There are a lot of talks these days about virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) and remote desktop services (RDS). What’s the difference between the two, and which one is right for your business? Let’s take a look at the pros and cons of each.
What is Remote Desktop Services (RDS)?
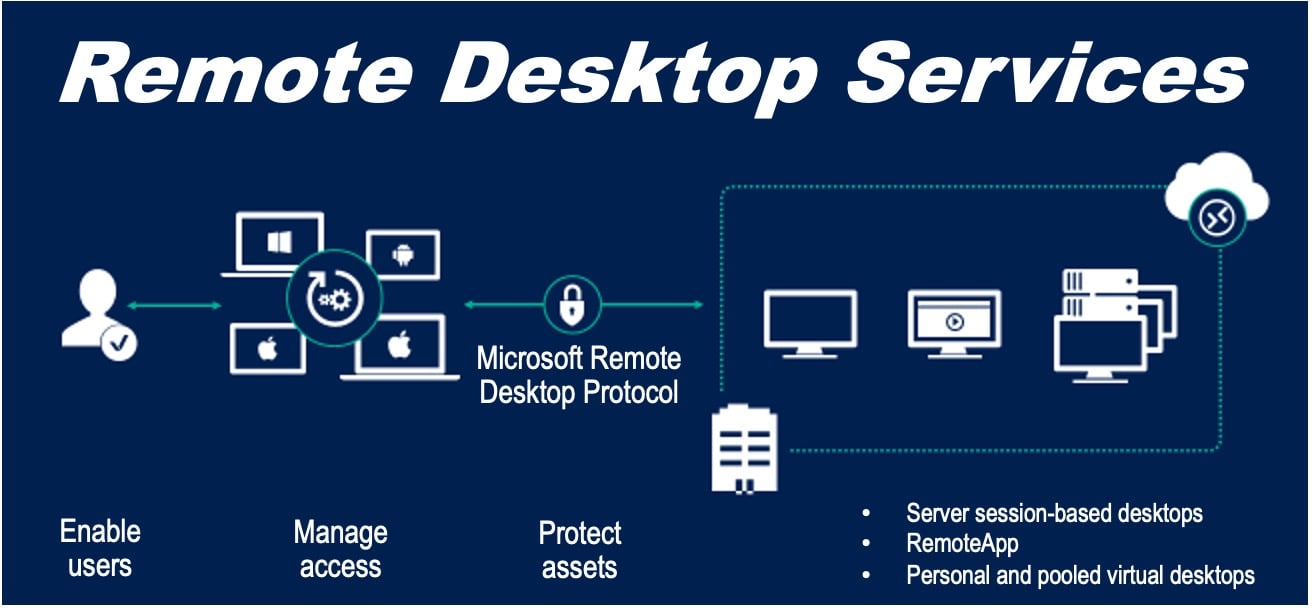
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a technology that allows users to securely connect to virtual desktops, applications, and data from any device. RDS uses a client-server model, with a remote desktop client installed on the user’s device and a remote desktop server hosted on a centralised server.
RDS provides a high-quality user experience using both graphical and audio data, and it supports multiple protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and RDP. Businesses commonly use RDS to provide employees with access to company resources from any location. Organisations also use it to deliver virtual desktop services to their customers.
Key Benefits of RDS
RDS has several key benefits, including reduced IT costs, increased productivity, and improved security.
- RDS can help reduce IT costs by eliminating the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure.
- Additionally, RDS can provide employees with access to work applications and data from any location, increasing productivity.
- Finally, RDS can improve security by providing a secure connection between users and their work resources.
RDS can provide a cost-effective and secure solution for businesses when implemented correctly.
What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)?

Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a type of desktop virtualization that allows users to remotely access their desktops and applications. VDI provides a user with a “virtual desktop” hosted on a remote server.
