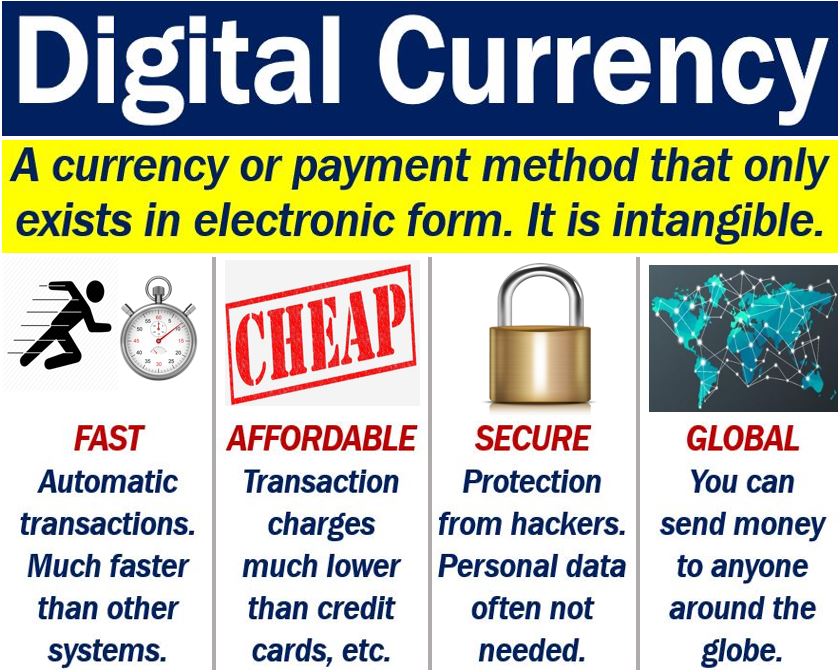
Digital Currency is a type of money that is only available electronically. Unlike banknotes and coins, digital currency is not available in physical form. We can transfer digital currency between users or entities using technology like smartphones, tablets, computers, or the Internet.
As with traditional money, we can use digital currencies to purchase goods and services.
Sometimes, however, you can only use a digital currency for specific purposes, such as a social network or online game.
We also call it digital money, virtual money, virtual currency, or cybercash. However, their meanings may vary slightly, depending on who is writing or speaking.
Cryptocurrency and central bank issued ‘digital base money,’ for example, are types of digital currency.
Physical vs. digital currency
Digital currencies are similar to traditional money. However, they differ in two main ways:
– First, digital currencies have no physical properties. You cannot hold them in your hand like you can a $10 bill, nor can you put them in a physical piggy-bank. In other words, they are intangible.
You can, however, hold digital currencies in a virtual wallet.
– Second, they allow for borderless transfer-of-ownership and instantaneous transactions.
Traditional vs. virtual vs. digital currency
We see many terms for traditional currency and currency in electronic form. People often use some of them interchangeably, both correctly and incorrectly.
However, when experts cannot agree on what virtual currencies and digital currencies mean, it is difficult to know who is right.
Digital or virtual currency?
A 2015 ECB (European Central Bank) report says that virtual currencies are a digital representation of value. No central bank, e-money institution, or credit institution has issued them.
In some cases, people use virtual currencies as alternatives to money.
An ECB article titled ‘Virtual Currency Schemes‘ defines virtual currency as a type of unregulated digital money.
The authors say that the currency’s developers issue and control it. Only members of a specific virtual community accept it, they add.
The Bank for International Settlements (BIS), on the other hand, defines digital currencies as assets represented in digital form. The BIS also said that digital currencies have some monetary characteristics.
Digital currencies may be traditional currencies
Sometimes, digital currencies represent sovereign (traditional) currencies which people can redeem for cash, just like digital money. In such cases, digital currency represents e-money, i.e., electronic money.
Therefore, the cryptocurrency Bitcoin is a digital currency. However, it is also a kind of virtual currency.
Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, and Ripple base themselves on cryptographic algorithms. Therefore, these types of virtual currencies are also cryptocurrencies.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are a type of digital currency. Their creators designed them to be ultra-secure, and in the majority of cases anonymous. In other words, people can perform transactions without revealing their identities.
Cryptocurrencies are secure thanks to cryptography. Cryptography is the art of creating and deciphering code.
Cryptocurrency creators use encryption techniques to regulate currency generation and also to verify the transfer of funds.
Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies do not have a central regulator, i.e., there is no central bank.
Despite their advantages, cryptocurrencies, particularly those based on ‘proof-of-work’ systems like Bitcoin, face criticism for their significant energy consumption and environmental impact, as they require extensive computational power for mining and transaction verification.
The first cryptocurrency was Bitcoin. Bitcoin, which is the most common cryptocurrency in circulation today, appeared n 2009. Ethereum (Ether) is the second most common.
The term “Digital”
There are many compound phrases with the word digital, apart from ‘digital currency.’ Let’s have a look at some of the most common ones:
-
Digital Money
Electronic form of currency used for online transactions, not physically tangible like coins or banknotes. Digital currency is a type of digital money.
-
Digital Economy
An economic system centered around digital technologies and online transactions.
-
Digital Wallet
A system for storing electronic payment information and passwords.
-
Digital Banking
Online and app-based banking services.
-
Digital Payment
Electronic methods for paying for goods and services.
The global economy is undergoing digitization, it is becoming more and more digital. It is driving changes in e-commerce, online services, digital banking, and the use of digital currencies.
