A Credit Bureau or Credit Agency is a firm that supplies data about people’s and companies’ financial strengths and credit histories. The credit bureau usually supplies this information to banks, credit card companies, retailers, and other lenders.
People also use the terms ‘consumer reporting agency’ in the US or a ‘credit reference agency’ in the UK. Australians may say ‘credit reporting body.’ An agency is an entity that specializes in something.
Companies that are deciding whether to grant a loan pay the credit bureau a fee for their information. The data also helps lenders determine how much interest to charge or what size deposit to request.
The credit bureau provides data on individuals and companies. However, it does not decide whether they qualify for credit. The lender does that.
Modern credit bureaus utilize advanced algorithms and machine learning to assess and update credit records, ensuring a more dynamic and real-time reflection of an individual’s financial behavior.
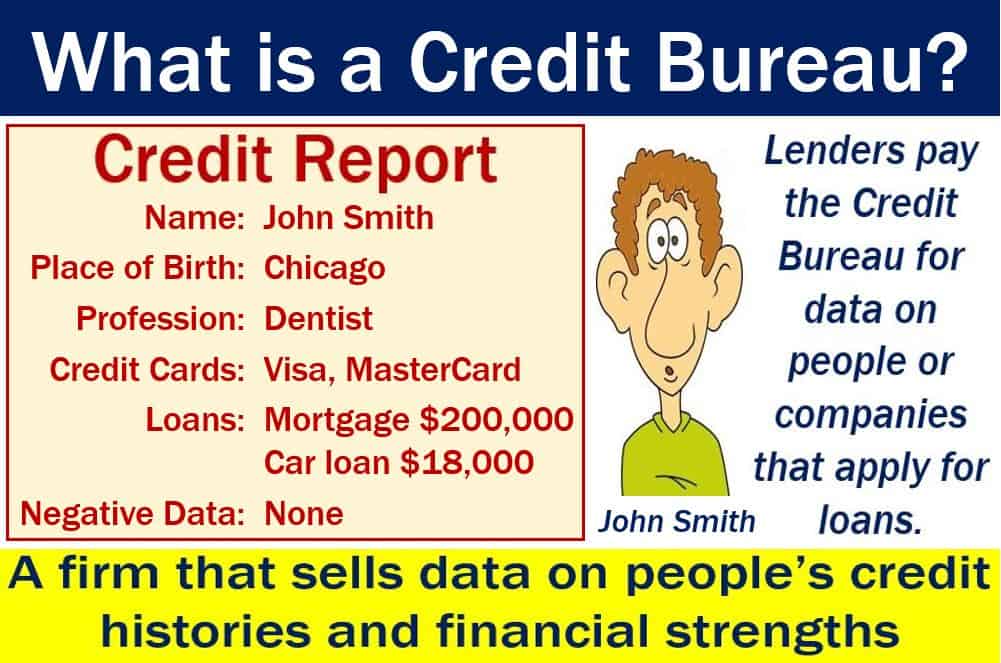
Credit bureau – credit report
The credit bureau sends a credit report. It contains information about the people’s bill repayment history. There is also data on the status of their credit accounts.
The report will show how often the loan applicant made payments on time and what current credit arrangements there are. It also says how much credit that person is using and whether a debt collector is collecting the money.
Credit reports might include rental repayment data if the person is a property tenant. They may also contain public records such as judgments, bankruptcies, and liens.
All this data gives the lender insight into people’s financial status and obligations.
“It’s important to check your credit report regularly to ensure that your personal information and financial accounts are being accurately reported and that no fraudulent accounts have been opened in your name.”
Americans can request a free credit report online at AnnualCreditReport.com.
Credit bureau – a for-profit business
The largest credit bureaus are Equifax, Experian and TransUnion, and CallCredit in the UK. They are for-profit private firms that do not share information with each other. Therefore, details about you may vary slightly in each bureau.
Personal data may stay on your credit reports forever. In other words, there is no expiration date on data regarding your name, address, etc.
Negative information in most countries stays on your credit report for six to eight years. In the United States, for example, how long bankruptcy data stays on record depends. For Chapter 7 filings it is ten years, and Chapter 13 filings it is seven years.
With so much debt in the world, it is surprising how little people know about their credit ratings. In fact, surveys have shown that most Americans have no idea what their credit score is.
The UK’s Money Advice Service warns that if you repeatedly apply for credit, you could be harming your chances of getting credit. Several credit searches may indicate you are having problems.
You can order a ‘credit freeze,‘ which makes it illegal for bureaus to sell your personal data. It is one of several ways to protect yourself from identity theft.
Additionally, consumers have the right to dispute any inaccuracies found in their credit report, which credit bureaus are legally obligated to investigate and resolve.
Video – What is a Credit Bureau?
This video, from our YouTube partner channel – Marketing Business Network, explains what ‘Credit Bureau’ means using simple and easy-to-understand language and examples.