The user can access their virtual desktop from any device with an internet connection, making it an ideal solution for users who need to access their desktops from multiple locations. Professional cloud VDI system is also more secure than traditional desktop computing, as all data is stored on the remote server and is not vulnerable to local security threats.
Key Benefits of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure
Virtual desktop infrastructure has several key benefits that make it an attractive solution for businesses.
- First, virtual desktop infrastructure provides a high level of security by isolating each user’s desktop environment from the others. This makes it more difficult for malware to spread and helps to protect sensitive data.
- In addition, virtual desktop infrastructure is highly scalable, making it easy to add or remove users as needed.
- Finally, virtual desktop infrastructure can be accessed anywhere, making it a convenient solution for employees who need to work remotely.
As a result, virtual desktop infrastructure provides a versatile and secure solution for businesses of all types.
The Differences Between RDS and VDI
When it comes to enterprise computing, there are two main approaches: remote desktop services (RDS) and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). Both have their benefits and drawbacks, and the best solution for a given organisation will depend on its specific needs.
RDS is a type of server-based computing that allows users to access applications and data remotely. It is typically less expensive to set up than VDI, and it offers good performance and scalability. However, RDS does not provide the same level of security as VDI, and it can be more difficult to manage.
VDI, on the other hand, is a type of desktop virtualization that delivers a consistent user experience regardless of location. It is more secure than RDS, but it can be more expensive to set up and manage.
Other several key differences between RDS and VDI:
- RDS is designed for remote access to virtual desktops, while VDI is intended for remote access to physical desktops.
- RDS uses a client-server model, while VDI uses a server-based model.
- RDS supports multiple protocols, while VDI only supports the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
- RDS provides a high-quality user experience, while VDI can provide a lower-quality user experience depending on the hardware and network conditions.
- Businesses typically use RDS to provide employees with access to company resources from any location, while organisations commonly use VDI to deliver virtual desktop services to their customers.
VDI vs. RDS What Is Better?
-
Performance
Both RDS and VDI have their advantages when it comes to enterprise-level performance. RDS is typically more scalable and easier to set up, while VDI can offer a more seamless user experience. Ultimately, the best solution for your organisation will depend on your specific needs and goals.
If you’re looking for maximum scalability and flexibility, RDS is likely the better option. However, if you need to support many users with high-end graphics requirements, VDI may be the way to go.
Ultimately, the best way to determine which solution is right for you is to work with a qualified IT consultant who can assess your needs and recommend the best course of action.
-
Cost
There is no clear answer when deciding between RDS and VDI regarding cost. Both options have their own unique set of benefits and drawbacks that need to be considered when making a decision.
For example, RDS is typically less expensive up-front, but it requires ongoing maintenance and support costs. VDI, on the other hand, may have a higher up-front cost but can offer significant savings in the long run.
Ultimately, the best option for your organisation will depend on several factors, including budget, projected usage, and technical requirements. By carefully evaluating your needs, you can make an informed decision that will help you save money in the long run.
-
Management
When it comes to enterprise management, two of the most popular acronyms are RDS and VDI. Both options have pros and cons, but ultimately it depends on the organisation’s specific needs. RDS is generally cheaper and easier to set up, while VDI offers greater flexibility and scalability.
However, VDI can be more complex to manage, requiring a higher upfront investment. Ultimately, the best option depends on the specific needs of the organisation. With RDS, organisations can get started quickly and cheaply, while VDI offers greater flexibility in the long run.
Conclusion
There is no clear winner when it comes to RDS vs. VDI. Both have their benefits and drawbacks, and the best solution for a given organisation will depend on its specific needs.
RDS is a type of server-based computing that allows users to access applications and data remotely. It is typically less expensive to set up than VDI, and it offers good performance and scalability.
However, RDS does not offer the same level of security as VDI, and it can be more difficult to manage. VDI, on the other hand, is a type of desktop virtualization that delivers a consistent user experience regardless of location. It is more secure than RDS, but it can be more expensive to set up and manage.
Interesting related article:

