Intellectual Property refers to things or processes our minds create as well as symbols, names, and images.
Things our minds create include works of literature, art music and inventions, while symbols could be company logos, trademarks, and slogans.
According to the World Intellectual Property Organization, intellectual property refers to creations of the mind. This includes inventions, literary and artistic works, designs, and the symbols, names, and images used in commerce (World Intellectual Property Organization).
Intellectual property is divided into two separate categories: 1. Copyright and, 2. Industrial Property.
What is copyright?
Copyright refers to:
- Works of literature, such as plays, poems, news articles and novels.
- Films and movies, including the famous Hollywood films, as well as TV adverts, TV shows, soaps and documentaries.
- Works of art, such as sculptures, paintings, photographs, melodies, songs and architectural designs.
What is industrial property?
Industrial property refers to:
- Trademarks, such as the names Google, Microsoft, and AT&T. The word ‘Coke’ has been a registered trademark of the Coca-Cola Company since March 27th, 1944. ‘Fanta’ and ‘Sprite’ are also trademarks of the Coca-Cola company. ‘Coca-Cola’ is also a trademark.

- Patents protect new inventions and cover how they work, what they do and how they do it, what their components are (what they are made of), and how they are made.
If an inventor is granted a patent, he or she has the legal right to take action under civil law to block others from selling the invention, using it, or making things using the invention without permission.
Patents are granted by a country (sovereign state) to an inventor or assignee for a fixed period in exchange for a detailed description of the invention
Patents do not include discoveries, they only apply to something that did not exist before. For example, if you are a scientists and discover a new element, that is not an invention, it was already there, therefore that element cannot be patented. However, if you invented the means of discovering that element, you might be able to patent that means if it never existed before.
In most countries a patent is valid for twenty years.
What are intellectual property rights?
The term Intellectual Property Rights simply refers to the acknowledgement and protection of intellectual property if it is properly registered. For example, writers, musicians and artists are protected by copyright for a period of 50 years after their death.
Peter Pan
The children’s fairy tale “Peter Pan” was written by Scottish playwright and novelist J.M. Barrie (1860-1937). Before he died he gave the rights of the Peter Pan works to Great Ormond Street Hospital in London, a children’s hospital, which has benefited enormously.
Pharmaceutical research and development
Without intellectual property rights it is doubtful that 95% of pharmaceutical drugs or vaccines would exist today. A new drug is usually on the market after several years of research and development, followed by animal and then human clinical trials.
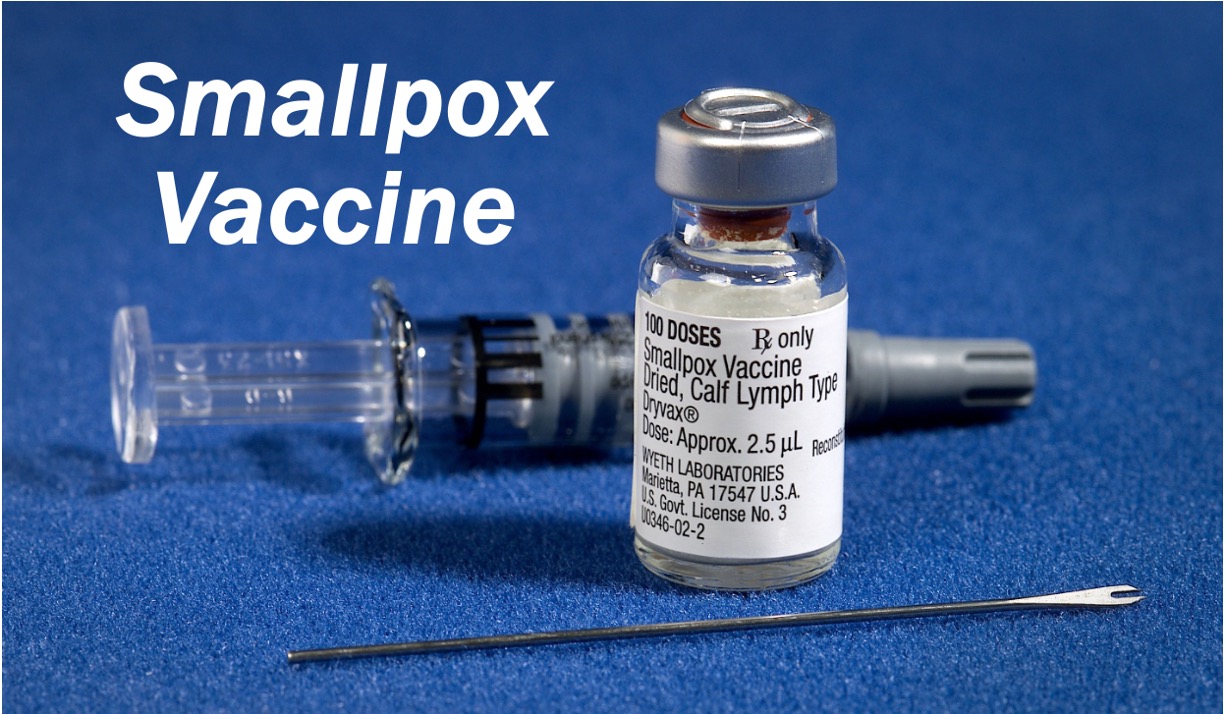
By the time the new medication or vaccine is approved tens of millions of dollars have been spent on that new medication with absolutely no income, plus tens and possibly hundreds of millions of dollars on other molecules that never made it to the market.
Most pharmaceutical drugs reach the market between 8 and 11 years into their 20-year patent life. So, they only have about ten years before their patent life expires and competitors can come in selling generic forms.
If intellectual property rights did not exist, drug companies would not carry out any research and then trials into new medications.
The same applies to hundreds of different types of companies. Intellectual property rights are crucial for scientific and commercial innovation.
Globalization and the rise of digital technology have significantly increased the complexity of protecting intellectual property, as creations can easily cross national borders and challenge traditional legal frameworks
Furthermore, the increasing importance of intellectual property in the digital era highlights the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect against unauthorized access and intellectual property theft.
Intellectual property rights protect consumers
If intellectual property rights did not exist, consumers would have no guarantee that what they were buying was really authentic. A client paying for a new Mercedes could never be completely sure that he or she was not buying a fake or copycat product.
International importance
The notion of intellectual property is familiar to business, scientific, and legal professionals all over the world. Here is a translation of the term in various widely spoken languages:
Propiedad Intelectual (Spanish), Propriedade Intelectual (Portuguese), Geistiges Eigentum (German), Propriété Intellectuelle (French), Proprietà Intellettuale (Italian), Własność Intelektualna (Polish), Интеллектуальная собственность (Russian), الملكية الفكرية (Arabic), مالکیت فکری (Farsi), बौद्धिक संपदा (Hindi), دانشی ملکیت (Urdu), বৌদ্ধিক সম্পত্তি (Bengali), 知識產權 (Cantonese Chinese), 知识产权 (Mandarin Chinese), 知的財産 (Japanese), 지적 재산권 (Korean), Kekayaan Intelektual (Indonesian), Sở hữu trí tuệ (Vietnamese), Fikri Mülkiyet (Turkish).
