 We use the Past Simple Tense to describe an action in the past, i.e., before the present. We also call it the Past Simple or Simple Past.
We use the Past Simple Tense to describe an action in the past, i.e., before the present. We also call it the Past Simple or Simple Past.
Add the letter -ed
With regular verbs, we form the past tense by adding the letters -ed to the end of the verb, as in:
| Work Worked |
Want Wanted |
Call Called |
Play Played |
There are many irregular verbs, such as give-gave, speak-spoke, drive-drove, lead-led, begin-began, buy-bought, build-built, etc.
Negative: did not (didn’t)
When we make a negative sentence using the Past Simple, we use ‘Didn’t’ (Did Not). For example:
I didn’t work yesterday.
I didn’t speak to the client last week.
Remember that when you add ‘didn’t’ to the sentence, the verb is in the present form ‘work.’ We CANNOT say ‘I didn’t worked‘ (incorrect).
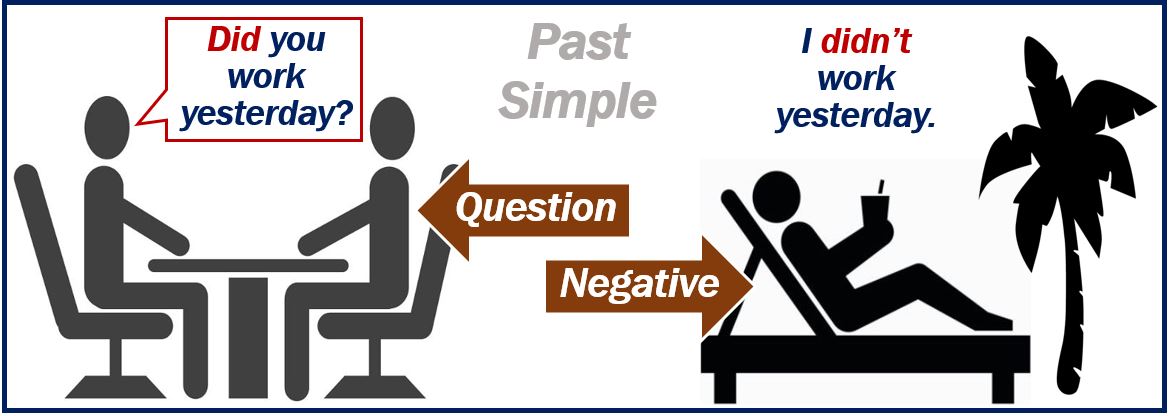 Question (Interrogative): did…?
Question (Interrogative): did…?
When you ask a question in the past simple, you start with ‘Did.’ For example:
Did you work yesterday?
Did you speak to the client last week.
When you start a question with ‘Did,’ the verb is in the present form ‘work.’
Past Simple Tense – recent or distant past
It does not matter how long the action occurred and whether it was in the distant or recent past.
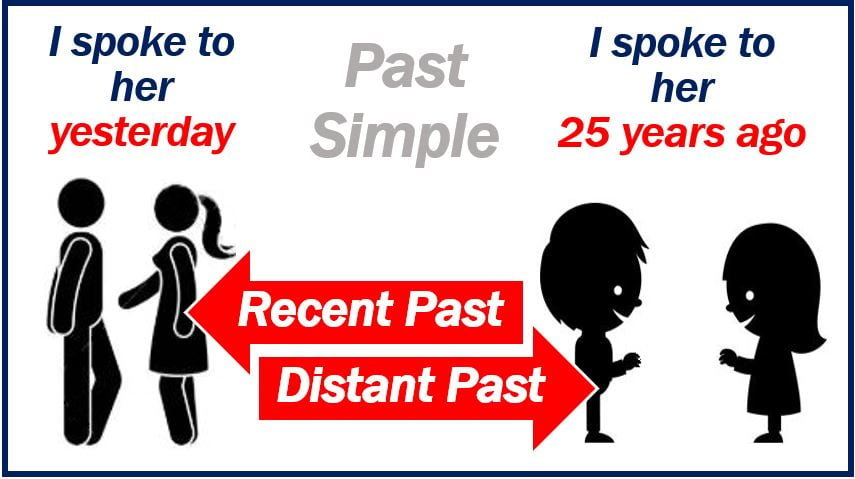 If I say “I worked in that office,” it might have happened yesterday (recent past) or twenty years ago (distant past). Therefore, to be more specific, we need to add a time word such as yesterday, last year, 20 years ago, etc.
If I say “I worked in that office,” it might have happened yesterday (recent past) or twenty years ago (distant past). Therefore, to be more specific, we need to add a time word such as yesterday, last year, 20 years ago, etc.
I can say:
“I spoke to her yesterday”
“I spoke to her 20 years ago.”
Related to past time expressions
We use the Past Simple when referring to an event or action that is related to time expressions.
A specific point in time:
Yesterday, last year, five days ago, last week, 2007, etc. In this case, the action only occurred once.
She attended the board meeting last week.
Yesterday, they worked in our head office.
I gave a presentation on team building in New York in 2018.
They went on a management course last year.
Frequency:
Always, sometimes, frequently, seldom, now-and-again, occasionally, never etc. In this case, the action may have happened several times.
I seldom took work home before the advent of the Internet.
When I was young, I always went to work by bicycle.
Indefinite (non-specific) point in time:
Once, the other week, several years ago, etc. In this case, the action may have occurred many times.
Many years ago, people communicated mainly by using paper, stamps, and envelopes.
I worked in the warehouse when I was a young woman.
Past Simple with Past Continuous
Look at these two sentences:
I worked (Past Simple)
I was working (Past Continuous)
 Interrupted Action:
Interrupted Action:
When we use these two tenses together, the Past Simple action interrupts the Past Continuous action. For example:
We were discussing salaries when the earthquake started.
The earthquake (Past Simple) interrupted the discussion (Past Continuous).
Background Information:
We also use the Past Continuous for background information. The main theme, however, is in the Past Simple.
For example, in this sentence, the story is about the Wall Streeet Crash (1929):
I was cleaning my car and Susan was chatting with a neighbor when Henry telephoned to tell me that stock prices had crashed.
Past Simple + Past Simple vs. Past Continuous + Past Simple
Look at these two sentences:
1. They left when the boss shouted. (Past Simple + Past Simple)
2. They were leaving when the boss shouted. (Past Continuous + Past Simple)
If I ask the questions:
- Why did they leave? Answer: Because the boss shouted.
- Why were they leaving? Answer: We don’t know.
When a sentence consists of Past Simple + when + Past Simple, we usually know why it happened. However, this is not the case when it is a Past Continuous + when + Past Simple sentence.
