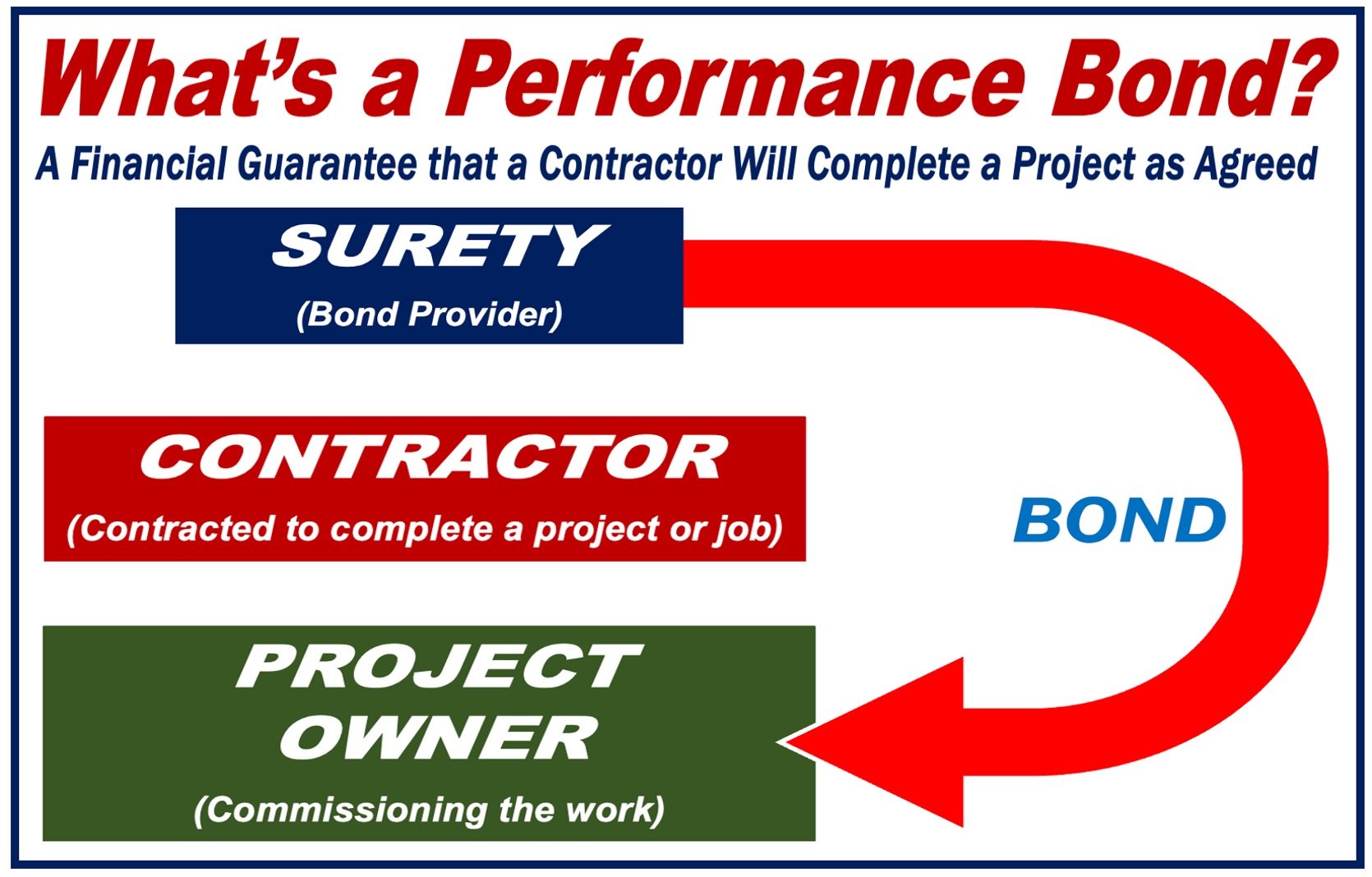
A Performance Bond, also known as a Contract Bond, is a surety bond issued by a bank or insurance provider as a guarantee for a contractor’s satisfactory completion of a project. The bond gives the project owner money if the contractor doesn’t complete the work in accordance with the contract.
In this context, the word “bond” has nothing to do with the government or large corporations trying to raise money.
The Cambridge Dictionary has the following definition of a contract bond (which means the same as a performance bond):
“An official promise from an organization such as a bank or insurance company to pay money to a company if its contractor (= person or company doing work for it) does not complete a job successfully.”
Key features
-
Parties involved
There are three main parties involved: the contractor, the project owner, and the bond issuer.
-
Purpose
To protect the obligee (the project owner) from damages brought about by the principal’s (contractor’s) inability to carry out the project’s obligations.
-
Cost
Based on the risk of the project and the creditworthiness of the contractor, the performance bond premium is usually expressed as a percentage of the overall contract sum.
How performance bonds work
Below, you can see a brief explanation of how performance bonds work:
-
Contract
When a contractor wins a bid, they may be required to secure a performance bond before the work begins.
-
Issuance
To issue the bond, the contractor contacts a surety firm. The surety firm will assess the contractor’s ability to fulfill the contract before issuing the bond.
-
In case of default
If the contractor defaults, the surety company has two main responsibilities. It must compensate the project owner financially and make arrangements to ensure the contract’s completion, which could include hiring a new contractor.
Benefits
Performance bonds have several benefits, including:
-
Security
They provide financial assurance that the project will be completed as per the contract’s terms.
-
Risk mitigation
They significantly lower the risk of financial loss due to contractor default.
-
Quality assurance
To secure a bond, contractors must demonstrate the ability to meet high-quality standards, which helps ensure project quality.
Performance bond vs payment bond
A performance bond ensures that the project will be completed; a payment bond assures that the contractor will pay their subcontractors and suppliers.
Industries where performance bonds are common
There are several industries where performance bonds are common, including:
-
Construction
Mainly in government and large commercial projects.
-
Public work
Performance bonds are frequently needed for government contracts in order to protect taxpayers’ interests.
Challenges
Individuals may encounter several challenges when dealing with performance bonds, including:
-
Cost
They can be quite expensive, especially with contractors who have poor credit histories.
-
Qualification
Securing a bond can be difficult for new contractors or those with financial difficulties, as sureties typically require a solid track record and strong financials.
Written by Nicolas Perez Diaz
