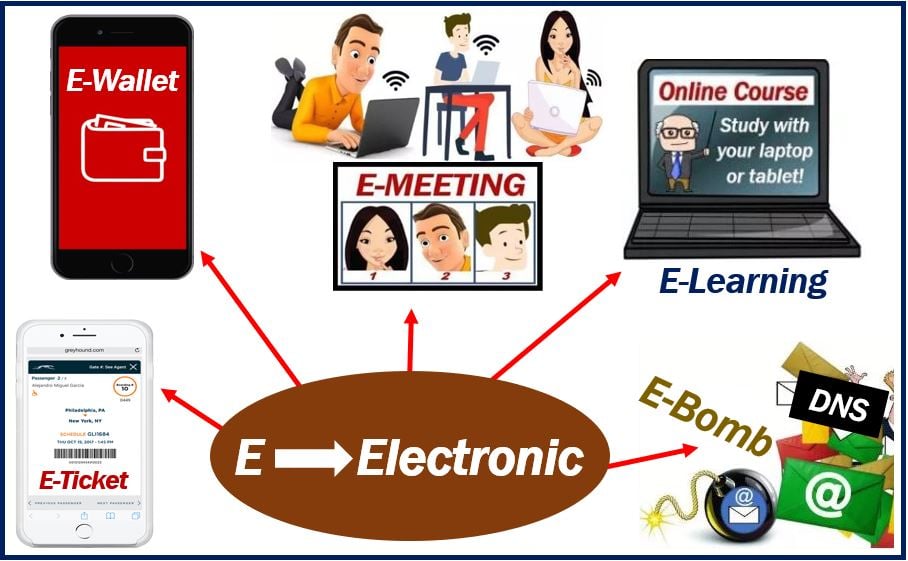 Since the birth of the Internet, many new terms have become common in the English language. Most of them begin with the letter ‘e’ followed by a hyphen. The letter ‘e’ stands for ‘electronic.’
Since the birth of the Internet, many new terms have become common in the English language. Most of them begin with the letter ‘e’ followed by a hyphen. The letter ‘e’ stands for ‘electronic.’
-
E-wallet
An e-wallet or digital wallet is a digital system that stores a person’s payment information. It has information on their credit cards, ID, loyalty card, address, etc.
-
E-ticket
This is an electronic ticket, i.e., paperless ticket that is equivalent to a paper one. It has details of the purchaser, plus his or her flight, event, etc.
-
E-meeting
An e-meeting is one that takes place over the Internet. The participants can see and hear each other. They talk in real time.
-
E-mail bomb
An E-mail bomb is an attack with thousands of emails, all of them going to one e-mail address.
It is a type of malicious cyber attack. The bomber’s aim is to crash the victim’s server, i.e., shut down their system.
-
E-learning
E-learning or electronic learning means online learning. There are thousands online courses today. People can even do an online post-graduate Master’s degree.
-
E-government
E-government uses the internet to provide public services, making government operations more accessible and efficient for citizens through digital means.
-
E-health
E-health is the use of electronic processes in healthcare, including telemedicine and electronic medical records, to improve efficiency and patient care.
-
E-reading
E-reading involves reading digital content on electronic devices, offering access to a vast range of books and documents conveniently and portably.
Three Videos
These three YouTube videos come from our sister channel, Marketing Business Network. They explain what the terms “E-Commerce”, “Online Business”, and “Online” mean using easy-to-understand language and examples:
-
What is E-Commerce?
-
What is Online Business?
-
What Does Online Mean?

