If you are considering studying for a university degree or any post-secondary course, you have three options. You can:
- Study full time and ask your parents to finance your tuition fees, educational materials, and living expenses.
- Study part-time and work part-time.
- Take out a Student Loan.
Most full-time students need to take out a loan. In the US and many other countries, loans designed for students tend to have significantly lower interest rates than other loans.
Also, the borrower’s repayment schedule may be deferred so that they do not have to start repayments until they have finished studying.
The following definition comes from Wikipedia:
“A student loan is a type of loan designed to help students pay for post-secondary education and the associated fees, such as tuition, books and supplies, and living expenses. It may differ from other types of loans in the fact that the interest rate may be substantially lower and the repayment schedule may be deferred while the student is still in school.”
In the advanced economies, loans are provided by or guaranteed by the state and are much more easily accessible than in other parts of the world. In some emerging economies, student loans do exist, but they are much harder to acquire due to smaller budgets.
Let’s take a look at the educational loan system in some countries:
The United States
In the US, there are two main types of student loans, federal loans and private student loans.
-
Federal Loans
Federal loans are sponsored by the federal government (central government). Most American student loans opt for federal loans.
They can be ‘subsidized’ or ‘unsubsidized.’ If you have a subsidized loan, it does not accrue interest while you are studying.
Federal Student Aid, which is part of the US Department of Education, says the following about subsidized student loans:
“If you have financial need, you may qualify for a loan for which the government pays the interest while you’re in school on at least a half-time basis and during certain other periods. This type of loan is called a ‘subsidized loan.'”
You can find out more about federal student loans here.
-
Private Student Loans
Private student loans, also known as personal student loans or non-federal loans, that is, they are not funded by the federal government. The lender may be a state agency, bank, credit union, or a school.
In this case, the lender sets the terms of the loan. They are typically more expensive than federal loans.
In most cases, repayments begin while the student is still in school. However, some may allow you to defer. Interest rates, as with other commercial loans, may be fixed or variable. The lender may require an established credit record or a cosigner.
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau says the following about private student loans:
“Private student loans—also known as personal student loans— are offered by private lenders to provide funds to pay for educational expenses. They are not part of the federal student loan program and generally do not feature the flexible repayment terms or borrower protections offered by federal student loans.”
If you are having difficulties with your loan or your lender, you may find this webpage of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau useful.
The United Kingdom
In the UK, student loans are primarily provided by the Student Loans Company, which belongs to the state (it is not a private company).
As soon as you receive it, interest starts accumulating on the loan. However, you do not have to start paying back until the beginning of the next tax year after you have completed (or abandoned) your studies.
Borrowers only start repaying after they earn more than a certain amount. How much you pay back each month depends on your income and not on how much you owe.
If the borrower dies or becomes unable to work (permanently), the loan is cancelled.
The Student Loan Company says the following about loans:
“You may be able to borrow money to help pay for university or college tuition fees and to help with living costs. You might get extra money on top of this, for example if you’re on a low income, are disabled or have children. You may be able to get student finance even if you’re not from the UK.”
“You start repaying once you earn over a certain amount. The size of your monthly repayments will depend on how much you earn, not what you owe.”
If you are a student and are have financial or debt problems, this you may find the Debt Advice Foundation useful.
Canada
Canadian student and people who have been resident in the country for at least one year are normally eligible for federal student loans through the CSLP (Canada Student Loans Program). CSLP is managed by ESDC (Employment and Social Development Canada), which is part of the federal government.
Some Canadian provinces have their own programs while those of others are integrated with CSLP. Banks also offer loans to students.
Regarding student loans and how much you can receive, ESDC says the following:
“The amount you can receive depends on many factors, including your province or territory of residence, your family income, if you have dependents, your tuition fees and living expenses, if you have a disability.”
“To find out how much you might get in Canada Student Grants or Loans, use the federal student aid estimator. The estimator does not take into account the provincial and territorial student grants and loans.”
The Canadian government also offers several student grants:
- Grant for full-time students.
- Grant for full-time students with dependents.
- Grant for part-time students.
- Grant for part-time students with dependents.
- Grant for students with disabilities
- Services and equipment for students with disabilities.
India
Vidya Lakshmi is a portal that the Indian government launched in 2015 for students seeking educational loans. Five domestic banks have integrated their systems with the portal. Today, 38 banks are registered on the Vidya Lakshmi portal, offering 84 student loan schemes.
This quote comes from the ‘About Us’ webpage on the Vidya Lakshmi website:
“Vidya Lakshmi is a first of its kind portal for students seeking Education Loan. Students can view, apply and track the education loan applications to banks anytime, anywhere by accessing the portal. The portal also provides linkages to National Scholarship Portal.”
