Do you gather and analyze data from every stage of your supply chain to improve overall performance, efficiency, and decision-making? If so, you are engaged in Supply Chain Intelligence.
By leveraging this intelligence, you can gain a clearer understanding of how each part of your supply chain operates, identify potential risks, and uncover opportunities for improvement.
B2b2.com has the following definition of supply chain intelligence:
“Supply chain intelligence involves the systematic gathering, analysis, and application of data to optimise the flow of goods and information across the entire supply chain.”
Definitions of ‘Supply Chain’ and ‘Intelligence”
Let’s look at the words that make up the term “supply chain intelligence” and see what they mean in isolation:
The supply chain is the entire process of making and selling commercial products—from their point of origin to their point of consumption.
It includes every stage, from the supply of raw materials to delivering the finished product to the ultimate consumer.
-
Intelligence
Intelligence, in this context, is all about information rather than how clever one is.
It refers to the collection, analysis, and application of data and insights that help you make informed decisions.
This intelligence provides you with the knowledge you need to optimize processes, predict trends, and address potential challenges within your supply chain.
Provides You with Insights
Supply chains are complex networks that involve the movement of goods, information, and finances from the initial supplier to the final customer. Managing this network efficiently is crucial to your business’s success.
This is where supply chain intelligence comes in. It provides you with the insights you need to optimize your operations, reduce costs, enhance transparency across the entire supply chain, ensure timely delivery of products, minimize risks, streamline inventory management, increase agility in responding to market changes, and improve customer satisfaction.
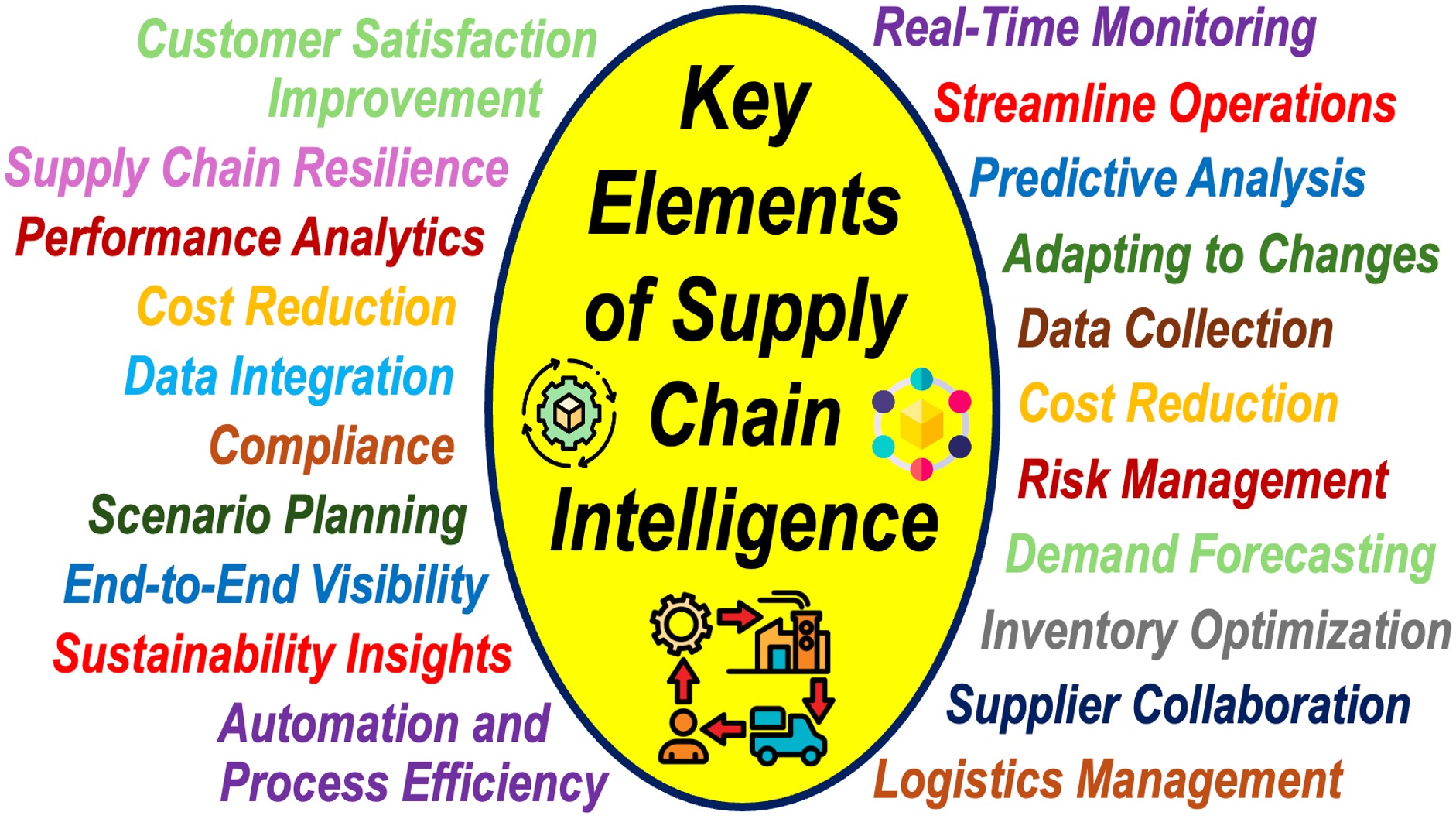
Supply Chain Intelligence – Key Elements
-
Data Collection
One of the key components of supply chain intelligence is data collection. Data is gathered from various sources, including suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and customers.
