IBM says it has made its quantum processor available to the public on IBM Cloud so that users can run experiments. The American multinational technology and consulting giant said it wants to accelerate innovation and see processors twenty times larger and more powerful than what is available today over the coming decade.
Computer engineers see quantum computing as the next step in the evolution of computer technology, which may allow for significantly faster calculations than today’s most powerful machines.
The technology is still in its very early stages. However, experts say IBM’s move is a step in the right direction into the exciting world of quantum computers.
 By opening up its technology for all of us to use, IBM believes we will reach the next major milestone of information technology – quantum computing – much more rapidly. (Image: research.ibm.com)
By opening up its technology for all of us to use, IBM believes we will reach the next major milestone of information technology – quantum computing – much more rapidly. (Image: research.ibm.com)
Quantum vs. current computers
Current computers have bits, and each bit is either zero or one. A quantum computer has quantum bits – they are made out of quantum particles that may be zero, one, or some type of state in between, i.e. they can have both values at the same time.
The quantum bit could be any fundamental particle, such as a photon, electron or nucleus (of an atom). It is a particle that can have two different properties at once – both in one place and the other place at the same time.
Why is quantum computing faster? In our current computers, a particular calculation might go through all the different possibilities of ones and zeros for one specific calculation. With a quantum computer, because the particles can be in all the states at the same time, just one calculation is done (testing a huge number of possibilities simultaneously), making it incredibly quicker.
The IBM quantum processor
IBM engineers have created a quantum processor that we all can access through the first-of-a-kind quantum computing platform delivered through the IBM Cloud onto any mobile device, laptop or desktop.
 In fifty years’ time, when computers are trillions of times faster than what we have available today, history books may mention IBM’s 5-qubit quantum processor that everybody was allowed to access. Perhaps they will say it was a turning point in global brain-storming. (Image: researcher.ibm.com)
In fifty years’ time, when computers are trillions of times faster than what we have available today, history books may mention IBM’s 5-qubit quantum processor that everybody was allowed to access. Perhaps they will say it was a turning point in global brain-storming. (Image: researcher.ibm.com)
In a press release, IBM wrote:
“IBM believes quantum computing is the future of computing and has the potential to solve certain problems that are impossible to solve on today’s supercomputers.”
“The cloud-enabled quantum computing platform, called IBM Quantum Experience, will allow users to run algorithms and experiments on IBM’s quantum processor, work with the individual quantum bits (qubits), and explore tutorials and simulations around what might be possible with quantum computing.”
IBM’s quantum processor that the public will be able to use freely is composed of five superconducting *qubits. It is housed at the IBM T.J. Watson Research Center in New York.
* A qubit, also known as a quantum bit (sometimes qbit), is a unit of quantum information — the quantum analogue of the classical bit.
The 5-qubit processor represents IBM’s quantum architecture’s latest advancement that can scale to larger quantum systems. “It is the leading approach towards building a universal quantum computer,” the company explained.
An ultra-fast computer
A universal quantum computer can be programmed to perform any kind of computing task thrown at it. It will be unimaginable faster than current computers for several key applications for business and science.
We do not yet have a universal quantum computer. However, IBM foresees medium-sized quantum processors of fifty to one-hundred qubits within the next ten years.
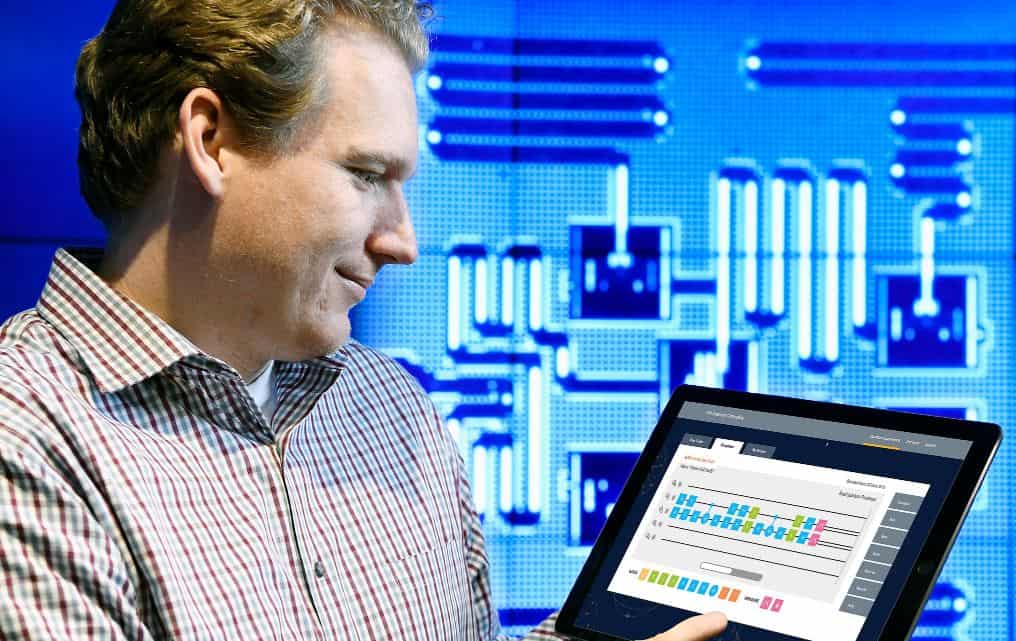 Jay Gambetta, an IBM Quantum Computing Scientist, uses a tablet to interact with the IBM Quantum Experience. (Image: flickr.com/photos/ibm_research_zurich)
Jay Gambetta, an IBM Quantum Computing Scientist, uses a tablet to interact with the IBM Quantum Experience. (Image: flickr.com/photos/ibm_research_zurich)
A 50-qubit quantum computer would leave today’s TOP500 supercomputers light-years behind.
