CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion in the European Union rose by 1.8% in 2017 compared to 2016, says Eurostat. CO2 stands for carbon dioxide. Eurostat provides statistical information to the institutions of the European Union (EU).
Carbon dioxide accounts for approximately eighty percent of all EU greenhouse gas emissions. It is a significant contributor to global warming.
What influences CO2 emissions?
According to Eurostat, industrial activity, transport, population sizes, and GDP growth influence CO2 emissions. GDP stands for gross domestic product. Transport, i.e., vehicles, airplanes, trains, and ships, also influence levels of carbon dioxide emissions.
The imports and exports of energy products also have an impact on carbon dioxide emissions. Particularly in the country that burns fossil fuels.
For example, importing of coal leads to a rise in emissions. Electricity imports, on the other hand, do not directly affect emissions in the importing nation. The country that exports electricity, on the other hand, does report CO2 emissions.
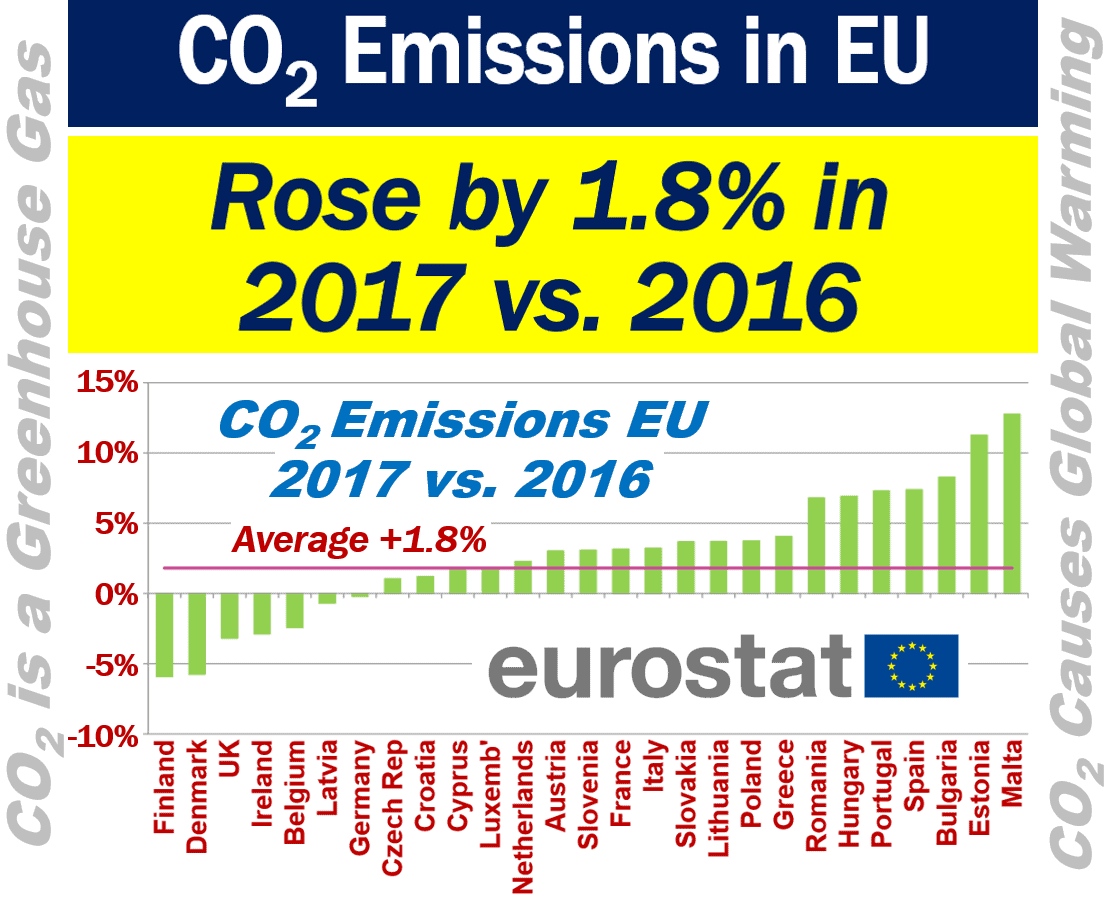
CO2 emissions – by country
Malta and Estonia registered the highest increase in carbon dioxide emissions, while Finland and Denmark reported the lowest.
Eurostat reports that, according to its estimates, CO2 emission rose in most EU Member States.
Largest increases in CO2 emissions
The following EU Member States recorded the highest emissions:
– Malta +12.8%
– Estonia +11.3%
– Bulgaria +8.3%
– Spain +7.4%
– Portugal +7.3%
Biggest declines in CO2 emissions
The following EU Member States recorded the greatest falls:
– Finland -5.9%
– Denmark -5.8%
– United Kingdom -3.2%
– Ireland -2.9%
– Belgium -2.4%
– Latvia -0.7%
– Germany -0.2%
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rise in temperatures of our planet’s oceans and atmosphere. The majority of scientists today believe that the rise in temperatures are due to the greenhouse effect.
Machines that humans make and other activities emit pollution, including CO2, a greenhouse gas.
These emissions subsequently exacerbate the greenhouse effect.
Since 1880, the average temperature of our planet’s lower atmosphere has gone up by 0.6°C. However, the rate of temperature increase is accelerating.
By 2070, scientists forecast that temperatures will be 1.5°C to 2°C higher than they are now.
The main greenhouse gases are:
– CO2
– Ozone (O3)
– Methane (CH4
