Japan has unveiled a massive $140 billion (¥21.9 trillion) economic stimulus package aimed at addressing rising costs, boosting wages, and kickstarting the economy.
The total projected economic impact, which includes both direct government spending ($140bn) and additional expected private sector investments and contributions, is forecast to total about $250 billion (¥39 trillion).
This initiative, led by Shigeru Ishiba, who has been Japan’s Prime Minister since October 1, 2024, marks a pivotal moment as Japan navigates economic challenges exacerbated by inflation and public discontent.
Here’s an overview of the plan and its potential impact on the country’s economy and society.
The Core of the Economic Stimulus Plan
The economic stimulus package focuses on three primary areas:
-
Raising Income Tax Thresholds
The minimum tax-free income threshold will rise from $6,640 to $11,500. The aim is to increase the size of the country’s workforce.
This measure should encourage more participation by women and low-income earners, the government believes.
-
Energy and Cash Subsidies
Support for low-income households includes direct cash handouts and subsidies for electricity and fuel costs to alleviate the rising cost of living.
-
Investments in Technology
The government plans significant investments in the country’s semiconductor and artificial intelligence (AI) sectors to strengthen Japan’s position as a technological leader.
Addressing Workforce and Wage Concerns
Wages in Japan have been stagnant for several decades. The country has also struggled with persistent deflation for many years. The government hopes that this new package can break that cycle:
-
Encouraging Higher Earnings
A higher tax-free threshold may encourage part-time workers and homemakers to work more hours. They will no longer need to keep their earnings below the previous tax ceiling.
-
Wage Growth Trends
According to a recent survey, 51% of Japanese companies plan to raise salaries by at least 3%. This is the highest increase in decades.
This supports the government’s broader aim of sustaining wage growth that benefits all generations.
Balancing Growth and Fiscal Discipline
Despite its ambitious goals, the economic stimulus package faces criticism:
-
Revenue Shortfall
Raising the tax threshold is expected to cost the government $45 billion annually in lost tax revenue.
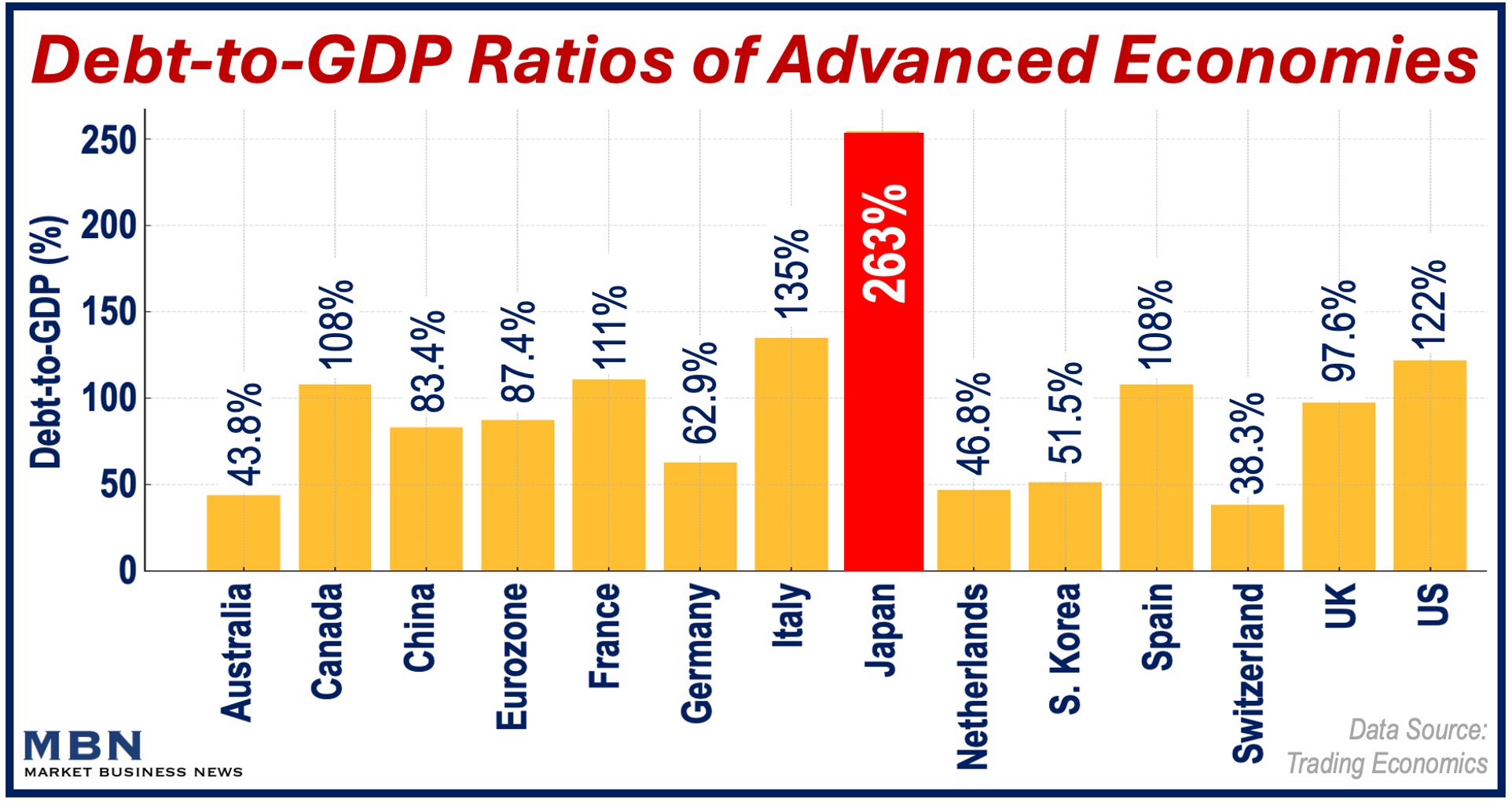
Japan’s debt-to-GDP ratio is 263%, the highest among the advanced economies. Critics say that the economic stimulus package will push the country even deeper into debt.
-
Concerns Over Inflation
Some inflation is not a bad thing – it can drive growth. Unchecked inflation, however, remains a worry, especially as the country emerges from a long period of deflation.
Political Implications of the Economic Stimulus
Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba’s Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) won 191 seats in October’s election, short of the 233 needed for a majority in the 465-seat House of Representatives. Even with its coalition partner, the Democratic Party for the People (DPP), totaling 215 seats, the LDP-led government remains a minority, relying on opposition support to govern:
-
Populist Policies
The inclusion of tax reforms advocated by the Democratic People’s Party (DPP) reflects Ishiba’s precarious political position. The LDP needs the DPP’s support to pass the economic stimulus package.
In an article published by The Japan Times, staff writer Kazuaki Nagata wrote:
“With the ruling Liberal Democratic Party and Komeito coalition having lost a majority in the Lower House in the snap election last month, concerns over lavish spending are growing.”
“The coalition needs the cooperation of opposition parties to pass legislation and will likely need to meet their demands, which could inflate the budget.”
-
Leadership Stability
Ishiba’s ability to implement these policies effectively will be key to restoring public trust and securing his position ahead of the next elections.

A Shift Toward Future Growth
Japan’s economic stimulus package also reflects its intent to adapt to modern economic realities:
-
Digital Asset Taxation
Proposed reforms aim to simplify cryptocurrency taxes, introducing a flat 20% rate to replace the current variable system. This is likely to bolster the growing blockchain and digital asset sectors.
Examples of digital assets include cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin and Ethereum), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized finance (DeFi) tokens, and stablecoins (e.g., USDT and USDC).
-
Regional Development
The government is prioritizing regional revitalization, though critics highlight a lack of clarity on how past efforts have achieved long-term results.
Conclusion
Japan’s $250 billion economic stimulus package is an ambitious attempt to address immediate challenges while laying the groundwork for sustainable growth.
By focusing on tax reforms, wage increases, and technological investments, the government aims to reinvigorate its economy and improve citizens’ quality of life.
However, the plan’s success will depend on the effective implementation of the new package and how carefully the government handles its impact on the country’s budget and finances.