Arvind Krishna, senior vice president and director, IBM Research, said regarding quantum computers:
“Quantum computers are very different from today’s computers, not only in what they look like and are made of, but more importantly in what they can do.”
“Quantum computing is becoming a reality and it will extend computation far beyond what is imaginable with today’s computers. This moment represents the birth of quantum cloud computing.”
“By giving hands-on access to IBM’s experimental quantum systems, the IBM Quantum Experience will make it easier for researchers and the scientific community to accelerate innovations in the quantum field, and help discover new applications for this technology.”
Moore’s Law running out of steam
Over the history of computing hardware, the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit has doubled on average every two years – this is known as the Moore’s Law observation.
This doubling every two years cannot go on forever. Computer experts say that Moore’s Law is running out of steam, i.e. we are reaching a point where increasing the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit is no longer possible.
Quantum computing is one of the technologies that could allow us to continue making faster and faster computers every year, just like we have been doing for the past fifty years.
IBM says:
“With Moore’s Law running out of steam, quantum computing will be among the technologies that could usher in a new era of innovation across industries.”
“This leap forward in computing could lead to the discovery of new pharmaceutical drugs and completely safeguard cloud computing systems.”
“It could also unlock new facets of artificial intelligence (which could lead to future, more powerful Watson technologies), develop new materials science to transform industries, and search large volumes of big data.”
IBM Quantum Experience
Quantum data is extremely fragile and needs to be protected from any mistakes that can result from electromagnetic radiation and heat. Signals are sent out and in of a cryogenic dilution refrigerator to measure operations on the quantum processor.
IBM researchers have made several robust engineering advances both at the device level and in the electronic controls to give users of the IBM Quantum Experience “unprecedented and reliably high-quality performance in this five-qubit processor.”
Together with software knowhow from the IBM Research ecosystem, the engineers have built a dynamic user interface on the IBM Cloud platform that allows users to easily connect to the quantum hardware through the cloud.
IBM says it sees the introduction to members of the public of this complete quantum computing framework as just the beginning of a new user community, which embraces the world of quantum computing and how it works.
IBM added:
“In the future, users will have the opportunity to contribute and review their results in the community hosted on the IBM Quantum Experience and IBM scientists will be directly engaged to offer more research and insights on new advances.”
“IBM plans to add more qubits and different processor arrangements to the IBM Quantum Experience over time, so users can expand their experiments and help uncover new applications for the technology.”
New frontiers for quantum computing
In recent years, there has been remarkable progress and interest in the field of quantum computing. By giving us all access to the IBM Quantum Experience, the company believes it will help organisations and businesses start to understand the technology’s colossal potential.
It will also allow universities to grow their teaching programs in quantum computing and associated subjects, and for students to become aware of some exciting new career paths.
Dario Gil, vice president of science and solutions, IBM Research, said:
“It is a beautiful challenge to pursue the path to build the first universal quantum computer, but it requires us to change how we think about the world.”
“Access to early quantum computing prototypes will be key in imagining and developing future applications. If you want to understand what a true quantum computer will do for you and how it works, this is the place to do it. You won’t experience it anywhere else.”
If you want to acces the IBM Quantum Experience and seek more information on the company’s quantum computing research, visit www.ibm.com/quantumcomputing.
To learn more about the IBM Research Frontiers Institute, visit www.ibm.com/frontiers.
Video – IBM Research Quantum Lab
This is a 360 video of the IBM Quantum Lab in New York. Inside, IBM engineers are researching and creating a practical quantum computer. When it is completed, it will be one of the greatest milestones in the history of information technology.
Video – Information Technology
IT (Information Technology) refers to the development, maintenance and use of computer systems, networks, software (programs), and hardware.
