Manufacturing Activity Sees Steady Growth
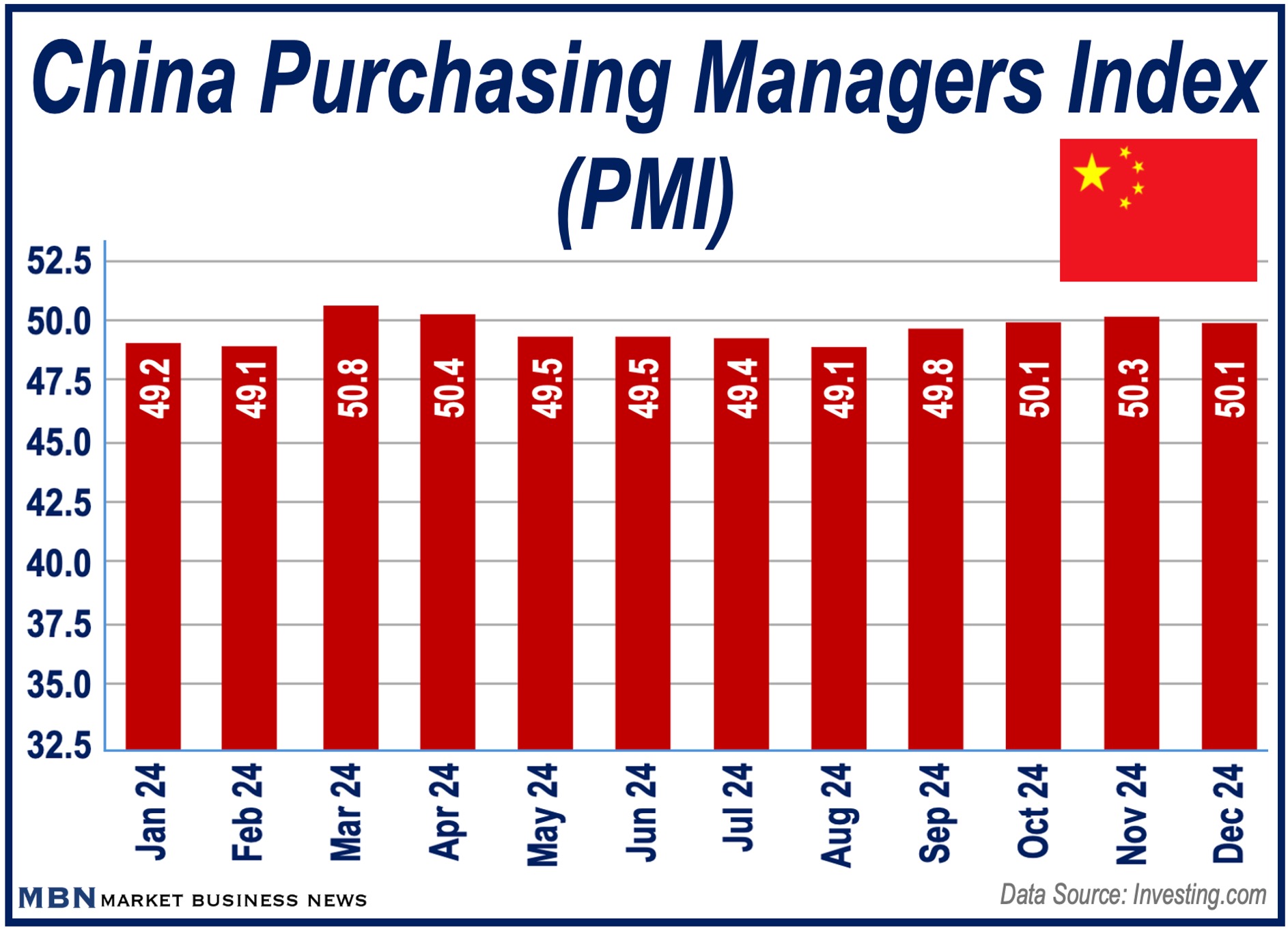
China’s economy is showing some positive signs as its manufacturing sector reported growth in December, marking its third consecutive month of expansion, according to the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), which registered at 50.1
What is the Purchasing Managers’ Index or PMI?
The PMI is an economic indicator that reflects the health of an economy’s manufacturing and services sectors through surveys of purchasing managers.
