A pension is a monthly income people get after they retire. In most cases, employees and their employers contribute money to a fund every month while the person is actively employed. After retirement, the money is used as an income, which is typically paid out monthly. Some plans hand out all the money in one lump sum.
 Pension schemes, a type of savings plan to help workers save money for when they reach the age of 60 or 65 (or older), exist in most countries. Compared to other forms of savings, there are special tax benefits for the contributor.
Pension schemes, a type of savings plan to help workers save money for when they reach the age of 60 or 65 (or older), exist in most countries. Compared to other forms of savings, there are special tax benefits for the contributor.
According to FT.com/lexicon, the Financial Times’ online dictionary, the term has the following meaning:
“An amount of money paid regularly by a government, company, or financial institution to someone who is officially considered to be too old or too ill to earn money by working.”
To dismiss from employment
We may use the term when a person is dismissed from employment. For example, somebody might say:
“John was pensioned off from the police force after the embarrassing incident.”
Lodgings
In many parts of Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, Latin America, Korea, the Philippines, and Japan, a pension is a boarding house or guest house.

They are similar to bed and breakfasts in the USA, Canada, UK, Ireland, and Australasia, but they offer lunch and supper as well as breakfast. In other words, pensions offer full board while bed and breakfasts only offer half board.
Wikipedia says the following about pension:
“These small businesses may offer special rates for travelers staying longer than a week, may be located in historic buildings, can be family-run, and are generally cheaper than other lodgings, such as hotels, although they offer more limited services.”
The rest of this article focuses on the term’s financial meaning.
Private pension
Hundreds of millions of workers across the world put some money away each month for when they are older, i.e., when they reach the age of retirement. They save a percentage of their monthly income during their working life. When they reach the age of retirement, they use the money they built up, plus the interest it earned, to live on. How much they receive depends on two things:
- The total contributions.
- The fund’s interest rates while they contributed.
There are dozens of different kinds of pension plans. Some companies and other employers run their own schemes. If your employer does not have one, you can set up a private pension plan on your own.
Some plans give you a lump sum of (usually) tax-free cash on a specific date in the future, while others provide a monthly income.
State pension
In some countries, the government pays people a regular salary, i.e., a pension, when they retire. How much they receive depends on many factors, such as the number of dependants there are in the household, their contribution record, and how much they earned.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, for example, there are two main types:
- Basic State Pension – which can be up to £129.20 a week.
- New State Pension – which can be up to £168.60 a week.
In the UK, the state pension age on 6 October 2020 will be 66 years for both men and women.
United States
In the United States, people call it a social security benefit rather than a state pension. How much people get depends on their contributions and lifetime earnings. People who did not contribute are not usually eligible, unless they had already been receiving social security benefits.
A higher percentage of Americans have a private pension plan, usually with employer’s contributions, than their counterparts in the UK.
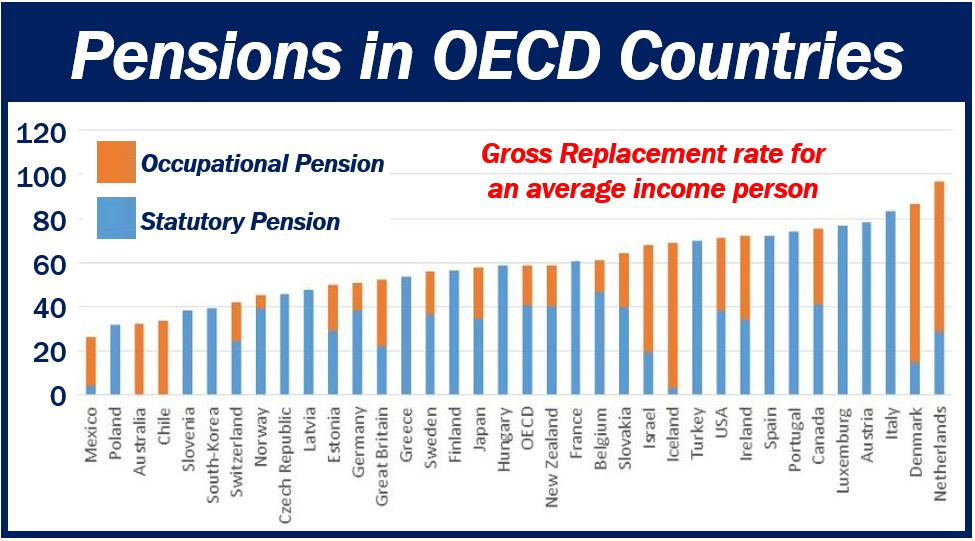
Percentage of working wage
According to the World Economic Forum, pensioners in Croatia, Turkey, and the Netherlands receive pensions greater than their working wages just before they retired. Croatians’ state pensions are 129% of their working wage.
Britons on the other hand, get state pensions that are worth just 29% of their working wage.
