A capital gain is the profit we make when we sell a capital asset. In other words, when we sell a capital asset for more than its purchase price.
Capital gain is the opposite of capital loss. A capital loss occurs when a capital asset is sold for less than its purchase price.
The gain is only made when the sale of the asset has concluded. There is no capital gain before a sale. In other words, if your asset rose in value, but you have not sold it, there is no capital gain.
Put simply, the term ‘capital gain’ refers to the investment income one gets from property, shares, bonds, and intangible assets.
Examples of capital gain
Selling art for a profit
- Purchase: You buy a rare painting for $100,000.
- Sale: A yeaar later you sell the painting for $125,000. T
- Capital gain: You originally paid $100,000 for the painting, and sold it for $125,000. You made a capital gain of $25,000 ($125,000 minus $100,000).
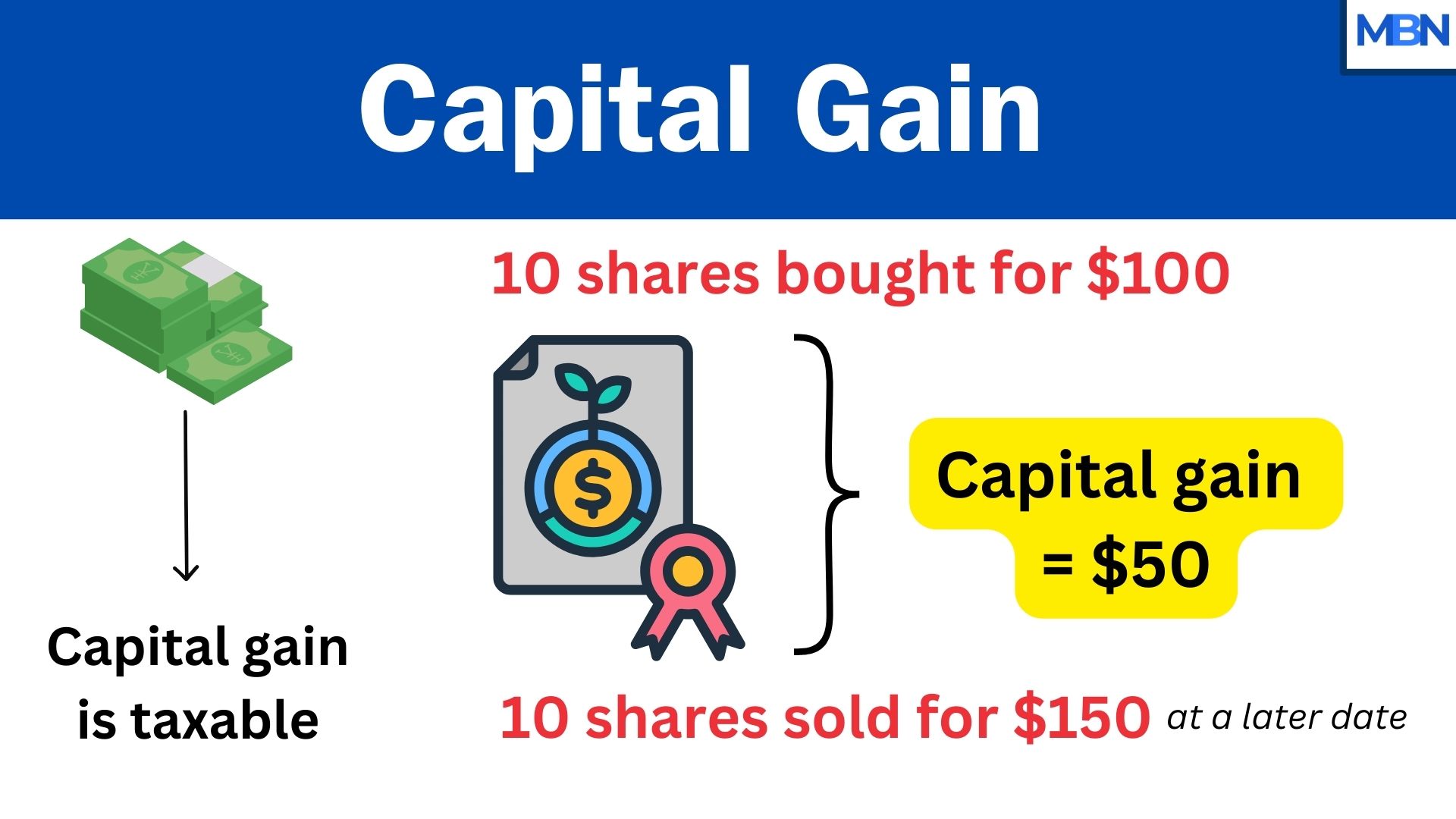
Selling stock for a profit
- Purchase: You buy 10 shares of a company’s stock for $10 each, spending $100 total.
- Sale: Several months later, the stock price rises to $15 per share, so you sell your 10 shares for $150 total.
- Capital Gain: You originally paid $100, and you sold for $150, giving you a $50 capital gain ($150 minus $100).
