Offshore fund – definition and meaning
An offshore fund is any fund, such as a mutual fund, that exists in an offshore financial center. Places that offer little or no government interference, such as Hong Kong, Jersey, and Antigua have offshore financial centers. A mutual fund in British English is a unit trust.
An offshore fund, if you are American, for example, exists outside the United States. We commonly use the term, perhaps incorrectly, to describe funds that exist in tax havens or low-tax nations.
Technically, offshore funds are simply funds that exist and operate abroad. However, if you do not specify, most people will think it is a fund in a tax haven.
A ‘tax haven‘ is a country or territory that offers amazingly favorable tax rates and other conditions. Antigua, the Cayman Islands, Jersey, the Isle of Wight, and Gibraltar are tax havens.
In its widest sense, we use the term to include any cross-border collective investment scheme.
While most people think of a mutual fund, an offshore fund refers to any collective investment scheme. Specifically, a collective investment scheme that operates abroad.
Definition of ‘offshore’
The term ‘offshore’ in business and finance means any country other than your own. In other words, foreign or overseas.
If you have an offshore bank account, it means a bank account abroad. An offshore company is registered in one country but is active in another.
Offshore manufacturing means relocating a production plant abroad, and importing the finished product. In other words, making it abroad and selling it in the home market.
If I create a trust abroad, it is an offshore trust. They are usually outside the jurisdiction of the country of residence of the trustor (trust’s creator).
The term ‘offshoring’ means relocating some of a company’s operations abroad.
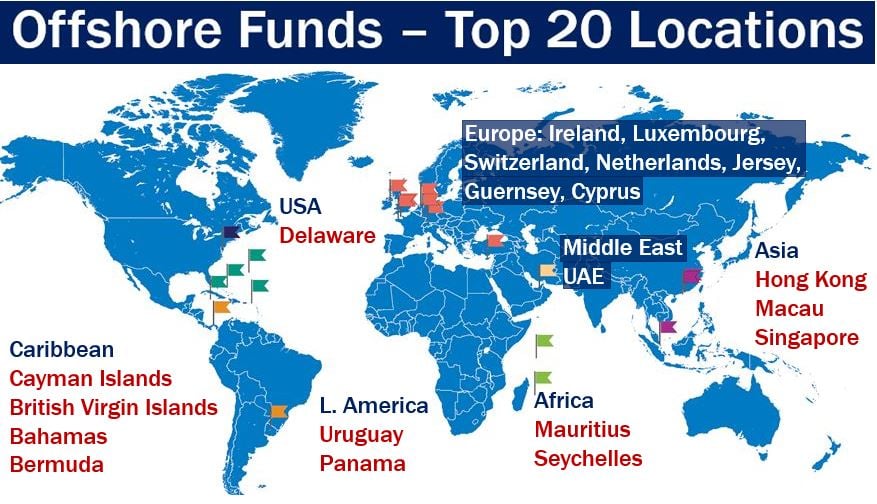
Offshore fund global market
We measure market share in offshore funds either by AUM or the number of funds. AUM stands for Assets Under Management.
However, Wikipedia informs that different sources may vary. The variations depend on which jurisdictions we deem as ‘offshore’ and which types of investment schemes we include.
For example, the dominant player in hedge funds is the Cayman Islands. However, Delaware dominates in offshore private equity funds.
The first image below shows us the market share for offshore hedge funds. The second image focuses on offshore private equity funds.

Assets Under Management (AUM) measures the total market value of all the financial assets of a fund. The term may refer to a venture capital firm, mutual fund, or brokerage house. Funds Under Management (FUM) means the same as AUM.

Compound words with “Offshore”
The term Offshore Fund is a compound word using the word Offshore. Here are some more compound words with Offshore:
-
Offshore Banking
Banking services provided by a financial institution outside the account holder’s country, often for tax benefits and privacy.
-
Offshore Wind Farm
A group of wind turbines in a body of water designed to generate electricity from wind power.
-
Offshore Investment
Investing capital in a foreign country to take advantage of favorable tax laws and other financial benefits.
-
Offshore Company
A corporation or LLC established in a foreign jurisdiction for legal and financial advantages. LLC stands for Limited Liability Company.
-
Offshore Drilling
Extracting petroleum from reserves located beneath the seabed.
-
Offshore Funds
Investment funds organized in tax havens, often used by investors to gain tax advantages or privacy.
-
Offshore Jurisdiction
Territories that offer legal and financial advantages like tax holidays, privacy, and limited regulation.
-
Offshore Outsourcing
Contracting out business processes or services to third-party vendors in foreign countries.
-
Offshore Account
A bank account maintained in a foreign country, often to benefit from reduced legal restrictions and taxes.
-
Offshore Trust
A trust established under the law of a foreign country that may offer financial benefits like asset protection and tax savings.
-
Offshore Incorporation
The process of establishing a corporate entity in a foreign jurisdiction.
-
Offshore License
A permit issued by a jurisdiction to allow the operation of certain businesses, such as banking, gaming, or insurance, in its offshore sector.
-
Offshore Haven
A country or jurisdiction that offers favorable tax and privacy laws to foreign investors and businesses.
-
Offshore Engineering
The branch of engineering focused on the development and maintenance of offshore structures, like oil platforms and wind farms.
-
Offshore Construction
Building structures at sea, from oil platforms to renewable energy installations.
-
Offshore Tax Planning
Strategies utilized by individuals and businesses to minimize taxation through offshore entities.
-
Offshore Logistics
Managing the flow of goods and materials to and from offshore installations.
-
Offshore Merchant Account
A type of bank account for businesses that enables them to process payments in various currencies from overseas customers.
-
Offshore Secrecy
The confidentiality provided by some jurisdictions for the entities and transactions made under their laws.
-
Offshore Energy Production
Generating energy from sources located offshore, especially from oil, gas, and wind.
Other languages
In non-English speaking countries, even though they have a word in their language for Offshore Funds, they often use the English term. Here is a translation of the term Offshore Funds in some widely-spoken languages:
- Fondos offshore, Fondos extraterritoriales (Spanish) – uses both a local and an English term.
- 基金海外 (Mandarin Chinese) – uses a fully translated term.
- ओफ़्शोर फंड (Hindi) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- صناديق خارج البلاد (Arabic) – uses a fully translated term.
- Offshore-Fonds (German) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- Fonds offshore (French) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- Фонды офшорные (Russian) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- Fundo offshore (Portuguese) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- Offshore-fondsen (Dutch) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- Offshore fonlar (Turkish) – uses the English term ‘offshore’ combined with the Turkish word for funds.
- Fondi offshore (Italian) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- Offshore-펀드 (Korean) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- オフショアファンド (Japanese) – uses a term that incorporates English ‘offshore’ in Katakana.
- Quỹ ngoại (Vietnamese) – uses a fully translated term.
- ऑफशोर फंड (Bengali) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- ऑफशोर निधि (Punjabi) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- Offshore funds (Filipino) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- Fonder offshore (Swedish) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- Fundusze offshore (Polish) – uses the English term ‘offshore’.
- अफशोर कोष (Nepali) – uses a combination of English ‘offshore’ with a local term.
Video – What’s an Offshore Fund?
Watch this video from our sister channel Marketing Business Network, in YouTube.