This data can cover a wide range of areas, such as inventory levels, production schedules, transportation routes, and customer demand.
By collecting and analyzing this information, you can make informed decisions that benefit your supply chain.
-
Predictive Analysis
Another important aspect of supply chain intelligence is predictive analytics. By using advanced algorithms and data models, you can predict potential disruptions, such as delays in shipping or fluctuations in demand.
This allows you to take measures in advance to reduce risks and ensure your supply chain runs smoothly.
For example, if your data analysis shows that a particular supplier is consistently late in delivering materials, you might decide to find an alternative supplier or adjust your production schedule.
Similarly, if you predict a spike in demand for a certain product, you can increase your inventory levels in advance to meet customer expectations.
-
Streamline Operations
Supply chain intelligence also helps you improve collaboration with your partners. By sharing relevant data and insights with your suppliers and logistics providers, you can work together to streamline operations, reduce lead times, and enhance overall efficiency.
This collaborative approach can lead to stronger partnerships and better outcomes for everyone involved.
-
Adapting to Market Changes
In today’s fast-paced business environment, being able to quickly adapt to changes in the market is essential. By having real-time insights into your supply chain, you can respond more effectively to customer demands, manage risks more efficiently, and stay ahead of your competitors.
Brief History
Supply chain intelligence, as a concept, has evolved over several decades as businesses recognized the need to optimize their supply chains through data-driven decision-making.
While supply chain management practices date back to the 1960s, the specific term “supply chain intelligence” began gaining traction until the turn of the century.
The rise of big data, advanced analytics, and technology integration in supply chains contributed to its emergence. It started to become a widely discussed topic in the business world around the mid-2010s as companies increasingly sought to leverage data and analytics for competitive advantage.
Since then, supply chain intelligence has become an essential strategy for businesses looking to enhance efficiency, reduce risks, and adapt quickly to market changes.
Other ‘Intelligence’ Types
In business English, several other forms of ‘intelligence’ are commonly used. Here are some of the most significant ones, along with their meanings:
The use of data and analytics to understand your sales processes, customer behaviors, and market trends, enabling you to improve your sales strategies and outcomes.
The simulation of human intelligence in machines, enabling them to perform tasks that typically require human cognition, such as learning and problem-solving.
The real-time analysis of data generated by your business’s operations to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall performance.
The process of collecting and analyzing data related to your brand’s performance and perception in the market to inform strategic decisions and improve brand positioning.
The use of data analysis tools and techniques to gather, process, and present business information that supports decision-making and enhances overall business operations.
The practice of collecting and analyzing data related to digital threats, vulnerabilities, and cyber activities to protect your business’s information systems and assets.
The ability to recognize, understand, and manage your own emotions, as well as those of others, to enhance interpersonal relationships and workplace dynamics.
The capacity for reasoning, problem-solving, and learning, typically referring to the intellectual abilities of individuals in the context of cognitive functions.
The collection and analysis of data about market conditions, trends, and customer preferences to inform your business’s marketing strategies and decisions.
The process of gathering and analyzing economic data to understand the broader economic environment and its potential impact on your business operations and strategies.
The collection and analysis of customer data to better understand their behaviors, preferences, and needs, allowing you to tailor your products, services, and marketing efforts more effectively.
The gathering and analysis of data related to your products’ performance, customer feedback, and market trends to inform product development and marketing strategies.
The ability to effectively navigate social interactions and relationships, understanding social dynamics and using this understanding to improve communication and collaboration.
The gathering and analysis of data about your competitors’ activities, strategies, and market position to inform your own business strategies and stay ahead in the marketplace.
Final Thoughts
Let’s recap. Supply chain intelligence is a powerful tool that can transform the way you manage your supply chain. It helps you gather and analyze crucial data, enabling you to optimize operations, reduce costs, and predict potential risks.
By improving collaboration with suppliers and logistics providers, you can streamline processes and enhance efficiency. Real-time insights also allow you to quickly adapt to market changes, respond effectively to customer demands, and gain a competitive edge.
Whether you’re focused on improving customer satisfaction or staying ahead of competitors, supply chain intelligence is an essential component of your strategy.