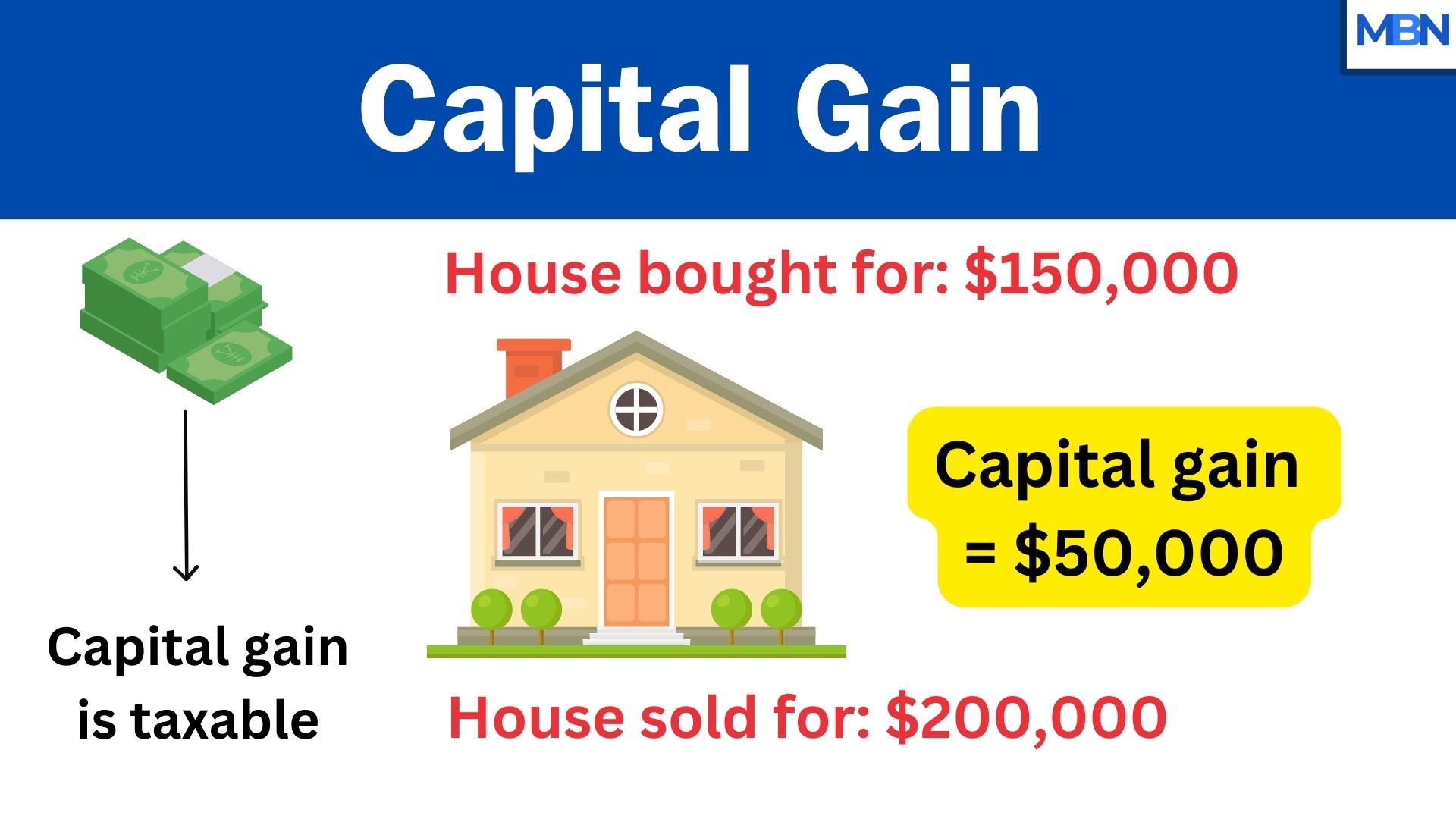
Real estate increase in value
- Purchase: You buy a house for $150,000.
- Renovations and Time: Over a few years, the neighborhood becomes popular, and you invest a bit of money in renovations, making the house more appealing.
- Sale: You sell the house for $200,000.
- Capital Gain: You paid $200,000 but sold it for $250,000, so your capital gain is $50,000 ($250,000 minus $200,000).
These examples show the basic idea: if you sell something for more than you bought it, the profit you make is typically considered a capital gain.
Capital gains tax
Most governments impose a tax on capital gain. It’s a tax levied on the profit (the “gain”) made from selling or disposing of an asset that has appreciated in value. The difference between the purchase price and the selling price is your capital gain and that is what most governments tax. Importantly, you are not taxed on the full sale price, but rather on the increase in the asset’s value from when you bought it.
In the US
In the United States, capital gains tax applies to the profit from the sale of capital assets. The US system distinguishes between short-term and long-term capital gains:
Short-Term Capital Gains:
- These are gains on assets held for one year or less. They are typically taxed at ordinary income tax rates, which can range (for federal taxes) from 10% to 37%, depending on your total taxable income.
Long-Term Capital Gains:
- These are gains on assets held for more than one year. They are taxed at preferential rates (often 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your income level). This system encourages longer-term investment. High-income taxpayers may also face an additional Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT).
State Taxes: Depending on where you live, you might also owe state-level capital gains tax in addition to federal tax. Rates and rules vary by state.
In the UK
According to the UK Government, capital gains tax is imposed on the profit you make when you sell (or “dispose of”) an asset that has appreciated in value. Crucially, it’s the gain (the increase in value) not the total amount received, that is subject to this tax.
Rates and Allowances: The tax rate depends on the type of asset and the taxpayer’s income bracket. UK taxpayers also have an annual tax-free allowance (which can change year to year). Only the gains above this threshold are taxed.
Definition of capital assets
Capital assets are, in theory, things that we use to produce goods and deliver services. For example, machinery, equipment, vehicles, etc., are capital goods.
However, most tax authorities, including the United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS), have a wide definition of the term. They classify stocks, bonds, and some other investments as capital assets.
According to the IRS, nearly everything you own and use (whether for personal enjoyment or investment) is classified as a capital asset. This encompasses assets such as your home, personal belongings like household furnishings, and investment instruments like stocks and bonds.
Most countries’ tax authorities classify capital gains and losses into long- or short-term. If you have held it for over 12 months before selling it, the capital gain is long-term. On the other hand, if you have owned it for one year or less, the capital gain is short-term.
