A registered investment advisor or RIA is an individual or firm that gives people advice or recommendations on investments. In the US, the registered investment advisor is registered with the state securities authorities or the SEC. SEC stands for the Securities and Exchange Commission.
A person that gives investment advice on, for example, stocks, mutual funds, bonds, or exchange-traded funds for compensation is an investment advisor. Managing clients’ portfolios may also form part of their duties.
A portfolio is a group of investment products, i.e., a person’s spread of investments.
The word ‘advisor’ also has another possible spelling – ‘adviser.’ Both spellings are correct. However, when you start a text with one spelling, do not switch over to the other.
The US Securities and Exchange Commission has the following definition of the term:
“An investment adviser is an individual or a firm that is in the business of giving advice about securities to clients.”
“For instance, individuals or firms that receive compensation for giving advice on investing in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or exchange traded funds are investment advisers. Some investment advisers manage portfolios of securities.”
Registered investment advisor
The term was first based on the Investment Advisers Act of 1940.
The US Government introduced that law after the Great Depression.
The Investment Advisers Act of 1940 defines a registered investment advisor as a:
“Person or firm that, for compensation, is engaged in the act of providing advice, making recommendations, issuing reports or furnishing analyses on securities, either directly or through publications.”
A registered investment advisor is someone that has the experience and knowledge to analyze annual reports and balance sheets. He or she also analyzes income statements, 10-k forms, and others forms. The aim is to come up with the best option for the client.
Acts as a fiduciary
A registered investment advisor must act as a fiduciary. This means that they have to follow certain practices to ensure they obey the law.
They also must, above all, put their client’s interest first. In some cases, they may also have the responsibility to manage assets.
They must file some forms such as ADV Parts I and II, with the SEC. In these forms, advisors present all the information their clients need so that they can properly decide and be aware of possible risks that may be present.
Conflicts of interest
RIAs must add information on their investment strategies and the risks that each investment may pose. They also need to include any information regarding potential conflicts of interest.
The Securities and Exchange Commission keeps track of these documents. It keeps them in case somebody needs them in an RIA complaint.
Through these documents, SEC staff can review old records and see the investor profile. They can also see what strategies investment advisors took, and the risks they put their clients through.
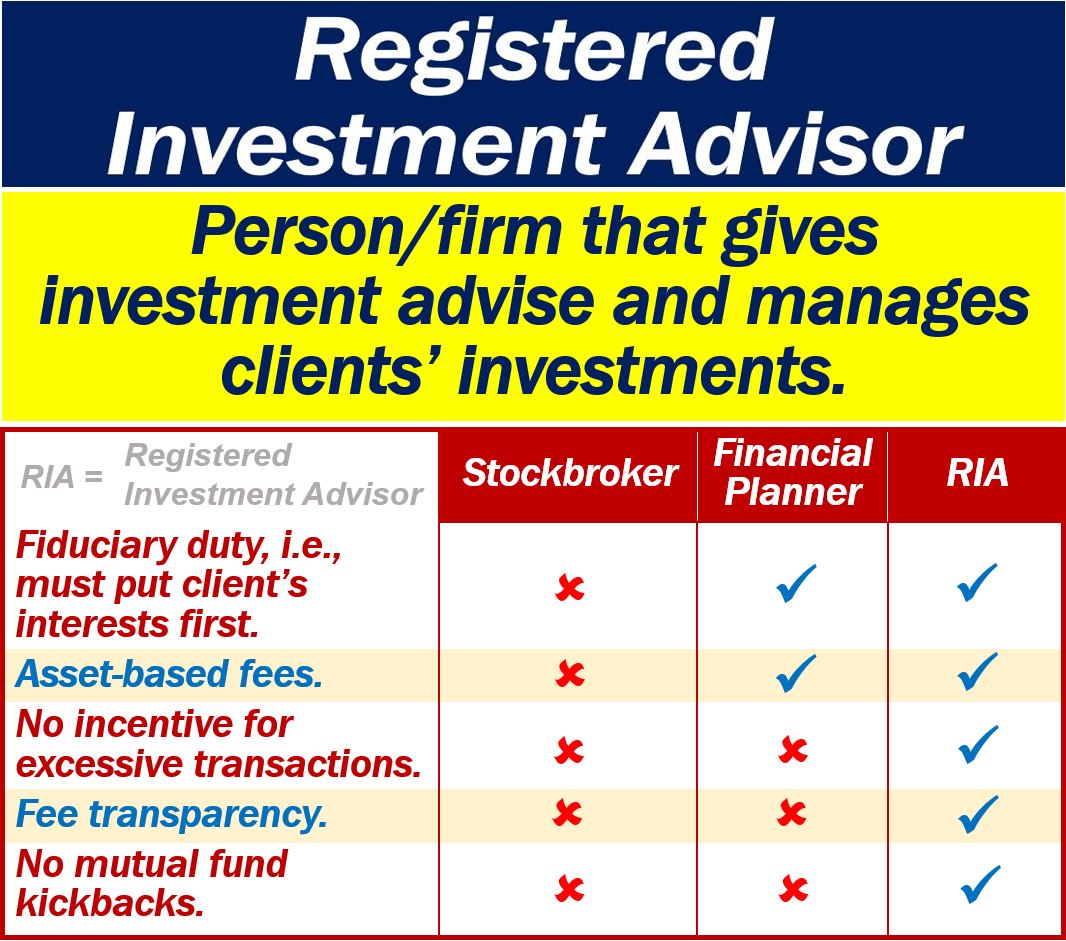
Stockbrokers vs. RIA
Do not confuse the terms registered investment advisor and stockbroker. Even though their duties are similar, an RIA has a fiduciary duty.
Also, a registered investment advisor works on fee-only, such as an hourly, tiered, or flat fee.
Stockbrokers, on the other hand, get a commission.
Video – Registered Investment Advisor
This Financial Synergies Wealth Advisors video explains what a registered investment advisor is. An RIA is a professional, independent advisory person or firm that offers personalized advice to clients.
RIAs have a fiduciary responsibility to put the interests of their clients ahead of their own.
