What is product differentiation? Definition and examples
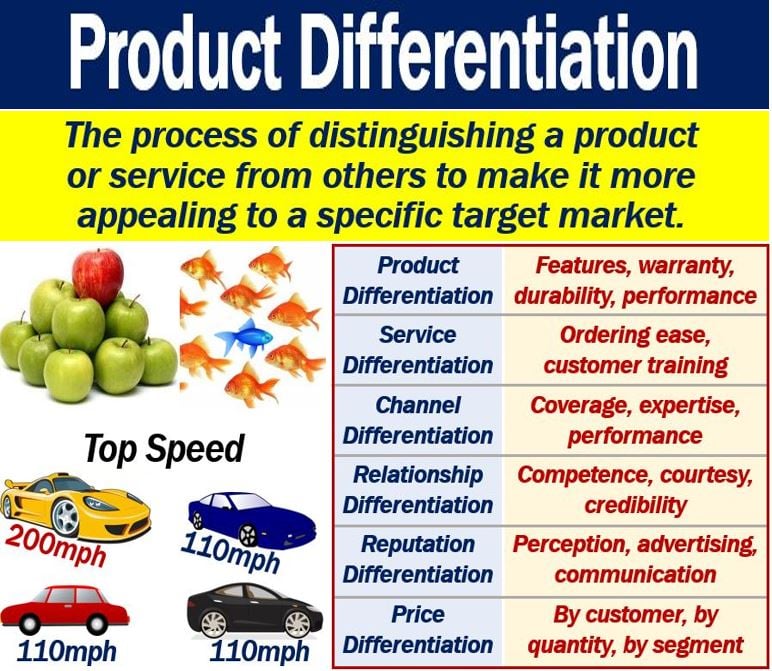
Product Differentiation is a marketing process in which a product is differentiated from others. Put simply; it is the process of distinguishing a good or service from others, i.e., making it stand out. Companies do this because they want to show customers their product’s attributes and uniqueness. This may include products within the company or of the same line.
In this context, ‘marketplace’ means the same as ‘market’ in its abstract sense. Some people simply say ‘differentiation‘ with the meaning ‘product differentiation.’
If the company implements it successfully, product differentiation can give a good a competitive advantage. Competitive advantage means having an edge over rivals in the provision of a certain product or service.
Product differentiation – small companies
For small companies, this can be great. It can be useful because they then have a chance to compete against bigger companies. It also gives them a better chance to compete against more popular products.
Effective product differentiation, especially in saturated markets, can lead to brand loyalty as customers begin to associate unique qualities with a company’s offerings.
When differentiating a product from others, it does not necessarily have to be completely different or new.
Product differentiation may involve, promotions, product packaging, product design, quality, and extra features. Customer service, experience, and advertising campaigns are also relevant.
In the digital era, product differentiation extends beyond the physical attributes to include the online customer experience, which has become a pivotal aspect of modern marketing strategies.
In a 1997 Harvard Business Review article, ‘Discovering New Points of Differentiation,’ Rita Gunther McGrath and Ian MacMillan wrote:
“[Product differentiation is] offering customers something they value that competitors don’t have.”
According to MarketResearh.com: “Differentiation allows you to provide superior value to customers at an affordable price, creating a win-win scenario that can boost the overall profitability and viability of your business.”
Product differentiation types
There are three types of product differentiation.
-
Vertical differentiation
Vertical differentiation exists when consumers compare a product according to one feature – quality.
Consumers can say “Product A is better than Product B.”
For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, a person can decide whether to get a branded medication or a generic. They know the quality of each one.
A feature that also differentiates the two medications is ‘price.’ Brand names are much more expensive than generic medications.
-
Horizontal differentiation
With horizontal differentiation, the product is harder to classify because it has many features. Therefore, we only consider one characteristic.
Consumers are not certain about the quality of the products that they compare.
For example, when considering drinks, consumers may choose one because of its taste. However, they cannot determine which one is superior in quality.
When we choose between a Coke, Pepsi, or Dr. Pepper, for example, taste drives our decision. Regarding their quality, we have no idea which one is best.
SmallBusiness.Chron.com says the following regarding vertical differentiation and horizontal differentiation:
“Horizontal differentiation refers to distinctions in products that cannot be easily evaluated in terms of quality.”
“This stands in contrast to vertical differentiation, where the distinctions between products are objectively measurable and are based on the products’ respective level of quality.”
-
Mixed differentiation
Mixed differentiation is a combination of both vertical and horizontal differentiation. It is common when consumers consider more complex products or marketing executives are looking at more sophisticated markets.
“Product differentiation” – vocabulary
There are many compound nouns containing the words “product differentiation.” A compound noun, such as “product differentiation strategy,” is a term consisting of two or more words. Let’s have a look at seven of them, their meanings, and how we can use them in a sentence:
-
Product Differentiation Strategy
A business strategy that involves making a product distinctive and attractive to stand out in the market.
Example: “The company’s product differentiation strategy focused on exceptional design and user experience to outshine the competition.”
-
Product Differentiation Level
The degree to which products are perceived as different by consumers.
Example: “Their high product differentiation level has allowed them to charge a premium price.”
-
Product Differentiation Effort
The amount of resources and work put into making a product stand out in its market.
Example: “The startup invested heavily in product differentiation effort to carve out a niche for itself.”
-
Product Differentiation Capability
A company’s ability to develop unique product features and market them effectively.
Example: “Their product differentiation capability has become their most valuable asset in the technology sector.”
-
Product Differentiation Index
A measure or indicator of the distinctiveness of a product in comparison to others.
Example: “Analysts use the product differentiation index to evaluate the potential success of new market entrants.”
-
Product Differentiation Advantage
The competitive edge a company gains through the process of distinguishing its products from those of competitors. Example: “Their commitment to sustainable materials has given them a significant product differentiation advantage.”
-
Product Differentiation Factor
An element or feature that helps to distinguish a product from its competitors.
Example: “Unique packaging became the key product differentiation factor for the brand’s success in the crowded cosmetics industry.”
Video – What is Product Differentiation?
This video presentation, from our sister channel on YouTube – Marketing Business Network, explains what a ‘Product Differentiation’ is using simple and easy-to-understand language and examples.

