Occupational Safety and Health or OSH is concerned with the health, safety, and welfare of employees in the workplace. We also call it Occupational Health and Safety (OHS), Workplace Health and Safety (WHS), and Occupational Health.
Apart from fostering a healthy and safe work environment, the term also includes the protection of co-workers and family members. In some cases, OSH may include other stakeholders, such as customers, employers, and other people who the workplace environment may affect. The term ‘stakeholder’ refers to any individual or group that has an interest in a specific issue or organization and can be affected by its actions or decisions.
Companies and other employers, in common-law jurisdictions, have a legal duty to take reasonable care and safety of their workers. State law usually introduces specific duties and creates government bodies that regulate workplace safety issues.
Occupational medicine, which focuses on the health of employees, is part of OSH. OSH is part of occupational psychology.
When referring to a specific case of a workplace injury, we use the term occupational injury.
The Importance of Training and Awareness
One of the key components in promoting Occupational Safety and Health is the emphasis on training and awareness.
A well-informed workforce can proactively identify potential hazards and mitigate risks before they escalate into significant issues. Regular training sessions ensure that employees are equipped with the latest safety procedures and are aware of the inherent dangers in their specific work environments. Moreover, fostering a culture of open communication allows employees to report unsafe conditions and recommend safety improvements.
A well-trained workforce tends to be a safer and more productive one.
Occupational Safety and Health concerns everybody
OSH concerns both employers and workers. Our workplaces have several different kinds of hazards. Every year, millions of workers globally are injured, disabled, or die on the job.
According to the National Safety Council, a 501 nonprofit, public service organization promoting health and safety in the United States:
“The costs associated with injuries and illnesses, lost wage compensation, insurance premiums, hiring replacement workers, damaged equipment, and lost production are immense expenses for businesses and the economy in general.”
Many companies, especially the larger ones, have a team of professionals with experience and degrees in occupational safety and health.
However, for most smaller employers, the task of creating and implementing illness and injury programs falls to employees. These employees specialize in other areas, such as HR, quality control, or security. The letters HR stand for Human Resources.

Occupational safety and health in the EU
In a report, the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA) informed that rates of ill health and injuries have declined over the past few decades.
However, employees still report persistent and emerging job-related risks to safety and health in the workplace.
In their report – “Management of Occupational Safety and Health” – the authors wrote:
” Poor health and safety, in addition to physical and emotional harm, has cost implications for the individual, the workplace and wider society.”
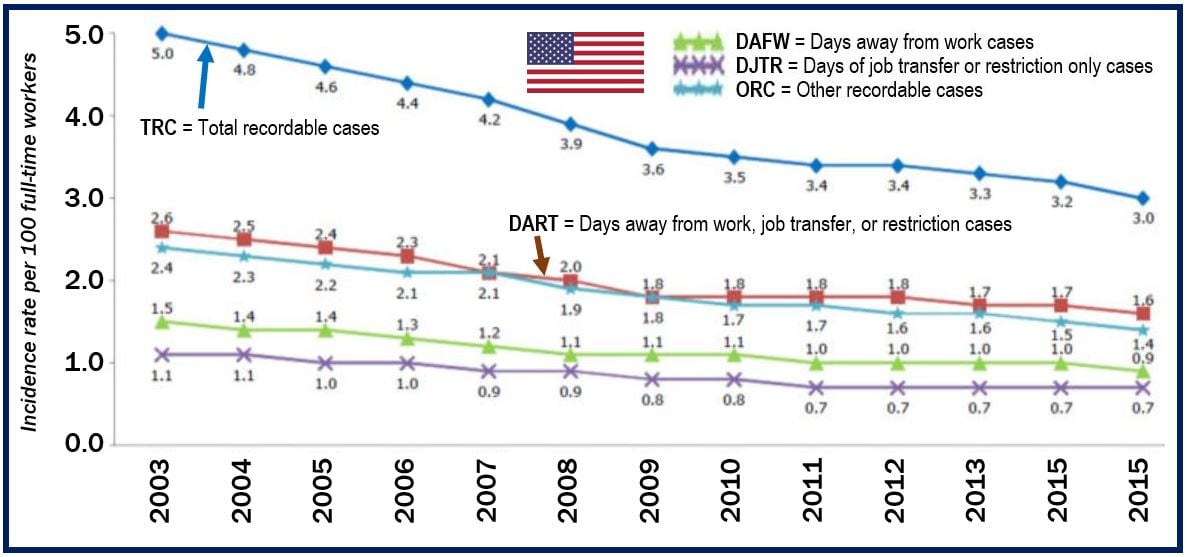
OSH in the USA
In the United States, legislation to protect worker safety and health came into force in 1970. The Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 required that research, recommendations, and guidance be developed to aid employees and employers.
The 1970 Act also required that employers adopted health and safety standard. Employers had to comply with the new rules, and the government had to police and enforce them.
In the United States, rates of injuries and ill health have also declined over the last few decades. American workers, however, like their European counterparts, still report persistent and emerging job-related risks.
