What is a gray market? Definition and examples
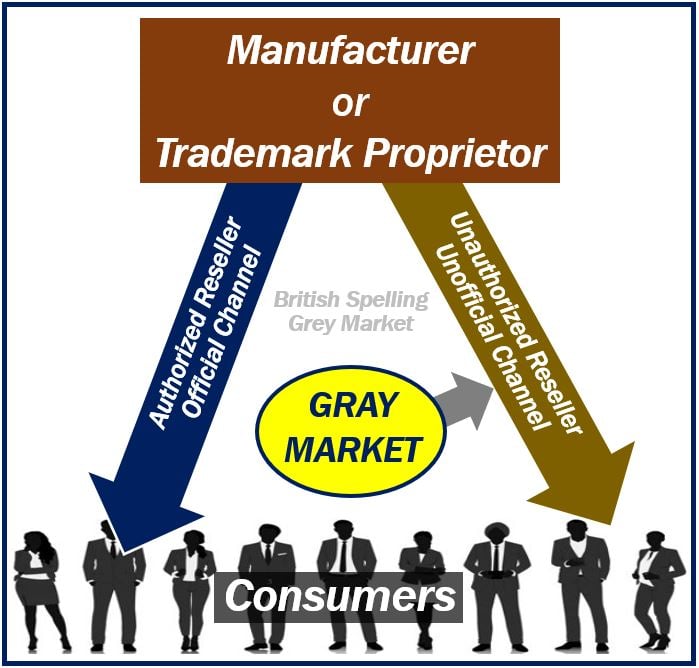
A Gray Market (British: Grey Market) trades a commodity through an unauthorized channel. In other words, the trademark proprietor or original manufacturer has not authorized the distribution channel.
If a manufacturer or authorized agent sells a product outside the terms of their agreements with resellers, we call those goods gray market products or gray market goods.
Cambridge Dictionary has two distinct definitions of the term:
1. “An unofficial but not completely illegal system in which products are bought and sold.”
2. “People over about 50, considered as a group to which products can be sold”.
 The term may also refer to an unofficial market where people buy and sell securities. The word securities, in this context, refers to financial instruments such as bonds or shares.
The term may also refer to an unofficial market where people buy and sell securities. The word securities, in this context, refers to financial instruments such as bonds or shares.
Vehicles
Manufacturers of cars and other vehicles segment the global market according to territory and price. This creates demand for a gray market, or gray import vehicles.
Often, the consumers who acquire gray import vehicles find that their cars do not meet all local regulation requirements. Finding services and parts for such vehicles may be difficult because their cars are different from the versions sold by local official dealers.
When consumers purchase a car in the gray market, for example, from another country, ensuring services history can be a problem.
Not long ago, hundreds of British consumers every year would buy their cars from Belgium because they were cheaper. Even after paying for moving the steering wheel and pedals to the other side, they saved money.
Securities
The term may refer to off-market trading, especially when a stock has been suspended. It may also refer to trading which occurs before the official trading of new securities starts.
Underwriters and issuers of stocks can use gray markets to test demand for a new offering.
Although this securities market is unofficial, it is not illegal. Trades are binding, but nobody can settle until official trading starts.
Marketing
The term can also be used to refer to the market of consumers who are generally 50 or older. This demographic is becoming increasingly significant as people are living longer.
Marketing to the gray market (in this context) involves understanding their specific need and preferences. Products may need to be more user-friendly for those with mobility issues, or advertising campaigns might need to focus on values or themes that resonate with older generations.


