Are you able to identify, assess, and manage risks effectively? Do you understand the potential dangers that could impact your business and find ways to minimize those risks? If so, you are practicing Risk Intelligence.
By developing strong risk intelligence, you can make more informed decisions that help protect your assets, reputation, and long-term success.
Risk intelligence involves gathering risk data, understanding potential dangers, analyzing their impact, and managing them effectively. It includes being aware of risks, making informed decisions, and continuously improving your approach.
The World Economy Forum says the following about risk intelligence:
“Risk intelligence is a crucial skill that enables individuals and organizations to gather and analyze relevant information, and use it to navigate uncertainty, make informed decisions and achieve their objectives while mitigating potential negative outcomes.”
“Market fluctuations, complex regulations, natural disasters, cyber threats, geopolitical instability, health crises, fake news, and more all represent potential risks they must be prepared for.”
Definition of ‘Risk’ and ‘Intelligence’
Before we proceed, let’s have a look at the meanings of the two words – ‘risk’ and ‘intelligence’ – on their own:
-
Risk
Risk refers to the threat or likelihood of damage, injury, loss, liability, or any other undesirable occurrence resulting from internal or external vulnerabilities.
In business, there are many types of risks, including capital risk, interest rate risk, settlement risk, liquidity risk, operations risk, political risk, country risk, sovereign risk, exchange rate risk, default risk, delivery risk, economic risk, reinvestment risk, underwriting risk, and refinancing risk.
Intelligence, in the context of this article, is the ability to gather, understand, analyze, and apply information to make informed decisions and solve problems effectively.
In this context, it is not about being smart or clever or having a high IQ.
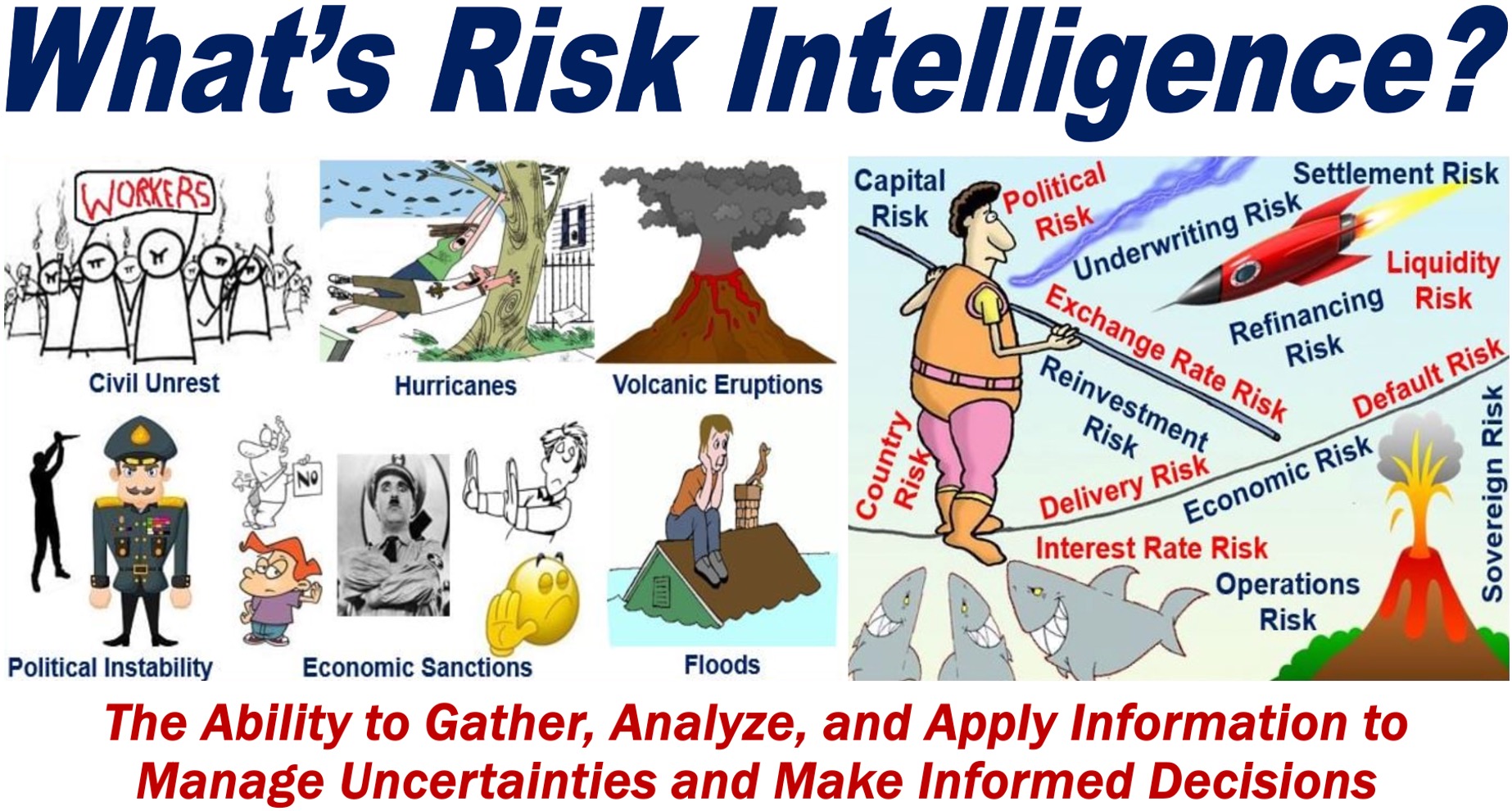
Risk Intelligence – Being Aware of Uncertainties
Fundamentally, risk intelligence is about being aware of the uncertainties that exist in any situation. Whether you’re running a business, investing in the stock market, or making decisions about your career, risks are always present.
