Laddering – definition and meaning
Laddering is a technique investors use in which they buy multiple financial products. Their products have different maturity dates. Subsequently, they can receive a steady income and spread their risk. Laddering also hedges against price fluctuations of individual investment products. Some people refer to the technique as having a ‘laddered portfolio‘ or a ‘ladder strategy.’
An investor who uses the laddering technique may focus on bonds with different maturities. For example, they may mature in two, four, six, and eight years. If they keep re-investing most of their bonds when they mature, they can keep the system going virtually forever.
When laddering with bonds, investors may refer to the whole portfolio as a ‘bond ladder.’
A bond is a fixed-income investment in which the purchaser loans money to a major company or the government.
Wikipedia has the following definition of the term:
“Laddering is an investment technique that requires investors to purchase multiple financial products with different maturity dates.”
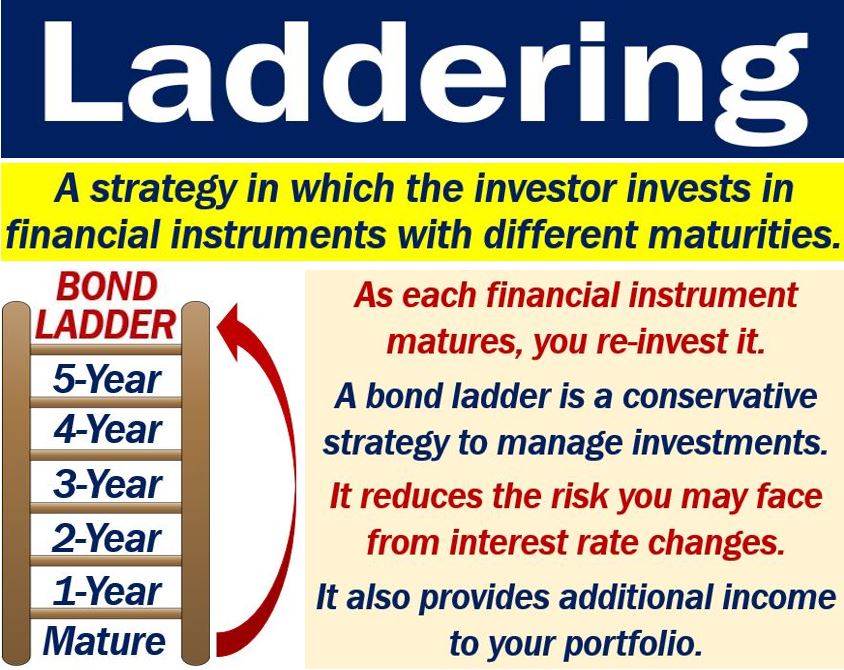
Setting up a bond ladder
If you want to set up a bond ladder, you should have their maturity dates evenly spaced across different years.
As the bonds mature, you re-invest them. The distance between maturity dates depends on the level of liquidity you are going to require.
For example, if you need a high level of liquidity, you should have short intervals between maturity dates.
Conservative investments
If you want a conservative investment, you are more likely to go for bonds. However, for the best yields, you will need to purchase bonds with long maturities.
Long maturities expose you to liquidity risk, credit risk, and also interest rate risk.
When interest rates increase, for example, demand for interest-paying bonds declines. Subsequently, the bond has less liquidity. It has less liquidity because investors can find similar financial instruments with greater interest payments.
In such a situation, the only way to get a better price is to wait for interest rates to decline. When interest rates go down again the bond price rises.
Credit and liquidity risks are also important hazards for which an investor needs to prepare.
Benefits of laddering
-
Several bonds, different maturities
Laddering, however, overcomes the problems mentioned above. If you have several bonds with different maturities, they are continuously maturing and being reinvested.
-
Flexibility
Laddering’s flexibility also enables investors to adjust their portfolios in response to changing economic climates, making it a dynamic tool for long-term financial planning.
-
Liquidity
If you require liquidity, you can sell the shorter maturity bond. You sell the shorter maturity one because you will probably get the best price.
-
Safer credit risk
Also, by having several different bonds, the credit risk is more evenly spread out. If one bond suffers a serious credit quality downgrade, it only affects part of your portfolio.
-
Choose best bonds
Video – What is Laddering?
This educational video, from our sister channel on YouTube – Marketing Business Network, explains what ‘Laddering’ is using simple and easy-to-understand language and examples.

