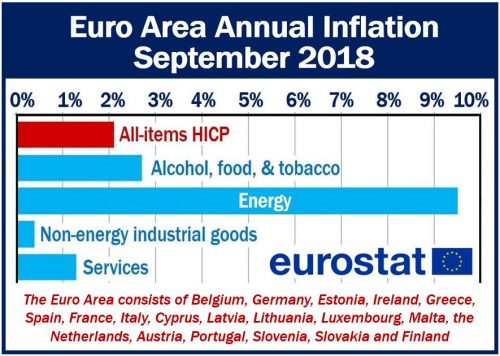
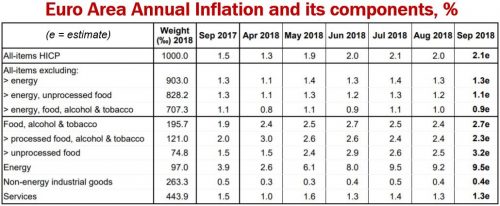
The euro area annual inflation rate estimate shows a higher price increase in September 2018, at 2.1%, compared to August’s 2.0%, says Eurostat. Eurostat is the statistical office of the European Union.
Among the euro area’s main drivers of inflation, Eurostat says that energy had the highest annual inflation rate in September. In September, energy inflation stood at 9.5%, compared to 9.2% in August. Food, alcohol, and tobacco came in second at 2.7% versus 2.4% in August, and then by services at 1.3%, which was the same as August.
The price increase of non-energy industrial goods, which was also stable compared with August, was 0.4% in September.
What is the euro area?
The euro area consists of nineteen countries that use the euro as their national currency. A couple of decades ago, EU member states began abandoning their currencies and adopting the euro. We also refer to those countries or the euro area as the EA19.
The euro area countries are Finland, Slovakia, Portugal, Austria, the Netherlands, Malta, Luxembourg, Lithuania, Latvia, Cyprus, Italy, France, Spain, Greece, Ireland, Estonia, Germany, and Belgium.
The term EU28 refers to the European Union and all its twenty-eight member states. Not all EU28 members belong to the EA19. In other words, not every EU member state has the euro as its national currency.
The United Kingdom and Denmark, for example, opted to stay out of the euro and have continued using their national currencies. Germany has the euro as its national currency. Therefore Germany belongs to both the EU28 and EA19. The UK, on the other hand, belongs to the EU28 but not the EA19.
Annual inflation rate
Inflation refers to the rise in prices. Annual inflation is the change in prices over a twelve-month period. For example, September 2018’s annual inflation refers to price rises since September 2017.