However, having the knowledge and skills to recognize and evaluate these risks can make a significant difference in your outcomes.
The Components of Risk Intelligence
Here are five key components that make up risk intelligence:
-
Awareness
Your first step in developing risk intelligence is being aware of the potential risks around you.
This means understanding the environment in which you operate and recognizing the factors that could lead to potential problems.
This awareness allows you to be proactive rather than reactive.
-
Analysis
Once you are aware of the risks, you need to analyze them. This involves evaluating the likelihood of these risks occurring and the potential impact they could have on your goals.
By analyzing risks, you can prioritize which ones require immediate attention and which ones are less critical.
-
Mitigation
After identifying and analyzing risks, you must find ways to mitigate or minimize them.
This could involve developing strategies to reduce the likelihood of the risk occurring, creating contingency plans, or purchasing insurance to cover potential losses.
Effective risk mitigation helps protect your interests and ensures that you’re prepared for any eventualities.
-
Decision-Making
Risk intelligence is crucial in the decision-making process. By considering the risks involved in any decision, you can weigh the pros and cons more effectively and choose the option that aligns best with your objectives.
This process helps you avoid unnecessary risks and take calculated ones that have a higher chance of success.
-
Continuous Improvement
Risk intelligence is not a one-time effort. It requires ongoing monitoring and reassessment of the risks you face.
In today’s fiercely competitive marketplace, things can change very quickly. New risks may emerge, and existing ones may evolve.
By continuously improving your risk intelligence, you can stay ahead of potential threats and adapt your strategies accordingly.
Why is Risk Intelligence Important?
Developing risk intelligence is essential because it allows you to make more informed decisions, protect your assets, and ensure the long-term success of your endeavors.
In today’s fast-paced and uncertain world, being able to navigate risks effectively is a key factor in achieving your goals.
The better you become at gathering and analyzing risk data, the greater your chances of achieving success and ensuring long-term growth for your business.
A Brief History
The concept of weighing risks against potential benefits has been integral to business practices since the earliest days of trade, thousands of years ago.
The term “risk intelligence” is attributed to various sources, but it was notably popularized by American business writer David Apgar in his 2006 book Risk Intelligence: Learning to Manage What We Don’t Know.
While the term itself likely entered the English language around this time, its underlying principles are rooted in earlier risk management practices.
As organizations increasingly sought to navigate uncertainty and make informed decisions in complex environments, risk intelligence gained traction and became widely discussed.
Thinkers like Leo Tilman and Dylan Evans have since expanded and refined the concept, contributing to its broader understanding and application across various industries.
Other ‘Intelligence’ Types
In business English, intelligence comes in various forms beyond just risk intelligence. Below are some of the most commonly referenced types, each with its unique focus:
Talent intelligence involves gathering and analyzing data on workforce trends, employee performance, and skill gaps to optimize hiring, development, and retention strategies.
This type of intelligence focuses on analyzing supply chain data to improve efficiency, reduce risks, and enhance the overall performance of the supply chain.
Social intelligence is the ability to understand and manage social relationships and dynamics within a business context, including networking and customer interactions.
Sales intelligence refers to collecting and analyzing data on prospects and customers to enhance sales strategies and improve customer engagement.
Product intelligence involves gathering and analyzing information on product performance, customer feedback, and market trends to guide product development and marketing strategies.
Operational intelligence focuses on monitoring and analyzing business operations data in real-time to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making.
Market intelligence is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data about market trends, competitors, and customer behavior to inform business strategies.
Human intelligence encompasses the cognitive abilities of individuals, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making, and how these are applied in business settings.
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s emotions and those of others, which is crucial for effective leadership and teamwork.
Economic intelligence involves analyzing economic data and trends to make informed decisions that impact the financial health and strategic direction of a business.
Data intelligence focuses on the ability to collect, analyze, and use data effectively to inform business decisions and strategies.
Cyber intelligence involves monitoring and analyzing digital threats to protect an organization’s information systems from cyber-attacks and data breaches.
Customer intelligence is about gathering and analyzing data on customer behaviors, preferences, and feedback to enhance customer experience and loyalty.
Competitive intelligence involves collecting and analyzing information about competitors to inform business strategies and gain a competitive edge.
Business intelligence refers to the tools and processes used to collect, analyze, and present business data, enabling informed decision-making.
Brand intelligence involves gathering and analyzing data related to brand perception, market positioning, and customer loyalty to enhance brand strategy.
Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines, enabling them to perform tasks that typically require human cognition, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Final Thoughts
Let’s recap. Risk intelligence is the ability to understand and manage uncertainties that can affect your decisions.
It involves gathering and analyzing risk data, being aware of potential dangers, prioritizing and mitigating risks, and continuously improving your approach.
By enhancing these skills, you can make informed decisions, protect your assets, and increase your chances of long-term success.
Risk intelligence is not about being smart or having a high IQ. It’s about effectively applying knowledge to navigate challenges and seize opportunities.
By developing strong risk intelligence, you equip your business with the tools needed to thrive in any environment.