- Higher Education in India
There are more than 58,000 higher educational institutions in India. In the year 2021/22, a total of 2,400 new institutions were added. The country has the world’s second largest education system.
Today, there are over 43.3 million students enrolled in university, colleges, and other higher education institutions. Almost 79% of them are attending undergraduate courses, 12% are doing a master’s degree, while 0.5% are studying for a PhD.
In 2024, there were 18% more adult students in the country compared to 2019. The states of Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal and Rajasthan have over half of the country’s total student population.
The British Council says the following regarding areas of study:
“The largest broad subject area at undergraduate level is Arts (34%), followed by Science (15%), Commerce (13%) and Engineering & Technology (12%).”
“At the postgraduate (master’s degree) level the top broad subject area is Social Science (21%) followed by Science (15%) and Management (14%), and at PhD level the largest number of students are enrolled in Engineering &Technology (25%) followed by Science (21%).”
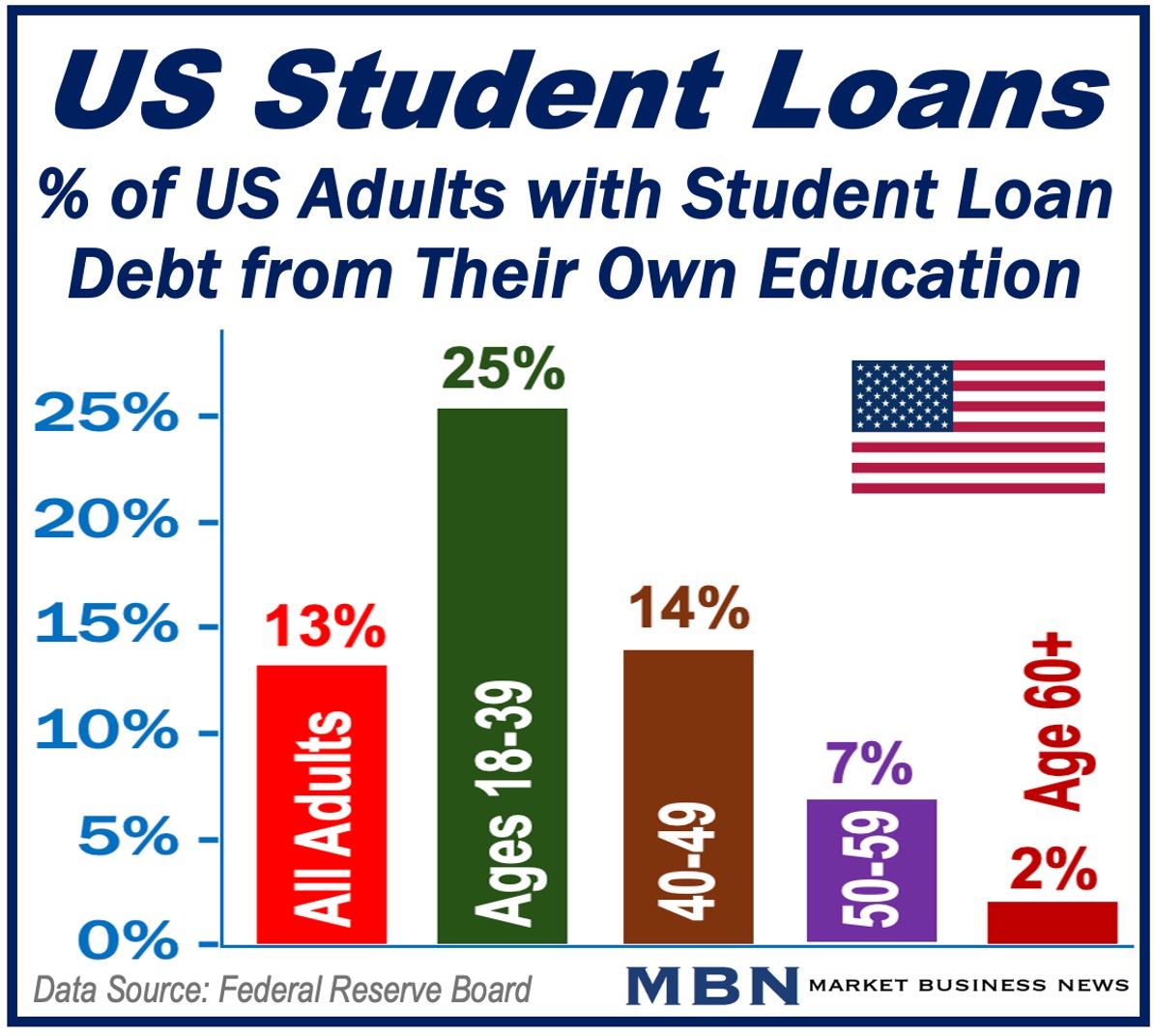
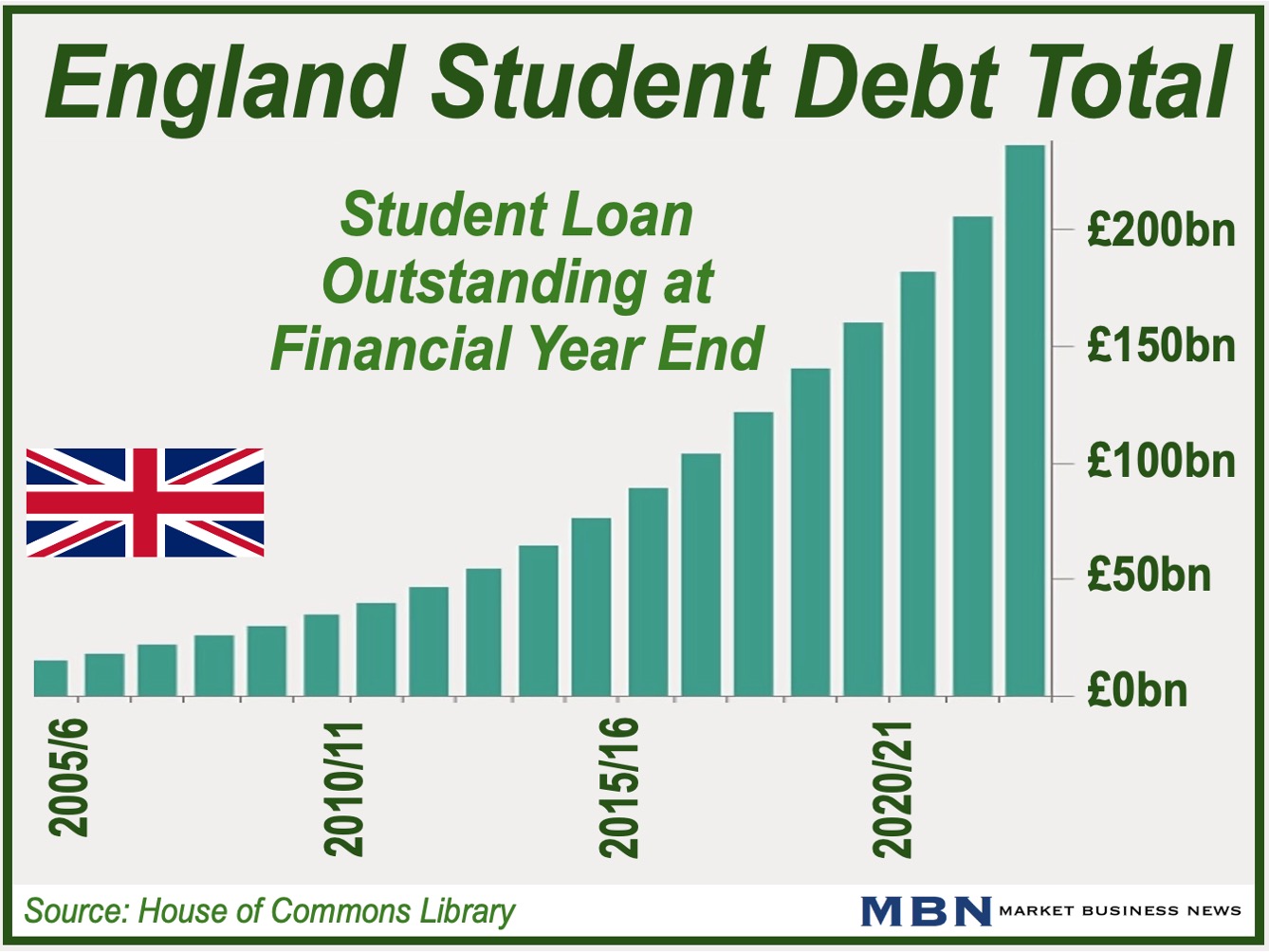
Growing Student Debt
Since the turn of the century, student debt has increased considerably in the United States, UK, and many other countries across the world.
According to the US Council on Foreign Relations, student debt is one of the largest forms of consumer borrowing in America today.
However, despite entering the job market burdened with heavy debts, most economists still believe that student loan programs are a sound investment for American workers.
In October 2023, US President Joe Biden said:
“While a college degree is still the ticket to a better life, that ticket has become excessively expensive. Americans who are saddled with unsustainable debt in exchange for a college degree has become the norm.”