It is derived from extensive surveys of private sector businesses and offers economists, analysts, investors, and policymakers a snapshot of economic trends.
Due to its rapidly growing significance, many members of the public today also follow their country’s PMI avidly.
In one of our previous articles, we wrote:
“At its core, the Purchasing Managers’ Index is constructed from the following components, which are weighted and compiled into a single figure: new orders, inventory levels, production, supplier deliveries, and the employment environment.
“A reading of 50 or above means the sector is expanding – business conditions are improving. Conversely, a reading below 50 signifies contraction – business conditions are deteriorating.”
China’s Economy – a Backdrop of Challenges
This encouraging manufacturing news comes amidst a backdrop of challenges, including a property market crisis, mounting government debt, and weak domestic consumption.
The Chinese government has responded by lowering interest rates and reducing home-buying restrictions, which have provided some momentum.
Some economists, however, emphasize the need for direct fiscal policies, such as tax rebates, subsidies for low-income households, and increased government spending on public infrastructure, to boost consumer spending further. China’s government has plans for some direct fiscal policies.
GDP Growth: Current Status and Projections
Most forecasters believe that China met its 5% Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth target for 2024. That is a significant marker for a nation facing global economic uncertainties and domestic pressures.
President Xi Jinping highlighted this projection during a New Year’s address, emphasizing the country’s stability and resilience.
In recent months, China has implemented fiscal and monetary policies designed to boost the economy, including increased public borrowing and targeted support for key sectors.
These measures have helped stabilize parts of the economy. However, challenges such as weak export demand and a struggling property market remain.
According to an article published by Xinhua:
“The economy is expected to have grown by around 5 percent, contributing nearly 30 percent to global economic growth and maintaining China’s position as a major engine of the world economy.”
Fiscal Policy vs. Monetary Policy
Fiscal policy is implemented by the government and includes spending on infrastructure, tax rate adjustments, and direct financial aid to households.
The central bank, on the other hand, decides and implements monetary policy, which involves actions like setting interest rates, adjusting the money supply, and implementing open market operations.
Economic Drivers of China’s Economy in 2024
-
Manufacturing and Industrial Output
Rising domestic orders have helped boost manufacturing growth in China this year, though global trade uncertainties, including potential tariffs, pose risks.
December’s PMI figures are great news, say analysts, who add that the government must keep the stimulus going to maintain momentum.
-
Consumption and Retail Recovery
Government initiatives, such as consumer goods trade-in schemes and increased household income support, have helped boost spending in sectors like home appliances and automobiles.
These efforts are complemented by growth in e-commerce and the hospitality industry, showcasing the potential for domestic consumption to drive economic recovery.
-
Real Estate Stabilization
China’s property sector, which has been experiencing serious problems, has shown signs of recovery following policy adjustments like reduced mortgage rates and relaxed purchase restrictions.
The government’s focus on affordable housing and the completion of unfinished projects should restore confidence and stimulate demand.
-
Green Development and Innovation
Sustainability is still a priority in China, with notable advances in electric vehicle (EV) production and the generation of renewable energy.
Investments in green technologies continue to attract foreign and domestic stakeholders.
Plans for China’s Economy – 2025 and Beyond
China’s leadership has outlined a number of strategies to address both the country’s immediate and long-term challenges. Key priorities include:
- Enhancing the integration of technological and industrial innovation.
- Expanding support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Helping the real estate sector achieve a steady recovery through tailored financial policies.
- Investing in green and digital economies, with a focus on artificial intelligence and data infrastructure. Components of digital economies, beyond AI, include digital infrastructure, e-commerce platforms, data-driven innovations, digital payment systems, a tech-skilled workforce, innovation ecosystems, and robust cybersecurity measures.
Regarding China’s economic plans, France 24 quoted President Xi Jinping as saying:
“We must… further comprehensively deepen reform, expand high-level opening up, better coordinate development and security, (and) implement more proactive and effective macroeconomic policies.”
Conclusion
Despite headwinds in 2024, the Chinese economy still managed to expand faster than those of the advanced economies, including the United States.
Through targeted reforms, increased domestic consumption, and strategic investments in green and digital sectors, the country aims to maintain steady growth.
We will have to wait and see whether the Trump Administration will impose heavy tariffs on Chinese imports, and what the consequences of such a move would be.
